LiteRT cho phép bạn chạy các mô hình TensorFlow, PyTorch và JAX trong ứng dụng Android. Hệ thống LiteRT cung cấp các môi trường thực thi có thể tuỳ chỉnh và được tạo sẵn để chạy các mô hình trên Android một cách nhanh chóng và hiệu quả, bao gồm cả các lựa chọn tăng tốc phần cứng.
Ví dụ: các ứng dụng Android sử dụng LiteRT, hãy xem kho lưu trữ các mẫu LiteRT.
Các mô hình học máy
LiteRT sử dụng các mô hình TensorFlow, PyTorch và JAX được chuyển đổi thành một định dạng mô hình học máy nhỏ hơn, di động và hiệu quả hơn. Bạn có thể sử dụng các mô hình dựng sẵn với LiteRT trên Android hoặc tạo mô hình của riêng mình và chuyển đổi chúng sang định dạng LiteRT.
Trang này thảo luận về việc sử dụng các mô hình học máy đã được xây dựng và không đề cập đến việc xây dựng, huấn luyện, kiểm thử hoặc chuyển đổi mô hình. Tìm hiểu thêm về cách chọn, sửa đổi, tạo và chuyển đổi các mô hình học máy cho LiteRT trong trang Mô hình.
Chạy các mô hình trên Android
Một mô hình LiteRT chạy trong ứng dụng Android sẽ nhận dữ liệu, xử lý dữ liệu và tạo ra một dự đoán dựa trên logic của mô hình. Mô hình LiteRT yêu cầu một môi trường thời gian chạy đặc biệt để thực thi và dữ liệu được truyền vào mô hình phải ở một định dạng dữ liệu cụ thể, được gọi là tensor. Khi một mô hình xử lý dữ liệu (còn gọi là chạy một suy luận), mô hình đó sẽ tạo ra kết quả dự đoán dưới dạng các tensor mới và truyền các kết quả đó đến ứng dụng Android để ứng dụng có thể thực hiện hành động, chẳng hạn như hiển thị kết quả cho người dùng hoặc thực thi logic nghiệp vụ bổ sung.
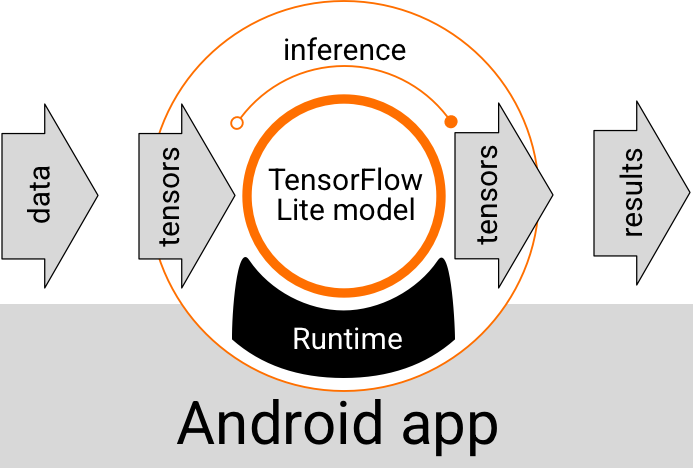
Hình 1. Quy trình thực thi chức năng cho các mô hình LiteRT trong ứng dụng Android.
Ở cấp độ thiết kế chức năng, ứng dụng Android của bạn cần có các phần tử sau để chạy một mô hình LiteRT:
- Môi trường thời gian chạy LiteRT để thực thi mô hình
- Trình xử lý dữ liệu đầu vào của mô hình để chuyển đổi dữ liệu thành tensor
- Trình xử lý đầu ra của mô hình để nhận các tensor kết quả đầu ra và diễn giải chúng dưới dạng kết quả dự đoán
Các phần sau đây mô tả cách các thư viện và công cụ LiteRT cung cấp những thành phần chức năng này.
Tạo ứng dụng bằng LiteRT
Phần này mô tả đường dẫn được đề xuất và phổ biến nhất để triển khai LiteRT trong Ứng dụng Android. Bạn nên chú ý nhất đến các phần môi trường thời gian chạy và thư viện phát triển. Nếu bạn đã phát triển một mô hình tuỳ chỉnh, hãy nhớ xem phần Các đường dẫn phát triển nâng cao.
Các lựa chọn về môi trường thời gian chạy
Bạn có thể bật môi trường thời gian chạy để thực thi các mô hình trong ứng dụng Android theo một số cách. Đây là những lựa chọn ưu tiên:
- LiteRT trong môi trường thời gian chạy của Dịch vụ Google Play (nên dùng)
- Môi trường thời gian chạy LiteRT độc lập
Nhìn chung, bạn nên sử dụng môi trường thời gian chạy do các dịch vụ Google Play cung cấp vì môi trường này tiết kiệm không gian hơn môi trường tiêu chuẩn do môi trường này tải động, giúp giảm kích thước ứng dụng. Các dịch vụ Google Play cũng tự động sử dụng bản phát hành ổn định và mới nhất của thời gian chạy LiteRT, mang đến cho bạn các tính năng bổ sung và hiệu suất được cải thiện theo thời gian. Nếu cung cấp ứng dụng trên những thiết bị không có Dịch vụ Google Play hoặc cần quản lý chặt chẽ môi trường thời gian chạy ML, thì bạn nên sử dụng thời gian chạy LiteRT tiêu chuẩn. Lựa chọn này sẽ kết hợp thêm mã vào ứng dụng của bạn, cho phép bạn kiểm soát thời gian chạy ML trong ứng dụng nhiều hơn với chi phí là tăng kích thước tải xuống của ứng dụng.
Bạn có thể truy cập vào các môi trường thời gian chạy này trong ứng dụng Android bằng cách thêm các thư viện phát triển LiteRT vào môi trường phát triển ứng dụng. Để biết thông tin về cách sử dụng các môi trường thời gian chạy tiêu chuẩn trong ứng dụng, hãy xem phần tiếp theo.
Thư viện
Bạn có thể truy cập vào Interpreter API bằng cách sử dụng Dịch vụ Google Play. Bạn có thể sử dụng các thư viện core và support của LiteRT trong ứng dụng Android. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về việc lập trình bằng cách sử dụng các thư viện LiteRT và môi trường thời gian chạy, hãy xem phần Công cụ phát triển cho Android.
Lấy mô hình
Để chạy một mô hình trong ứng dụng Android, bạn cần có một mô hình ở định dạng LiteRT. Bạn có thể sử dụng các mô hình dựng sẵn hoặc tạo một mô hình và chuyển đổi mô hình đó sang định dạng Lite. Để biết thêm thông tin về cách lấy các mô hình cho ứng dụng Android, hãy xem trang Mô hình LiteRT.
Xử lý dữ liệu đầu vào
Mọi dữ liệu bạn truyền vào một mô hình học máy đều phải là một tensor có cấu trúc dữ liệu cụ thể, thường được gọi là hình dạng của tensor. Để xử lý dữ liệu bằng một mô hình, mã ứng dụng của bạn phải chuyển đổi dữ liệu từ định dạng gốc (chẳng hạn như dữ liệu hình ảnh, văn bản hoặc âm thanh) thành một tensor có hình dạng bắt buộc cho mô hình của bạn.
Chạy suy luận
Xử lý dữ liệu thông qua một mô hình để tạo kết quả dự đoán được gọi là chạy một suy luận. Để chạy một quy trình suy luận trong ứng dụng Android, bạn cần có một môi trường thời gian chạy LiteRT, một mô hình và dữ liệu đầu vào.
Tốc độ mà một mô hình có thể tạo ra suy luận trên một thiết bị cụ thể phụ thuộc vào kích thước của dữ liệu được xử lý, độ phức tạp của mô hình và các tài nguyên điện toán có sẵn như bộ nhớ và CPU hoặc các bộ xử lý chuyên dụng được gọi là trình tăng tốc. Các mô hình học máy có thể chạy nhanh hơn trên những bộ xử lý chuyên dụng này (chẳng hạn như bộ xử lý đồ hoạ (GPU) và bộ xử lý tensor (TPU)) bằng cách sử dụng trình điều khiển phần cứng LiteRT có tên là delegate. Để biết thêm thông tin về các đại biểu và tính năng tăng tốc phần cứng của quá trình xử lý mô hình, hãy xem Tổng quan về tính năng tăng tốc phần cứng.
Xử lý kết quả đầu ra
Các mô hình tạo ra kết quả dự đoán dưới dạng tensor. Ứng dụng Android của bạn phải xử lý các kết quả này bằng cách thực hiện hành động hoặc hiển thị kết quả cho người dùng. Kết quả đầu ra của mô hình có thể đơn giản như một số tương ứng với một kết quả duy nhất (0 = chó, 1 = mèo, 2 = chim) cho một hoạt động phân loại hình ảnh, cho đến kết quả phức tạp hơn nhiều, chẳng hạn như nhiều khung hình chữ nhật cho một số đối tượng được phân loại trong một hình ảnh, với điểm số độ tin cậy dự đoán từ 0 đến 1.
Các đường dẫn phát triển nâng cao
Khi sử dụng các mô hình LiteRT phức tạp và tuỳ chỉnh hơn, bạn có thể cần sử dụng các phương pháp phát triển nâng cao hơn so với những phương pháp được mô tả ở trên. Các phần sau đây mô tả các kỹ thuật nâng cao để thực thi các mô hình và phát triển chúng cho LiteRT trong các ứng dụng Android.
Môi trường thời gian chạy nâng cao
Ngoài môi trường thời gian chạy tiêu chuẩn và môi trường thời gian chạy Dịch vụ Google Play cho LiteRT, còn có các môi trường thời gian chạy khác mà bạn có thể sử dụng với ứng dụng Android của mình. Khả năng sử dụng cao nhất cho các môi trường này là khi bạn có một mô hình học máy sử dụng các hoạt động học máy không được môi trường thời gian chạy tiêu chuẩn cho LiteRT hỗ trợ.
- Thời gian chạy linh hoạt cho LiteRT
- Thời gian chạy LiteRT được tạo riêng
Thời gian chạy linh hoạt của LiteRT cho phép bạn thêm các toán tử cụ thể cần thiết cho mô hình của mình. Là một lựa chọn nâng cao để chạy mô hình, bạn có thể tạo LiteRT cho Android để đưa các toán tử và chức năng khác cần thiết để chạy mô hình học máy TensorFlow. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem phần Tạo LiteRT cho Android.
API C và C++
LiteRT cũng cung cấp một API để chạy các mô hình bằng C và C++. Nếu ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng Android NDK, bạn nên cân nhắc sử dụng API này. Bạn cũng có thể cân nhắc sử dụng API này nếu muốn có thể chia sẻ mã giữa nhiều nền tảng. Để biết thêm thông tin về lựa chọn phát triển này, hãy xem trang Công cụ phát triển.
Thực thi mô hình dựa trên máy chủ
Nhìn chung, bạn nên chạy các mô hình trong ứng dụng trên thiết bị Android để tận dụng độ trễ thấp hơn và cải thiện quyền riêng tư của dữ liệu cho người dùng. Tuy nhiên, trong một số trường hợp, việc chạy một mô hình trên máy chủ đám mây (ngoài thiết bị) là một giải pháp tốt hơn. Ví dụ: nếu bạn có một mô hình lớn không dễ dàng nén xuống kích thước phù hợp với thiết bị Android của người dùng hoặc có thể thực thi với hiệu suất hợp lý trên các thiết bị đó. Đây cũng có thể là giải pháp bạn ưu tiên nếu hiệu suất nhất quán của mô hình trên nhiều thiết bị là ưu tiên hàng đầu.
Google Cloud cung cấp một bộ dịch vụ toàn diện để chạy các mô hình AI. Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem trang Các sản phẩm AI và học máy của Google Cloud.
Phát triển và tối ưu hoá mô hình tuỳ chỉnh
Các lộ trình phát triển nâng cao hơn có thể bao gồm việc phát triển các mô hình học máy tuỳ chỉnh và tối ưu hoá những mô hình đó để sử dụng trên thiết bị Android. Nếu bạn dự định tạo các mô hình tuỳ chỉnh, hãy nhớ cân nhắc việc áp dụng các kỹ thuật lượng tử hoá cho các mô hình để giảm chi phí bộ nhớ và xử lý. Để biết thêm thông tin về cách tạo các mô hình hiệu suất cao để sử dụng với LiteRT, hãy xem Các phương pháp hay nhất về hiệu suất trong phần Mô hình.
Các phiên bản Android được hỗ trợ
| Phiên bản LiteRT | Trạng thái | Cấp độ SDK tối thiểu | Phiên bản NDK tối thiểu (nếu dùng) | Ngày phát hành |
|---|---|---|---|---|
v1.2.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ Không dùng nữa | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-03-13 |
v1.3.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ Không dùng nữa | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-05-19 |
v1.4.0 ⭐ |
⚠️ Không dùng nữa | 26 (Android 8 Oreo) |
r26a |
2025-06-25 |
v1.4.1 ⭐ |
✅ Đang hoạt động | 21 (Android 5 Lollipop) |
r26a |
2025-11-07 |
v2.0.3 ⭐ |
✅ Đang hoạt động | 26 (Android 8 Oreo) |
r26a |
2025-11-08 |
v2.1.0 ⭐ |
Sắp tới | 23 (Android 6 Marshmallow) |
r26a |
Chưa phát hành |
Lưu ý quan trọng: Luôn cập nhật các phần phụ thuộc để đảm bảo khả năng tương thích với các tính năng mới nhất và bản cập nhật bảo mật.
Compiled Model API so với Interpreter API
- Compiled Model API – ưu tiên bộ tăng tốc, thực thi được biên dịch AOT/JIT với khả năng tương tác bộ đệm thống nhất và các quy trình không đồng bộ.
- Interpreter API – tương thích ngược với mã kiểu TensorFlow Lite hiện có.
Bạn có thể chọn API tại thời gian chạy; hầu hết các tính năng mới về hiệu suất và trình tăng tốc đều nằm trong Compiled Model API.
Để xem ví dụ về cách triển khai, hãy xem:
- Phân đoạn hình ảnh (Kotlin, CPU/GPU)
- Phân đoạn không đồng bộ (C++, CPU/GPU/NPU)
- Tính tương đồng về mặt ngữ nghĩa (C++) – mẫu cục bộ
Chung và CPU
| Tính năng thời gian chạy | Interpreter API | API Mô hình đã biên dịch |
|---|---|---|
| Phân tích tài nguyên | ✅ | ✅ |
| Trình báo cáo lỗi | ✅ | ✅ |
| Khả năng tương tác vùng đệm I/O (TensorBuffer/Environment) | -- | ✅ |
| Lựa chọn trình tăng tốc trọn gói | -- | ✅ |
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| Thao tác tuỳ chỉnh | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cấu hình XNNPACK | ✅ | ✅ |
| Hình dạng động | ✅ | ✅ |
GPU
| Tính năng thời gian chạy | Interpreter API | API Mô hình đã biên dịch |
|---|---|---|
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| Lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm | ✅ | ✅ |
| CPU dự phòng | ✅ | ✅ |
| Thực thi không đồng bộ | -- | ✅ |
| Vùng đệm sao chép bằng 0 (AHWB/GLBuffer/Texture) | -- | ✅ |
| Phần phụ trợ MLD OpenCL | ✅ | ✅ |
| Phần phụ trợ WebGPU MLD (mới) | -- | ✅ |
| Hỗ trợ MLD Metal (mới) | -- | ✅ |
NPU
| Tính năng thời gian chạy | Interpreter API | API Mô hình đã biên dịch |
|---|---|---|
| Sync exec | ✅ | ✅ |
| Async exec (Pixel) | -- | ✅ |
| CPU dự phòng | ✅ | ✅ |
| Dự phòng GPU | -- | ✅ |
| Sao chép không có bộ nhớ đệm (AHWB) | -- | ✅ |
| QC/MTK AOT | -- | ✅ |
| AOT của Pixel | -- | ✅ |
| QC/MTK/Pixel JIT | -- | ✅ |
Hướng dẫn nhanh (Compiled Model API)
Việc chạy suy luận bằng Compiled Model API bao gồm các bước chính sau:
- Tải một mô hình tương thích.
- Phân bổ vùng đệm tensor đầu vào và đầu ra.
- Gọi mô hình đã biên dịch.
- Đọc các suy luận vào một vùng đệm đầu ra.
Các đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy cách triển khai cơ bản của toàn bộ quy trình bằng Kotlin và C++.
C++
// Load model and initialize runtime
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto model, Model::CreateFromFile("mymodel.tflite"));
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto env, Environment::Create({}));
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto compiled_model,
CompiledModel::Create(env, model, kLiteRtHwAcceleratorCpu));
// Preallocate input/output buffers
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto input_buffers, compiled_model.CreateInputBuffers());
LITERT_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(auto output_buffers, compiled_model.CreateOutputBuffers());
// Fill the first input
float input_values[] = { /* your data */ };
input_buffers[0].Write<float>(absl::MakeConstSpan(input_values, /*size*/));
// Invoke
compiled_model.Run(input_buffers, output_buffers);
// Read the output
std::vector<float> data(output_data_size);
output_buffers[0].Read<float>(absl::MakeSpan(data));
Kotlin
// Load model and initialize runtime
val model =
CompiledModel.create(
context.assets,
"mymodel.tflite",
CompiledModel.Options(Accelerator.CPU)
)
// Preallocate input/output buffers
val inputBuffers = model.createInputBuffers()
val outputBuffers = model.createOutputBuffers()
// Fill the first input
inputBuffers[0].writeFloat(FloatArray(data_size) { data_value /* your data */ })
// Invoke
model.run(inputBuffers, outputBuffers)
// Read the output
val outputFloatArray = outputBuffers[0].readFloat()
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem hướng dẫn Bắt đầu sử dụng Kotlin và Bắt đầu sử dụng C++.
Các chức năng chính (Compiled Model API)
- Lựa chọn trình tăng tốc trọn gói và không đồng bộ – chọn CPU/GPU/NPU tại thời điểm tạo và chạy không đồng bộ mà không cần chuyển tiếp uỷ quyền.
- Vùng đệm hợp nhất không sao chép – chia sẻ vùng đệm AHWB/GL/OpenCL/WebGPU/Metal trên các giai đoạn tiền xử lý/hậu xử lý và suy luận.
- Thông lượng sẵn sàng cho AI tạo sinh – được tối ưu hoá cho các mô hình lớn có tính năng lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm và dự phòng GPU/NPU.
Interpreter API vẫn là đường dẫn tương thích cho các cơ sở mã TensorFlow Lite hiện có; hãy sử dụng API này khi bạn cần hành vi uỷ quyền ổn định hoặc trình bao bọc của bên thứ ba dự kiến sẽ có trình thông dịch cổ điển.
Trình tăng tốc
- CPU (mặc định): XNNPACK được tối ưu hoá, hỗ trợ các hình dạng động.
- GPU: Phần phụ trợ OpenCL hiện tại; phần phụ trợ WebGPU và Metal có sẵn thông qua Compiled Model API.
- NPU: Qualcomm AI Engine Direct và MediaTek NeuroPilot được hỗ trợ cho AOT/JIT; có sẵn AOT của Pixel; chúng tôi dự kiến sẽ hỗ trợ NPU của Apple/Intel.
Thời điểm chọn API
- Sử dụng Compiled Model API khi bạn muốn đường dẫn nhanh nhất đến GPU/NPU, bộ đệm sao chép bằng 0 hoặc quá trình thực thi không đồng bộ.
- Sử dụng Interpreter API khi bạn cần khả năng tương thích tối đa với mã, công cụ hoặc đại biểu TensorFlow Lite hiện có.

