| |  Запустить в Google Colab Запустить в Google Colab |  Посмотреть исходный код на GitHub Посмотреть исходный код на GitHub |
Обзор
В этом руководстве показано, как использовать внедрения из API Gemini для обнаружения потенциальных выбросов в вашем наборе данных. Вы визуализируете подмножество набора данных 20 групп новостей с помощью t-SNE и обнаруживаете выбросы за пределами определенного радиуса центральной точки каждого категориального кластера.
Для получения дополнительной информации о начале работы с встраиваниями, созданными с помощью API Gemini, ознакомьтесь с кратким руководством по Python .
Предварительные условия
Вы можете запустить это краткое руководство в Google Colab.
Чтобы выполнить это краткое руководство по созданию собственной среды разработки, убедитесь, что ваша среда соответствует следующим требованиям:
- Питон 3.9+
- Установка
jupyterдля запуска ноутбука.
Настраивать
Сначала загрузите и установите библиотеку Python Gemini API.
pip install -U -q google.generativeai
import re
import tqdm
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import google.generativeai as genai
import google.ai.generativelanguage as glm
# Used to securely store your API key
from google.colab import userdata
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
Получите ключ API
Прежде чем вы сможете использовать API Gemini, вам необходимо сначала получить ключ API. Если у вас его еще нет, создайте ключ одним щелчком мыши в Google AI Studio.
В Colab добавьте ключ к менеджеру секретов под знаком «🔑» на левой панели. Дайте ему имя API_KEY .
Получив ключ API, передайте его в SDK. Вы можете сделать это двумя способами:
- Поместите ключ в переменную среды
GOOGLE_API_KEY(SDK автоматически подберет его оттуда). - Передайте ключ в
genai.configure(api_key=...)
# Or use `os.getenv('API_KEY')` to fetch an environment variable.
API_KEY=userdata.get('API_KEY')
genai.configure(api_key=API_KEY)
for m in genai.list_models():
if 'embedContent' in m.supported_generation_methods:
print(m.name)
models/embedding-001 models/embedding-001
Подготовить набор данных
Набор текстовых данных 20 групп новостей содержит 18 000 сообщений групп новостей по 20 темам, разделенным на обучающие и тестовые наборы. Разделение наборов обучающих и тестовых данных основано на сообщениях, опубликованных до и после определенной даты. В этом руководстве используется подмножество обучения.
newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train')
# View list of class names for dataset
newsgroups_train.target_names
['alt.atheism', 'comp.graphics', 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc', 'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware', 'comp.sys.mac.hardware', 'comp.windows.x', 'misc.forsale', 'rec.autos', 'rec.motorcycles', 'rec.sport.baseball', 'rec.sport.hockey', 'sci.crypt', 'sci.electronics', 'sci.med', 'sci.space', 'soc.religion.christian', 'talk.politics.guns', 'talk.politics.mideast', 'talk.politics.misc', 'talk.religion.misc']
Вот первый пример в обучающем наборе.
idx = newsgroups_train.data[0].index('Lines')
print(newsgroups_train.data[0][idx:])
Lines: 15 I was wondering if anyone out there could enlighten me on this car I saw the other day. It was a 2-door sports car, looked to be from the late 60s/ early 70s. It was called a Bricklin. The doors were really small. In addition, the front bumper was separate from the rest of the body. This is all I know. If anyone can tellme a model name, engine specs, years of production, where this car is made, history, or whatever info you have on this funky looking car, please e-mail. Thanks, - IL ---- brought to you by your neighborhood Lerxst ----
# Apply functions to remove names, emails, and extraneous words from data points in newsgroups.data
newsgroups_train.data = [re.sub(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', '', d) for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove email
newsgroups_train.data = [re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", d) for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove names
newsgroups_train.data = [d.replace("From: ", "") for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove "From: "
newsgroups_train.data = [d.replace("\nSubject: ", "") for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove "\nSubject: "
# Cut off each text entry after 5,000 characters
newsgroups_train.data = [d[0:5000] if len(d) > 5000 else d for d in newsgroups_train.data]
# Put training points into a dataframe
df_train = pd.DataFrame(newsgroups_train.data, columns=['Text'])
df_train['Label'] = newsgroups_train.target
# Match label to target name index
df_train['Class Name'] = df_train['Label'].map(newsgroups_train.target_names.__getitem__)
df_train
Затем выполните выборку некоторых данных, взяв 150 точек данных в наборе обучающих данных и выбрав несколько категорий. В этом уроке используются научные категории.
# Take a sample of each label category from df_train
SAMPLE_SIZE = 150
df_train = (df_train.groupby('Label', as_index = False)
.apply(lambda x: x.sample(SAMPLE_SIZE))
.reset_index(drop=True))
# Choose categories about science
df_train = df_train[df_train['Class Name'].str.contains('sci')]
# Reset the index
df_train = df_train.reset_index()
df_train
df_train['Class Name'].value_counts()
sci.crypt 150 sci.electronics 150 sci.med 150 sci.space 150 Name: Class Name, dtype: int64
Создайте вложения
В этом разделе вы увидите, как создавать внедрения для различных текстов в кадре данных, используя внедрения из API Gemini.
Изменения API для внедрения с использованием модели-001
Для новой модели внедрения, embedding-001, имеется новый параметр типа задачи и необязательный заголовок (действителен только с Task_type= RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT ).
Эти новые параметры применяются только к новейшим моделям внедрения. Типы задач:
| Тип задачи | Описание |
|---|---|
| RETRIEVAL_QUERY | Указывает, что данный текст является запросом в настройках поиска/извлечения. |
| ПОЛУЧЕНИЕ_ДОКУМЕНТА | Указывает, что данный текст является документом в настройках поиска/извлечения. |
| СЕМАНТИЧЕСКОЕ_ПОХОЖИЕ | Указывает, что данный текст будет использоваться для семантического текстового сходства (STS). |
| КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ | Указывает, что внедрения будут использоваться для классификации. |
| КЛАСТЕРИЗАЦИЯ | Указывает, что внедрения будут использоваться для кластеризации. |
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()
from google.api_core import retry
def make_embed_text_fn(model):
@retry.Retry(timeout=300.0)
def embed_fn(text: str) -> list[float]:
# Set the task_type to CLUSTERING.
embedding = genai.embed_content(model=model,
content=text,
task_type="clustering")['embedding']
return np.array(embedding)
return embed_fn
def create_embeddings(df):
model = 'models/embedding-001'
df['Embeddings'] = df['Text'].progress_apply(make_embed_text_fn(model))
return df
df_train = create_embeddings(df_train)
df_train.drop('index', axis=1, inplace=True)
0%| | 0/600 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Уменьшение размерности
Размерность вектора внедрения документа равна 768. Чтобы визуализировать, как внедренные документы сгруппированы вместе, вам необходимо применить уменьшение размерности, поскольку вы можете визуализировать внедрения только в 2D или 3D пространстве. Контекстуально схожие документы должны располагаться ближе друг к другу в пространстве, в отличие от документов, которые не так похожи.
len(df_train['Embeddings'][0])
768
# Convert df_train['Embeddings'] Pandas series to a np.array of float32
X = np.array(df_train['Embeddings'].to_list(), dtype=np.float32)
X.shape
(600, 768)
Вы примените подход t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) для уменьшения размерности. Этот метод уменьшает количество измерений, сохраняя при этом кластеры (точки, расположенные близко друг к другу, остаются близко друг к другу). Для исходных данных модель пытается построить распределение, в котором другие точки данных являются «соседями» (например, имеют схожее значение). Затем он оптимизирует целевую функцию, чтобы сохранить аналогичное распределение в визуализации.
tsne = TSNE(random_state=0, n_iter=1000)
tsne_results = tsne.fit_transform(X)
df_tsne = pd.DataFrame(tsne_results, columns=['TSNE1', 'TSNE2'])
df_tsne['Class Name'] = df_train['Class Name'] # Add labels column from df_train to df_tsne
df_tsne
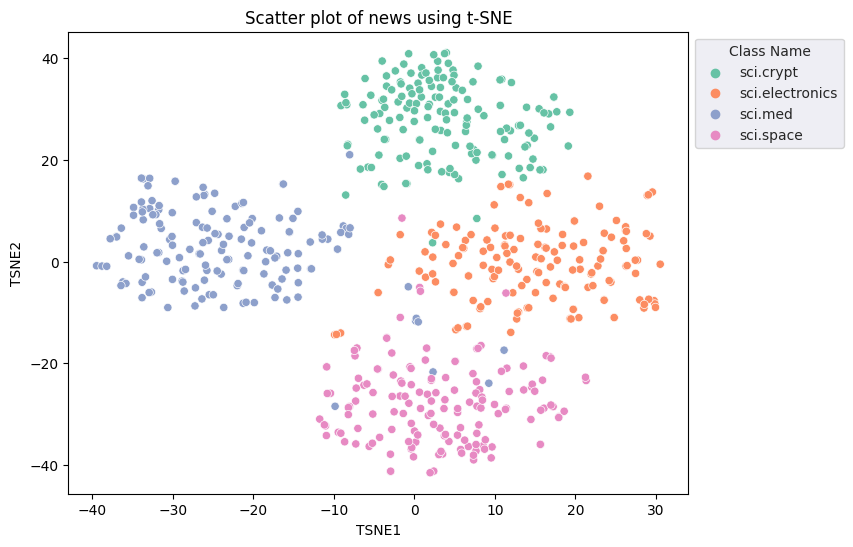
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6)) # Set figsize
sns.set_style('darkgrid', {"grid.color": ".6", "grid.linestyle": ":"})
sns.scatterplot(data=df_tsne, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', hue='Class Name', palette='Set2')
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
plt.title('Scatter plot of news using t-SNE')
plt.xlabel('TSNE1')
plt.ylabel('TSNE2');
Обнаружение выбросов
Чтобы определить, какие точки являются аномальными, вы определите, какие точки являются выбросами и выбросами. Начните с поиска центроида или местоположения, которое представляет центр кластера, и используйте расстояние, чтобы определить точки, которые являются выбросами.
Начните с получения центроида каждой категории.
def get_centroids(df_tsne):
# Get the centroid of each cluster
centroids = df_tsne.groupby('Class Name').mean()
return centroids
centroids = get_centroids(df_tsne)
centroids
def get_embedding_centroids(df):
emb_centroids = dict()
grouped = df.groupby('Class Name')
for c in grouped.groups:
sub_df = grouped.get_group(c)
# Get the centroid value of dimension 768
emb_centroids[c] = np.mean(sub_df['Embeddings'], axis=0)
return emb_centroids
emb_c = get_embedding_centroids(df_train)
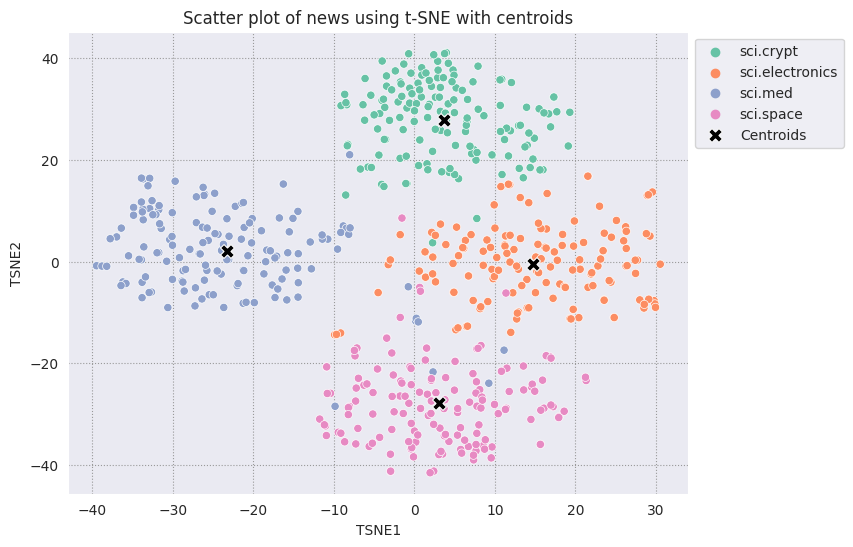
Постройте график каждого найденного центроида относительно остальных точек.
# Plot the centroids against the cluster
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6)) # Set figsize
sns.set_style('darkgrid', {"grid.color": ".6", "grid.linestyle": ":"})
sns.scatterplot(data=df_tsne, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', hue='Class Name', palette='Set2');
sns.scatterplot(data=centroids, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', color="black", marker='X', s=100, label='Centroids')
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
plt.title('Scatter plot of news using t-SNE with centroids')
plt.xlabel('TSNE1')
plt.ylabel('TSNE2');
Выберите радиус. Все, что выходит за эту границу от центроида этой категории, считается выбросом.
def calculate_euclidean_distance(p1, p2):
return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(p1 - p2)))
def detect_outlier(df, emb_centroids, radius):
for idx, row in df.iterrows():
class_name = row['Class Name'] # Get class name of row
# Compare centroid distances
dist = calculate_euclidean_distance(row['Embeddings'],
emb_centroids[class_name])
df.at[idx, 'Outlier'] = dist > radius
return len(df[df['Outlier'] == True])
range_ = np.arange(0.3, 0.75, 0.02).round(decimals=2).tolist()
num_outliers = []
for i in range_:
num_outliers.append(detect_outlier(df_train, emb_c, i))
# Plot range_ and num_outliers
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (14, 8))
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 12})
plt.bar(list(map(str, range_)), num_outliers)
plt.title("Number of outliers vs. distance of points from centroid")
plt.xlabel("Distance")
plt.ylabel("Number of outliers")
for i in range(len(range_)):
plt.text(i, num_outliers[i], num_outliers[i], ha = 'center')
plt.show()
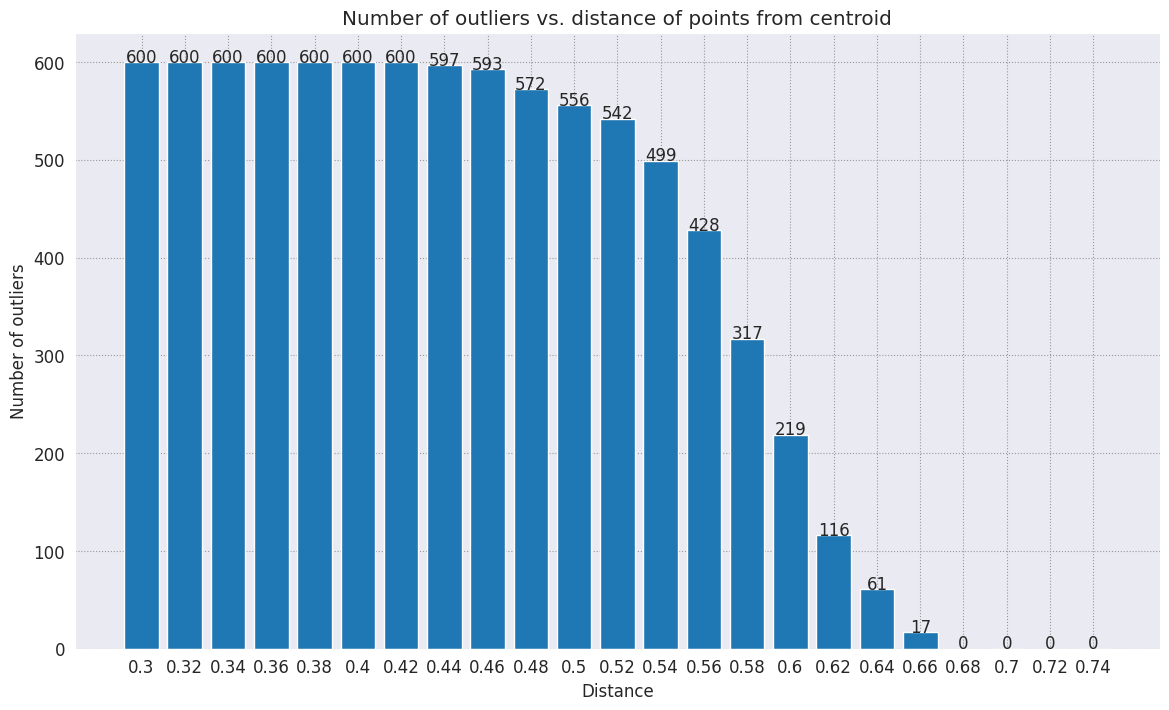
В зависимости от того, насколько чувствителен ваш детектор аномалий, вы можете выбрать, какой радиус вы хотите использовать. На данный момент используется 0,62, но вы можете изменить это значение.
# View the points that are outliers
RADIUS = 0.62
detect_outlier(df_train, emb_c, RADIUS)
df_outliers = df_train[df_train['Outlier'] == True]
df_outliers.head()
# Use the index to map the outlier points back to the projected TSNE points
outliers_projected = df_tsne.loc[df_outliers['Outlier'].index]
Постройте выбросы и обозначьте их прозрачным красным цветом.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6)) # Set figsize
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 10})
sns.set_style('darkgrid', {"grid.color": ".6", "grid.linestyle": ":"})
sns.scatterplot(data=df_tsne, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', hue='Class Name', palette='Set2');
sns.scatterplot(data=centroids, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', color="black", marker='X', s=100, label='Centroids')
# Draw a red circle around the outliers
sns.scatterplot(data=outliers_projected, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', color='red', marker='o', alpha=0.5, s=90, label='Outliers')
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
plt.title('Scatter plot of news with outliers projected with t-SNE')
plt.xlabel('TSNE1')
plt.ylabel('TSNE2');
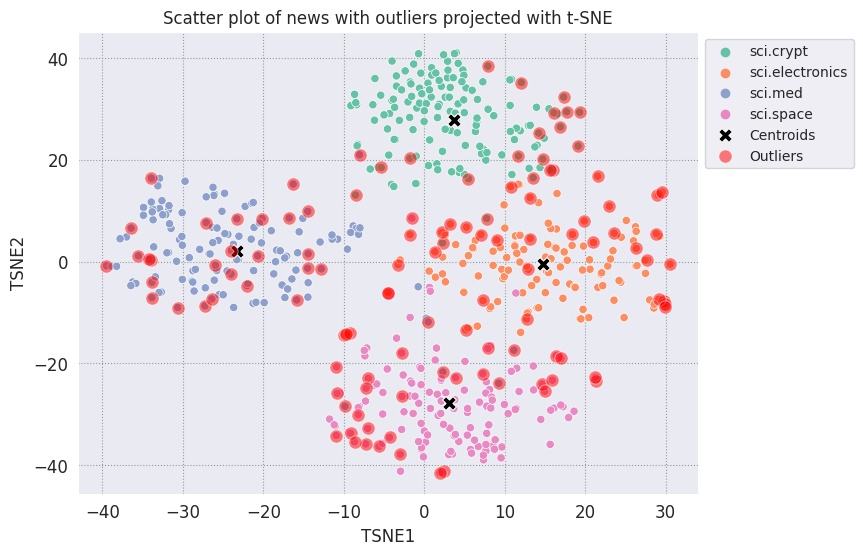
Используйте значения индексов файлов данных, чтобы распечатать несколько примеров того, как могут выглядеть выбросы в каждой категории. Здесь распечатывается первая точка данных из каждой категории. Изучите другие точки в каждой категории, чтобы увидеть данные, которые считаются выбросами или аномалиями.
sci_crypt_outliers = df_outliers[df_outliers['Class Name'] == 'sci.crypt']
print(sci_crypt_outliers['Text'].iloc[0])
Re: Source of random bits on a Unix workstation Lines: 44 Nntp-Posting-Host: sandstorm >>For your application, what you can do is to encrypt the real-time clock >>value with a secret key. Well, almost.... If I only had to solve the problem for myself, and were willing to have to type in a second password whenever I logged in, it could work. However, I'm trying to create a solution that anyone can use, and which, once installed, is just as effortless to start up as the non-solution of just using xhost to control access. I've got religeous problems with storing secret keys on multiuser computers. >For a good discussion of cryptographically "good" random number >generators, check out the draft-ietf-security-randomness-00.txt >Internet Draft, available at your local friendly internet drafts >repository. Thanks for the pointer! It was good reading, and I liked the idea of using several unrelated sources with a strong mixing function. However, unless I missed something, the only source they suggested that seems available, and unguessable by an intruder, when a Unix is fresh-booted, is I/O buffers related to network traffic. I believe my solution basically uses that strategy, without requiring me to reach into the kernel. >A reasonably source of randomness is the output of a cryptographic >hash function , when fed with a large amount of >more-or-less random data. For example, running MD5 on /dev/mem is a >slow, but random enough, source of random bits; there are bound to be >128 bits of entropy in the tens of megabytes of data in >a modern workstation's memory, as a fair amount of them are system >timers, i/o buffers, etc. I heard about this solution, and it sounded good. Then I heard that folks were experiencing times of 30-60 seconds to run this, on reasonably-configured workstations. I'm not willing to add that much delay to someone's login process. My approach takes a second or two to run. I'm considering writing the be-all and end-all of solutions, that launches the MD5, and simultaneously tries to suck bits off the net, and if the net should be sitting __SO__ idle that it can't get 10K after compression before MD5 finishes, use the MD5. This way I could have guaranteed good bits, and a deterministic upper bound on login time, and still have the common case of login take only a couple of extra seconds. -Bennett
sci_elec_outliers = df_outliers[df_outliers['Class Name'] == 'sci.electronics']
print(sci_elec_outliers['Text'].iloc[0])
Re: Laser vs Bubblejet?
Reply-To:
Distribution: world
X-Mailer: cppnews \\(Revision: 1.20 \\)
Organization: null
Lines: 53
Here is a different viewpoint.
> FYI: The actual horizontal dot placement resoution of an HP
> deskjet is 1/600th inch. The electronics and dynamics of the ink
> cartridge, however, limit you to generating dots at 300 per inch.
> On almost any paper, the ink wicks more than 1/300th inch anyway.
>
> The method of depositing and fusing toner of a laster printer
> results in much less spread than ink drop technology.
In practice there is little difference in quality but more care is needed
with inkjet because smudges etc. can happen.
> It doesn't take much investigation to see that the mechanical and
> electronic complement of a laser printer is more complex than
> inexpensive ink jet printers. Recall also that laser printers
> offer a much higher throughput: 10 ppm for a laser versus about 1
> ppm for an ink jet printer.
A cheap laser printer does not manage that sort of throughput and on top of
that how long does the _first_ sheet take to print? Inkjets are faster than
you say and in both cases the computer often has trouble keeping up with the
printer.
A sage said to me: "Do you want one copy or lots of copies?", "One",
"Inkjet".
> Something else to think about is the cost of consumables over the
> life of the printer. A 3000 page yield toner cartridge is about
> $US 75-80 at discount while HP high capacity
> cartridges are about $US 22 at discount. It could be that over the
> life cycle of the printer that consumables for laser printers are
> less than ink jet printers. It is getting progressively closer
> between the two technologies. Laser printers are usually desinged
> for higher duty cycles in pages per month and longer product
> replacement cycles.
Paper cost is the same and both can use refills. Long term the laserprinter
will need some expensive replacement parts and on top of that
are the amortisation costs which favour the lowest purchase cost printer.
HP inkjets understand PCL so in many cases a laserjet driver will work if the
software package has no inkjet driver.
There is one wild difference between the two printers: a laserprinter is a
page printer whilst an inkjet is a line printer. This means that a
laserprinter can rotate graphic images whilst an inkjet cannot. Few drivers
actually use this facility.
TC.
E-mail: or
sci_med_outliers = df_outliers[df_outliers['Class Name'] == 'sci.med']
print(sci_med_outliers['Text'].iloc[0])
Re: THE BACK MACHINE - Update Organization: University of Nebraska--Lincoln Lines: 15 Distribution: na NNTP-Posting-Host: unlinfo.unl.edu I have a BACK MACHINE and have had one since January. While I have not found it to be a panacea for my back pain, I think it has helped somewhat. It MAINLY acts to stretch muscles in the back and prevent spasms associated with pain. I am taking less pain medication than I was previously. The folks at BACK TECHNOLOGIES are VERY reluctant to honor their return policy. They extended my "warranty" period rather than allow me to return the machine when, after the first month or so, I was not thrilled with it. They encouraged me to continue to use it, abeit less vigourously. Like I said, I can't say it is a cure-all, but it keeps me stretched out and I am in less pain. -- *********************************************************************** Dale M. Webb, DVM, PhD * 97% of the body is water. The Veterinary Diagnostic Center * other 3% keeps you from drowning. University of Nebraska, Lincoln *
sci_space_outliers = df_outliers[df_outliers['Class Name'] == 'sci.space']
print(sci_space_outliers['Text'].iloc[0])
MACH 25 landing site bases? Article-I.D.: aurora.1993Apr5.193829.1 Organization: University of Alaska Fairbanks Lines: 7 Nntp-Posting-Host: acad3.alaska.edu The supersonic booms hear a few months ago over I belive San Fran, heading east of what I heard, some new super speed Mach 25 aircraft?? What military based int he direction of flight are there that could handle a Mach 25aircraft on its landing decent?? Odd question?? == Michael Adams, -- I'm not high, just jacked
Следующие шаги
Теперь вы создали детектор аномалий с помощью вложений! Попробуйте использовать свои собственные текстовые данные, чтобы визуализировать их как вложения, и выберите некоторую границу, позволяющую обнаруживать выбросы. Вы можете выполнить уменьшение размерности, чтобы завершить этап визуализации. Обратите внимание, что t-SNE хорошо справляется с кластеризацией входных данных, но сходимость может занять больше времени или может застрять на локальных минимумах. Если вы столкнулись с этой проблемой, вы можете рассмотреть еще один метод — анализ главных компонентов (PCA) .
Чтобы узнать, как использовать другие сервисы API Gemini, посетите краткое руководство по Python .
Чтобы узнать больше о том, как можно использовать вложения, ознакомьтесь с доступными примерами . Чтобы узнать, как создавать их с нуля, см. учебник TensorFlow Word Embeddings .

