LiteRT מאפשר להפעיל מודלים של TensorFlow, PyTorch ו-JAX באפליקציות ל-Android. מערכת LiteRT מספקת סביבות הפעלה מוכנות מראש שניתנות להתאמה אישית להרצת מודלים ב-Android במהירות וביעילות, כולל אפשרויות להאצת חומרה.
לדוגמה, אפליקציות ל-Android שמשתמשות ב-LiteRT, אפשר לעיין במאגר הדוגמאות של LiteRT.
מודלים של למידת מכונה
LiteRT משתמש במודלים של TensorFlow, PyTorch ו-JAX שהומרו לפורמט קטן יותר, נייד ויעיל יותר של מודל למידת מכונה. אפשר להשתמש במודלים מוכנים מראש עם LiteRT ב-Android, או לבנות מודלים משלכם ולהמיר אותם לפורמט LiteRT.
בדף הזה מוסבר איך להשתמש במודלים של למידת מכונה שכבר נוצרו, ולא מוסבר איך ליצור, לאמן, לבדוק או להמיר מודלים. מידע נוסף על בחירה, שינוי, בנייה והמרה של מודלים של למידת מכונה ל-LiteRT זמין בדף Models.
הפעלת מודלים ב-Android
מודל LiteRT שפועל בתוך אפליקציית Android מקבל נתונים, מעבד אותם ומפיק תחזית על סמך הלוגיקה של המודל. כדי להפעיל מודל LiteRT, צריך סביבת זמן ריצה מיוחדת, והנתונים שמועברים למודל צריכים להיות בפורמט נתונים ספציפי שנקרא טנסור. כשמודל מעבד את הנתונים, בתהליך שנקרא הסקת מסקנות, הוא יוצר תוצאות חיזוי כטנסורים חדשים ומעביר אותם לאפליקציית Android כדי שהיא תוכל לבצע פעולה, כמו הצגת התוצאה למשתמש או הפעלת לוגיקה עסקית נוספת.
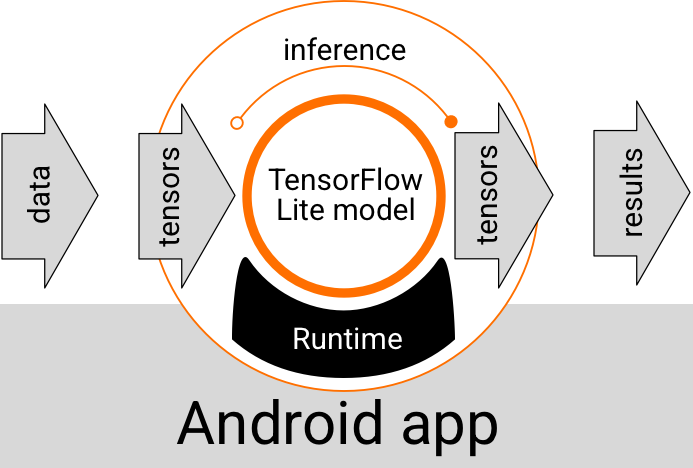
איור 1. תהליך ביצוע פונקציונלי למודלים של LiteRT באפליקציות ל-Android.
ברמת התכנון הפונקציונלי, אפליקציית Android צריכה לכלול את הרכיבים הבאים כדי להפעיל מודל LiteRT:
- סביבת זמן ריצה של LiteRT להפעלת המודל
- Model input handler כדי להפוך נתונים לטנסורים
- Model output handler כדי לקבל טנסורים של תוצאות פלט ולפרש אותם כתוצאות חיזוי
בקטעים הבאים מוסבר איך ספריות וכלים של LiteRT מספקים את הרכיבים הפונקציונליים האלה.
פיתוח אפליקציות באמצעות LiteRT
בקטע הזה מתואר הנתיב המומלץ והנפוץ ביותר להטמעה של LiteRT באפליקציית Android. כדאי לשים לב במיוחד לקטעים סביבת זמן הריצה וספריות הפיתוח. אם פיתחתם מודל בהתאמה אישית, כדאי לעיין בקטע נתיבי פיתוח מתקדמים.
אפשרויות של סביבת זמן הריצה
יש כמה דרכים להפעיל סביבת זמן ריצה להרצת מודלים באפליקציית Android. אלה האפשרויות המומלצות:
- LiteRT בסביבת זמן הריצה של Google Play Services (מומלץ)
- סביבת זמן ריצה עצמאית של LiteRT
באופן כללי, מומלץ להשתמש בסביבת זמן הריצה שמסופקת על ידי שירותי Google Play, כי היא חוסכת יותר מקום מאשר הסביבה הרגילה, כי היא נטענת באופן דינמי, וכך גודל האפליקציה קטן יותר. בנוסף, שירותי Google Play משתמשים באופן אוטומטי בגרסה היציבה העדכנית ביותר של זמן הריצה LiteRT, וכך אתם מקבלים תכונות נוספות וביצועים משופרים לאורך זמן. אם אתם מציעים את האפליקציה שלכם במכשירים שלא כוללים את Google Play Services או שאתם צריכים לנהל באופן מדויק את סביבת זמן הריצה של ה-ML, אתם צריכים להשתמש בזמן הריצה הרגיל של LiteRT. האפשרות הזו כוללת קוד נוסף באפליקציה, וכך מאפשרת לכם לשלוט יותר בזמן הריצה של ה-ML באפליקציה, אבל מגדילה את גודל ההורדה של האפליקציה.
כדי לגשת לסביבות זמן הריצה האלה באפליקציית Android, צריך להוסיף ספריות פיתוח של LiteRT לסביבת פיתוח האפליקציה. בקטע הבא מוסבר איך להשתמש בסביבות זמן הריצה הרגילות באפליקציה.
ספריות
אפשר לגשת ל-Interpreter API באמצעות Google Play Services. אתם יכולים להשתמש בספריות הליבה והתמיכה של LiteRT באפליקציית Android שלכם. לפרטים על תכנות באמצעות ספריות LiteRT וסביבות זמן ריצה, אפשר לעיין במאמר כלי פיתוח ל-Android.
קבלת מודלים
כדי להריץ מודל באפליקציית Android, צריך מודל בפורמט LiteRT. אתם יכולים להשתמש במודלים מוכנים מראש או ליצור מודל ולהמיר אותו לפורמט Lite. מידע נוסף על השגת מודלים לאפליקציית Android זמין בדף Models (מודלים) של LiteRT.
טיפול בנתוני קלט
כל נתון שמעבירים למודל למידת מכונה חייב להיות טנסור עם מבנה נתונים ספציפי, שלעתים קרובות נקרא צורה של הטנסור. כדי לעבד נתונים באמצעות מודל, קוד האפליקציה צריך להמיר את הנתונים מהפורמט המקורי שלהם, כמו נתוני תמונה, טקסט או אודיו, לטנסור בצורה הנדרשת למודל.
הרצת מסקנות
עיבוד נתונים באמצעות מודל כדי ליצור תוצאת חיזוי נקרא הסקת מסקנות. כדי להריץ הסקה באפליקציית Android, צריך סביבת זמן ריצה של LiteRT, מודל ונתוני קלט.
המהירות שבה מודל יכול ליצור הסקה במכשיר מסוים תלויה בגודל הנתונים שעוברים עיבוד, במורכבות של המודל ובמשאבי המחשוב הזמינים, כמו זיכרון ומעבד (CPU), או במעבדים מיוחדים שנקראים מאיצים. מודלים של למידת מכונה יכולים לפעול מהר יותר במעבדים מיוחדים כאלה, כמו מעבדים גרפיים (GPU) ומעבדי טנסור (TPU), באמצעות מנהלי התקנים של חומרה מסוג LiteRT שנקראים delegates. מידע נוסף על נציגים והאצת חומרה של עיבוד מודלים זמין במאמר סקירה כללית על האצת חומרה.
ניהול תוצאות הפלט
המודלים יוצרים תוצאות חיזוי כטנסורים, שהאפליקציה שלכם ל-Android צריכה לטפל בהם על ידי ביצוע פעולה או הצגת תוצאה למשתמש. תוצאות הפלט של המודל יכולות להיות פשוטות כמו מספר שמתאים לתוצאה יחידה (0 = כלב, 1 = חתול, 2 = ציפור) בסיווג תמונה, או מורכבות הרבה יותר, כמו תיבות תוחמות מרובות למספר אובייקטים מסווגים בתמונה, עם דירוגי מהימנות של התחזית בין 0 ל-1.
תוכניות פיתוח מתקדמות
כשמשתמשים במודלים מתוחכמים יותר של LiteRT בהתאמה אישית, יכול להיות שיהיה צורך בגישות פיתוח מתקדמות יותר מאלה שמתוארות למעלה. בקטעים הבאים מתוארות טכניקות מתקדמות להרצת מודלים ולפיתוח שלהם עבור LiteRT באפליקציות ל-Android.
סביבות הרצה מתקדמות
בנוסף לסביבות הרגילות של זמן הריצה ושל זמן הריצה של שירותי Google Play עבור LiteRT, יש סביבות נוספות של זמן ריצה שאפשר להשתמש בהן באפליקציית Android. השימוש בסביבות האלה הכי סביר אם יש לכם מודל של למידת מכונה שמשתמש בפעולות ML שלא נתמכות על ידי סביבת זמן הריצה הרגילה של LiteRT.
- זמן ריצה גמיש ל-LiteRT
- זמן ריצה של LiteRT בהתאמה אישית
Flex runtime של LiteRT מאפשר לכם לכלול אופרטורים ספציפיים שנדרשים למודל שלכם. כאפשרות מתקדמת להפעלת המודל, אפשר ליצור LiteRT ל-Android כדי לכלול אופרטורים ופונקציות אחרות שנדרשות להפעלת מודל למידת מכונה של TensorFlow. למידע נוסף, ראו Build LiteRT for Android.
ממשקי C ו-C++ APIs
LiteRT מספק גם API להרצת מודלים באמצעות C ו-C++. אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת ב-Android NDK, כדאי לשקול שימוש ב-API הזה. כדאי גם לשקול להשתמש ב-API הזה אם רוצים לשתף קוד בין כמה פלטפורמות. מידע נוסף על אפשרות הפיתוח הזו זמין בדף כלים למפתחים.
הרצת מודל שמבוסס על שרת
באופן כללי, מומלץ להריץ מודלים באפליקציה במכשיר Android כדי ליהנות משיפורים בפרטיות הנתונים של המשתמשים ומהשהיה נמוכה יותר. עם זאת, יש מקרים שבהם הפעלת מודל בשרת ענן, מחוץ למכשיר, היא פתרון טוב יותר. לדוגמה, אם יש לכם מודל גדול שלא ניתן לדחוס בקלות לגודל שמתאים למכשירי Android של המשתמשים, או שלא ניתן להפעיל אותו בביצועים סבירים במכשירים האלה. הגישה הזו עשויה להיות הפתרון המועדף עליכם גם אם חשוב לכם שהמודל יפעל באופן עקבי במגוון רחב של מכשירים.
ב-Google Cloud יש חבילה מלאה של שירותים להפעלת מודלים של AI. מידע נוסף זמין בדף מוצרי AI ולמידת מכונה של Google Cloud.
פיתוח ואופטימיזציה של מודלים בהתאמה אישית
במסלולי פיתוח מתקדמים יותר סביר להניח שתצטרכו לפתח מודלים מותאמים אישית של למידת מכונה ולבצע אופטימיזציה של המודלים האלה לשימוש במכשירי Android. אם אתם מתכננים ליצור מודלים בהתאמה אישית, כדאי להשתמש בטכניקות קוונטיזציה כדי לצמצם את עלויות הזיכרון והעיבוד. מידע נוסף על בניית מודלים עם ביצועים גבוהים לשימוש עם LiteRT זמין במאמר שיטות מומלצות לביצועים בקטע 'מודלים'.
גרסאות Android נתמכות
| גרסת LiteRT | סטטוס | רמת ה-SDK המינימלית | גרסת ה-NDK המינימלית (אם נעשה בו שימוש) | תאריך פרסום |
|---|---|---|---|---|
v1.2.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ הוצא משימוש | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-03-13 |
v1.3.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ הוצא משימוש | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-05-19 |
v1.4.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ הוצא משימוש | 26 (Android 8 Oreo) |
r26a |
2025-06-25 |
v1.4.1 ⭐ |
✅ פעיל | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-11-07 |
v2.0.3 ⭐ |
✅ פעיל | 26 (Android 8 Oreo) |
r26a |
2025-11-08 |
v2.1.0 ⭐ |
בקרוב | 23 (Android 6 Marshmallow) |
r26a |
עדיין לא הושק |
חשוב: כדי להבטיח תאימות לתכונות העדכניות ולעדכוני האבטחה, חשוב לעדכן את התלות שלכם.
Compiled Model API לעומת Interpreter API
- Compiled Model API – ביצוע הידור AOT/JIT עם אינטראופרביליות מאוחדת של מאגרים וצינורות אסינכרוניים, עם עדיפות למאיץ.
- Interpreter API – תואם לאחור לקוד בסגנון TensorFlow Lite קיים.
אפשר לבחור באחד מממשקי ה-API בזמן הריצה. רוב התכונות החדשות שקשורות לביצועים ולמאיצים מופיעות ב-Compiled Model API.
דוגמאות להטמעה:
- פילוח תמונות (Kotlin, CPU/GPU)
- פילוח אסינכרוני (C++, CPU/GPU/NPU)
- דמיון סמנטי (C++) – דוגמה מקומית
Common & CPU
| תכונה של זמן ריצה | Interpreter API | Compiled Model API |
|---|---|---|
| יצירת פרופילים | ✅ | ✅ |
| דיווח על שגיאות | ✅ | ✅ |
| יכולת פעולה הדדית של מאגר קלט/פלט (TensorBuffer/Environment) | -- | ✅ |
| בחירת מאיץ מוכן להפעלה | -- | ✅ |
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| פעולה מותאמת אישית | ✅ | ✅ |
| הגדרות XNNPACK | ✅ | ✅ |
| צורה דינמית | ✅ | ✅ |
GPU
| תכונה של זמן ריצה | Interpreter API | Compiled Model API |
|---|---|---|
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| שמירה במטמון של זיכרון | ✅ | ✅ |
| מעבר חזרה למעבד | ✅ | ✅ |
| ביצוע אסינכרוני | -- | ✅ |
| מאגר זמני ללא העתקה (AHWB/GLBuffer/Texture) | -- | ✅ |
| קצה עורפי של MLD OpenCL | ✅ | ✅ |
| MLD WebGPU backend (חדש) | -- | ✅ |
| תמיכה ב-MLD Metal (חדש) | -- | ✅ |
NPU
| תכונה של זמן ריצה | Interpreter API | Compiled Model API |
|---|---|---|
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| ביצוע אסינכרוני (Pixel) | -- | ✅ |
| מעבר חזרה למעבד | ✅ | ✅ |
| מעבר חזרה ל-GPU | -- | ✅ |
| העתקה ללא מאגר (AHWB) | -- | ✅ |
| QC/MTK AOT | -- | ✅ |
| Pixel AOT | -- | ✅ |
| QC/MTK/Pixel JIT | -- | ✅ |
מדריך למתחילים (Compiled Model API)
הפעלת הסקה באמצעות Compiled Model API כוללת את השלבים העיקריים הבאים:
- טוענים מודל תואם.
- הקצאת מאגרי טנסורים של קלט ופלט.
- מפעילים את המודל שעבר קומפילציה.
- קוראים את ההסקות לתוך מאגר פלט.
בקטעי הקוד הבאים מוצגת הטמעה בסיסית של התהליך כולו ב-Kotlin וב-C++.
C++
// Load model and initialize runtime
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto model, Model::CreateFromFile("mymodel.tflite"));
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto env, Environment::Create({}));
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto compiled_model,
CompiledModel::Create(env, model, kLiteRtHwAcceleratorCpu));
// Preallocate input/output buffers
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto input_buffers, compiled_model.CreateInputBuffers());
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto output_buffers, compiled_model.CreateOutputBuffers());
// Fill the first input
float input_values[] = { /* your data */ };
input_buffers[0].Write<float>(absl::MakeConstSpan(input_values, /*size*/));
// Invoke
compiled_model.Run(input_buffers, output_buffers);
// Read the output
std::vector<float> data(output_data_size);
output_buffers[0].Read<float>(absl::MakeSpan(data));
Kotlin
// Load model and initialize runtime
val model =
CompiledModel.create(
context.assets,
"mymodel.tflite",
CompiledModel.Options(Accelerator.CPU)
)
// Preallocate input/output buffers
val inputBuffers = model.createInputBuffers()
val outputBuffers = model.createOutputBuffers()
// Fill the first input
inputBuffers[0].writeFloat(FloatArray(data_size) { data_value /* your data */ })
// Invoke
model.run(inputBuffers, outputBuffers)
// Read the output
val outputFloatArray = outputBuffers[0].readFloat()
מידע נוסף זמין במדריכים תחילת העבודה עם Kotlin ותחילת העבודה עם C++.
יכולות עיקריות (Compiled Model API)
- בחירה מוכנה לשימוש של מאיץ וסנכרון אסינכרוני – בוחרים CPU/GPU/NPU בזמן היצירה ומריצים סנכרון אסינכרוני ללא צינורות נתונים של נציגים.
- מאגרי נתונים זמניים מאוחדים ללא העתקה – שיתוף מאגרי נתונים זמניים של AHWB/GL/OpenCL/WebGPU/Metal בין עיבוד מקדים, עיבוד סופי והסקת מסקנות.
- תפוקה שמוכנה לשימוש ב-AI גנרטיבי – מותאמת למודלים גדולים עם שמירת נתונים במטמון וגיבויים של GPU/NPU.
Interpreter API הוא עדיין נתיב התאימות לבסיסי קוד קיימים של TensorFlow Lite. כדאי להשתמש בו כשצריך התנהגות יציבה של delegate או כשמשתמשים בעטיפות של צד שלישי שמצפות ל-interpreter הקלאסי.
מאיצים
- מעבד (ברירת מחדל): אופטימיזציה של XNNPACK, תמיכה בצורות דינמיות.
- GPU: קצה עורפי של OpenCL היום; קצוות עורפיים של WebGPU ו-Metal זמינים דרך Compiled Model API.
- NPU: יש תמיכה ב-Qualcomm AI Engine Direct וב-MediaTek NeuroPilot ל-AOT/JIT. יש תמיכה ב-Pixel AOT. מתוכננת תמיכה ב-NPU של Apple/Intel.
מתי כדאי לבחור API
- משתמשים ב-Compiled Model API כשרוצים להגיע הכי מהר ל-GPU/NPU, למאגרי נתונים ללא העתקה או להפעלה אסינכרונית.
- משתמשים ב-Interpreter API כשרוצים להשיג תאימות מקסימלית לקוד, לכלים או לנציגים קיימים של TensorFlow Lite.

