LiteRT에서 사용하는 머신러닝 (ML) 모델은 원래 TensorFlow 핵심 라이브러리와 도구를 사용하여 빌드되고 학습됩니다. TensorFlow 핵심으로 모델을 빌드한 후에는 LiteRT 모델이라는 더 작고 효율적인 ML 모델 형식으로 변환할 수 있습니다. 이 섹션에서는 TensorFlow 모델을 LiteRT 모델 형식으로 변환하는 방법을 안내합니다.
변환 워크플로
TensorFlow 모델을 LiteRT 형식으로 변환하는 방법은 ML 모델의 콘텐츠에 따라 몇 가지가 있습니다. 이 프로세스의 첫 번째 단계로 모델을 평가하여 직접 변환할 수 있는지 확인해야 합니다. 이 평가에서는 모델의 콘텐츠가 사용하는 TensorFlow 작업을 기반으로 표준 LiteRT 런타임 환경에서 지원되는지 확인합니다. 모델에서 지원되는 집합 외부의 작업을 사용하는 경우 모델을 리팩터링하거나 고급 변환 기법을 사용할 수 있습니다.
아래 다이어그램은 모델 변환의 대략적인 단계를 보여줍니다.
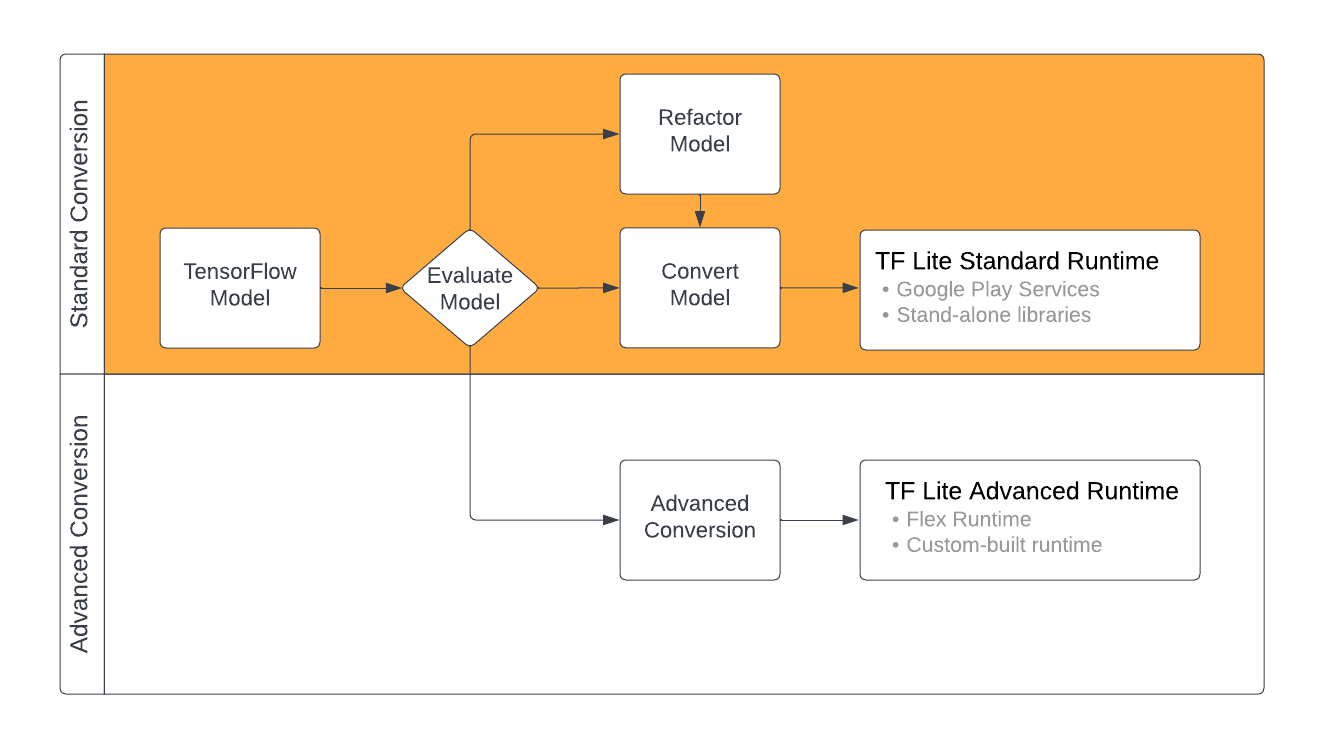
그림 1. LiteRT 변환 워크플로
다음 섹션에서는 LiteRT에서 사용할 모델을 평가하고 변환하는 프로세스를 간략하게 설명합니다.
입력 모델 형식
다음 입력 모델 형식으로 변환기를 사용할 수 있습니다.
- SavedModel(권장): 디스크에 파일 집합으로 저장된 TensorFlow 모델입니다.
- Keras 모델: 상위 Keras API를 사용하여 생성된 모델입니다.
- Keras H5 형식: Keras API에서 지원하는 SavedModel 형식의 경량 대안입니다.
- 구체적 함수에서 빌드된 모델: 하위 수준 TensorFlow API를 사용하여 생성된 모델입니다.
Keras 모델과 구체적 함수 모델을 모두 SavedModel로 저장하고 권장 경로를 사용하여 변환할 수 있습니다.
Jax 모델이 있는 경우 TFLiteConverter.experimental_from_jax API를 사용하여 LiteRT 형식으로 변환할 수 있습니다. 이 API는 실험 모드에서 변경될 수 있습니다.
전환 평가
모델을 평가하는 것은 모델을 변환하기 전에 중요한 단계입니다. 평가할 때는 모델의 콘텐츠가 LiteRT 형식과 호환되는지 확인해야 합니다. 또한 모델이 사용하는 데이터의 크기, 하드웨어 처리 요구사항, 모델의 전체 크기 및 복잡성 측면에서 모델이 모바일 및 에지 기기에서 사용하기에 적합한지 확인해야 합니다.
많은 모델의 경우 변환기가 기본적으로 작동합니다. 하지만 LiteRT 내장 연산자 라이브러리는 TensorFlow 핵심 연산자의 하위 집합을 지원하므로 일부 모델은 LiteRT로 변환하기 전에 추가 단계가 필요할 수 있습니다. 또한 LiteRT에서 지원하는 일부 작업에는 성능상의 이유로 사용이 제한되는 요구사항이 있습니다. 연산자 호환성 가이드를 참고하여 변환을 위해 모델을 리팩터링해야 하는지 확인하세요.
모델 변환
LiteRT 변환기는 TensorFlow 모델을 사용하고 LiteRT 모델 (.tflite 파일 확장자로 식별되는 최적화된 FlatBuffer 형식)을 생성합니다. SavedModel을 로드하거나 코드에서 만든 모델을 직접 변환할 수 있습니다.
변환기는 모델의 변환을 맞춤설정하는 3가지 주요 플래그 (또는 옵션)를 사용합니다.
- 호환성 플래그를 사용하면 전환에서 맞춤 연산자를 허용할지 여부를 지정할 수 있습니다.
- 최적화 플래그를 사용하면 변환 중에 적용할 최적화 유형을 지정할 수 있습니다. 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 최적화 기법은 학습 후 양자화입니다.
- 메타데이터 플래그를 사용하면 변환된 모델에 메타데이터를 추가할 수 있으므로 기기에 모델을 배포할 때 플랫폼별 래퍼 코드를 더 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다.
Python API 또는 명령줄 도구를 사용하여 모델을 변환할 수 있습니다. 모델에서 변환기를 실행하는 단계별 안내는 TF 모델 변환 가이드를 참고하세요.
일반적으로 표준 LiteRT 런타임 환경 또는 LiteRT (베타)용 Google Play 서비스 런타임 환경에 맞게 모델을 변환합니다. 일부 고급 사용 사례에서는 모델 런타임 환경을 맞춤설정해야 하며, 이 경우 변환 프로세스에 추가 단계가 필요합니다. 자세한 내용은 Android 개요의 고급 런타임 환경 섹션을 참고하세요.
고급 전환
모델에서 변환기를 실행하는 동안 오류가 발생하면 연산자 호환성 문제가 있을 가능성이 가장 높습니다. TensorFlow Lite에서는 일부 TensorFlow 작업이 지원되지 않습니다. 모델을 리팩터링하거나 수정된 LiteRT 형식 모델과 해당 모델의 맞춤 런타임 환경을 만들 수 있는 고급 변환 옵션을 사용하여 이러한 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- TensorFlow 및 LiteRT 모델 호환성 고려사항에 관한 자세한 내용은 모델 호환성 개요를 참고하세요.
- 모델 호환성 개요의 주제에서는 연산자 선택 가이드와 같은 모델 리팩터링을 위한 고급 기법을 다룹니다.
- 작업 및 제한사항의 전체 목록은 LiteRT 작업 페이지를 참고하세요.
다음 단계
- TF 모델 변환 가이드를 참고하여 모델 변환을 빠르게 시작하세요.
- 학습 후 양자화와 같은 기법을 사용하여 변환된 모델을 최적화하는 방법에 관한 안내는 최적화 개요를 참고하세요.
- 모델에 메타데이터를 추가하는 방법을 알아보려면 메타데이터 추가 개요를 참고하세요. 메타데이터는 모델에 대한 설명과 코드 생성기에서 활용할 수 있는 정보를 제공합니다.

