|
|
 הפעלה ב-Google Colab הפעלה ב-Google Colab
|
 הצגת המקור ב-GitHub הצגת המקור ב-GitHub
|
סקירה
ב-notebook הזה תלמדו להשתמש בהטמעות שמופק על ידי Gemini API כדי לאמן מודל שיכול לסווג סוגים שונים של פוסטים בקבוצות דיון על סמך הנושא.
במדריך הזה תאמנו מסווג לחזות לאיזו כיתה שייך פוסט בקבוצת דיון.
דרישות מוקדמות
אפשר להריץ את המדריך למתחילים ב-Google Colab.
כדי להשלים את המדריך למתחילים בסביבת הפיתוח שלכם, ודאו שהסביבה עומדת בדרישות הבאות:
- Python 3.9 ואילך
- התקנה של
jupyterלהפעלת ה-notebook.
הגדרה
קודם כול, מורידים ומתקינים את ספריית Python ל-Gemini API.
pip install -U -q google.generativeai
import re
import tqdm
import keras
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import google.generativeai as genai
# Used to securely store your API key
from google.colab import userdata
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras import layers
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
import sklearn.metrics as skmetrics
תפוס מפתח API
כדי להשתמש ב-Gemini API, עליך לקבל מפתח API. אם עדיין אין לך מפתח, אפשר ליצור מפתח בלחיצה אחת ב-Google AI Studio.
ב-Colab, מוסיפים את המפתח למנהל הסודות בקטע '🔑' בחלונית שמשמאל. נותנים לו את השם API_KEY.
אחרי שמוצאים את מפתח ה-API, מעבירים אותו ל-SDK. תוכל לעשות זאת בשתי דרכים:
- מזינים את המפתח במשתנה הסביבה
GOOGLE_API_KEY(ה-SDK יאסוף אותו משם באופן אוטומטי). - יש להעביר את המפתח אל
genai.configure(api_key=...)
# Or use `os.getenv('API_KEY')` to fetch an environment variable.
API_KEY=userdata.get('API_KEY')
genai.configure(api_key=API_KEY)
for m in genai.list_models():
if 'embedContent' in m.supported_generation_methods:
print(m.name)
models/embedding-001 models/embedding-001
מערך נתונים
מערך נתוני הטקסט של קבוצות דיון של 20 קבוצות דיון מכיל 18,000 פוסטים של קבוצות דיון ב-20 נושאים, המחולקים לקבוצות אימון ולקבוצות בדיקה. החלוקה בין מערכי הנתונים של האימון לבין מערכי הנתונים של הבדיקה מבוססת על הודעות שפורסמו לפני ואחרי תאריך מסוים. במדריך הזה תשתמשו בקבוצות המשנה של מערכי הנתונים של האימון והבדיקה. תצטרכו לעבד מראש את הנתונים ולסדר אותם במסגרות נתונים של Pandas.
newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train')
newsgroups_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test')
# View list of class names for dataset
newsgroups_train.target_names
['alt.atheism', 'comp.graphics', 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc', 'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware', 'comp.sys.mac.hardware', 'comp.windows.x', 'misc.forsale', 'rec.autos', 'rec.motorcycles', 'rec.sport.baseball', 'rec.sport.hockey', 'sci.crypt', 'sci.electronics', 'sci.med', 'sci.space', 'soc.religion.christian', 'talk.politics.guns', 'talk.politics.mideast', 'talk.politics.misc', 'talk.religion.misc']
לפניכם דוגמה למצב של נקודה על הגרף מקבוצת האימון.
idx = newsgroups_train.data[0].index('Lines')
print(newsgroups_train.data[0][idx:])
Lines: 15 I was wondering if anyone out there could enlighten me on this car I saw the other day. It was a 2-door sports car, looked to be from the late 60s/ early 70s. It was called a Bricklin. The doors were really small. In addition, the front bumper was separate from the rest of the body. This is all I know. If anyone can tellme a model name, engine specs, years of production, where this car is made, history, or whatever info you have on this funky looking car, please e-mail. Thanks, - IL ---- brought to you by your neighborhood Lerxst ----
עכשיו תתחילו לעבד מראש את הנתונים עבור המדריך. מומלץ להסיר מידע רגיש כמו שמות, כתובות אימייל או חלקים מיותרים מהטקסט כמו "From: " ו-"\nSubject: ". מסדרים את המידע במסגרת נתונים של Pandas כדי שיהיה קריא יותר.
def preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroup_dataset):
# Apply functions to remove names, emails, and extraneous words from data points in newsgroups.data
newsgroup_dataset.data = [re.sub(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', '', d) for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove email
newsgroup_dataset.data = [re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", d) for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove names
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d.replace("From: ", "") for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove "From: "
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d.replace("\nSubject: ", "") for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove "\nSubject: "
# Cut off each text entry after 5,000 characters
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d[0:5000] if len(d) > 5000 else d for d in newsgroup_dataset.data]
# Put data points into dataframe
df_processed = pd.DataFrame(newsgroup_dataset.data, columns=['Text'])
df_processed['Label'] = newsgroup_dataset.target
# Match label to target name index
df_processed['Class Name'] = ''
for idx, row in df_processed.iterrows():
df_processed.at[idx, 'Class Name'] = newsgroup_dataset.target_names[row['Label']]
return df_processed
# Apply preprocessing function to training and test datasets
df_train = preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroups_train)
df_test = preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroups_test)
df_train.head()
בשלב הבא דוגמים חלק מהנתונים באמצעות 100 נקודות נתונים במערך הנתונים לאימון, ומשחררים כמה מהקטגוריות כדי לעבור על המדריך. בחר את הקטגוריות המדעיות להשוואה.
def sample_data(df, num_samples, classes_to_keep):
df = df.groupby('Label', as_index = False).apply(lambda x: x.sample(num_samples)).reset_index(drop=True)
df = df[df['Class Name'].str.contains(classes_to_keep)]
# Reset the encoding of the labels after sampling and dropping certain categories
df['Class Name'] = df['Class Name'].astype('category')
df['Encoded Label'] = df['Class Name'].cat.codes
return df
TRAIN_NUM_SAMPLES = 100
TEST_NUM_SAMPLES = 25
CLASSES_TO_KEEP = 'sci' # Class name should contain 'sci' in it to keep science categories
df_train = sample_data(df_train, TRAIN_NUM_SAMPLES, CLASSES_TO_KEEP)
df_test = sample_data(df_test, TEST_NUM_SAMPLES, CLASSES_TO_KEEP)
df_train.value_counts('Class Name')
Class Name sci.crypt 100 sci.electronics 100 sci.med 100 sci.space 100 dtype: int64
df_test.value_counts('Class Name')
Class Name sci.crypt 25 sci.electronics 25 sci.med 25 sci.space 25 dtype: int64
יצירת ההטמעות
בקטע הזה נסביר איך ליצור הטמעות לקטע טקסט באמצעות ההטמעות מ-Gemini API. למידע נוסף על הטמעות, אפשר לעיין במדריך להטמעות.
שינויים ב-API של הטמעות מוטמעות 001
למודל ההטמעות החדש יש פרמטר חדש של סוג משימה, וגם כותרת אופציונלית (תקינה רק כאשר מדובר ב-task_type=RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT).
הפרמטרים החדשים האלה חלים רק על המודלים החדשים ביותר של הטמעות.סוגי המשימות הם:
| סוג המשימה | תיאור |
|---|---|
| RETRIEVAL_QUERY | מציין שהטקסט הנתון הוא שאילתה בהגדרת חיפוש/אחזור. |
| RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT | מציינת שהטקסט הנתון הוא מסמך בהגדרת חיפוש/אחזור. |
| SEMANTIC_SIMILARITY | קובעת שהטקסט הנתון ישמש לדמיון טקסט סמנטי (STS). |
| סיווג | מציינת שההטמעות ישמשו לסיווג. |
| אשכול | המדיניות קובעת שההטמעות ישמשו לאשכולות. |
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()
from google.api_core import retry
def make_embed_text_fn(model):
@retry.Retry(timeout=300.0)
def embed_fn(text: str) -> list[float]:
# Set the task_type to CLASSIFICATION.
embedding = genai.embed_content(model=model,
content=text,
task_type="classification")
return embedding['embedding']
return embed_fn
def create_embeddings(model, df):
df['Embeddings'] = df['Text'].progress_apply(make_embed_text_fn(model))
return df
model = 'models/embedding-001'
df_train = create_embeddings(model, df_train)
df_test = create_embeddings(model, df_test)
0%| | 0/400 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
df_train.head()
בניית מודל סיווג פשוט
כאן תגדירו מודל פשוט עם שכבה מוסתרת אחת ופלט הסתברות של מחלקה אחת. החיזוי יתאים להסתברות שקטע טקסט מסוים יהיה סוג מסוים של חדשות. כשיוצרים את המודל, Keras משנה באופן אוטומטי את הנקודות על הגרף.
def build_classification_model(input_size: int, num_classes: int) -> keras.Model:
inputs = x = keras.Input(input_size)
x = layers.Dense(input_size, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='sigmoid')(x)
return keras.Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=x)
# Derive the embedding size from the first training element.
embedding_size = len(df_train['Embeddings'].iloc[0])
# Give your model a different name, as you have already used the variable name 'model'
classifier = build_classification_model(embedding_size, len(df_train['Class Name'].unique()))
classifier.summary()
classifier.compile(loss = keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=['accuracy'])
Model: "model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 768)] 0
dense (Dense) (None, 768) 590592
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 4) 3076
=================================================================
Total params: 593668 (2.26 MB)
Trainable params: 593668 (2.26 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
embedding_size
768
אימון המודל לסיווג של קבוצות דיון
לבסוף, אפשר לאמן מודל פשוט. יש להשתמש במספר קטן של תקופות של זמן מערכת כדי להימנע מחיבור יתר. ה-epoch הראשון לוקח הרבה יותר זמן מהשאר, מכיוון שצריך לחשב את ההטמעות רק פעם אחת.
NUM_EPOCHS = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 32
# Split the x and y components of the train and validation subsets.
y_train = df_train['Encoded Label']
x_train = np.stack(df_train['Embeddings'])
y_val = df_test['Encoded Label']
x_val = np.stack(df_test['Embeddings'])
# Train the model for the desired number of epochs.
callback = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='accuracy', patience=3)
history = classifier.fit(x=x_train,
y=y_train,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
callbacks=[callback],
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,)
Epoch 1/20 /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/keras/src/backend.py:5729: UserWarning: "`sparse_categorical_crossentropy` received `from_logits=True`, but the `output` argument was produced by a Softmax activation and thus does not represent logits. Was this intended? output, from_logits = _get_logits( 13/13 [==============================] - 1s 30ms/step - loss: 1.2141 - accuracy: 0.6675 - val_loss: 0.9801 - val_accuracy: 0.8800 Epoch 2/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.7580 - accuracy: 0.9400 - val_loss: 0.6061 - val_accuracy: 0.9300 Epoch 3/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.4249 - accuracy: 0.9525 - val_loss: 0.3902 - val_accuracy: 0.9200 Epoch 4/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.2561 - accuracy: 0.9625 - val_loss: 0.2597 - val_accuracy: 0.9400 Epoch 5/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.1693 - accuracy: 0.9700 - val_loss: 0.2145 - val_accuracy: 0.9300 Epoch 6/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.1240 - accuracy: 0.9850 - val_loss: 0.1801 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 7/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0931 - accuracy: 0.9875 - val_loss: 0.1623 - val_accuracy: 0.9400 Epoch 8/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 16ms/step - loss: 0.0736 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.1418 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 9/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0613 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.1315 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 10/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0479 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1235 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 11/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0399 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1219 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 12/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0326 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1158 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 13/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0263 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1127 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 14/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 17ms/step - loss: 0.0229 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1123 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 15/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0195 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1063 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 16/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 17ms/step - loss: 0.0172 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1070 - val_accuracy: 0.9700
הערכת ביצועי המודל
משתמשים ב-Keras Model.evaluate כדי לקבל נתונים על אובדן ודיוק של מערך הנתונים לבדיקה.
classifier.evaluate(x=x_val, y=y_val, return_dict=True)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1070 - accuracy: 0.9700
{'loss': 0.10700511932373047, 'accuracy': 0.9700000286102295}
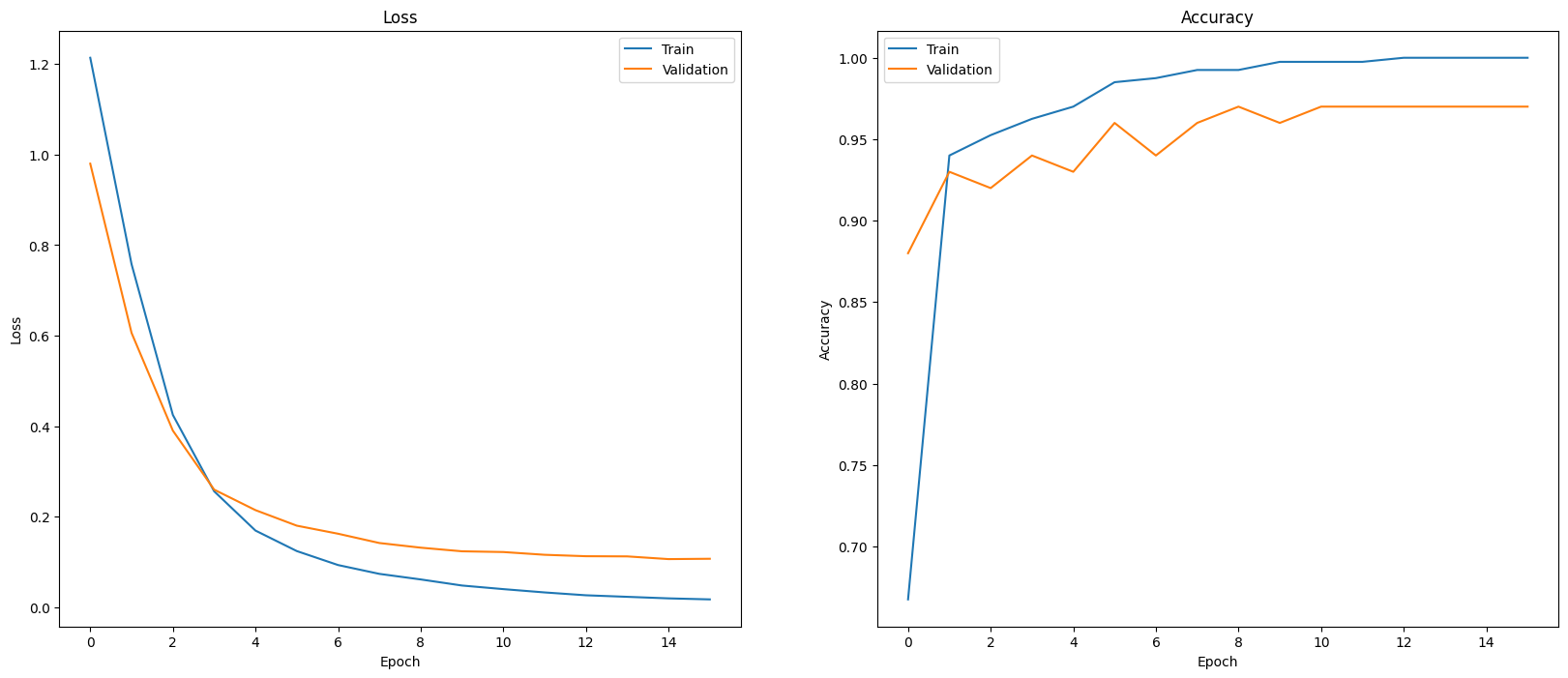
אחת הדרכים להעריך את ביצועי המודל היא להציג באופן חזותי את ביצועי המסווג. אפשר להשתמש ב-plot_history כדי לראות את מגמות האובדן והדיוק במהלך התקופות של השנים הקודמות.
def plot_history(history):
"""
Plotting training and validation learning curves.
Args:
history: model history with all the metric measures
"""
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1,2)
fig.set_size_inches(20, 8)
# Plot loss
ax1.set_title('Loss')
ax1.plot(history.history['loss'], label = 'train')
ax1.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label = 'test')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
# Plot accuracy
ax2.set_title('Accuracy')
ax2.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label = 'train')
ax2.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label = 'test')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
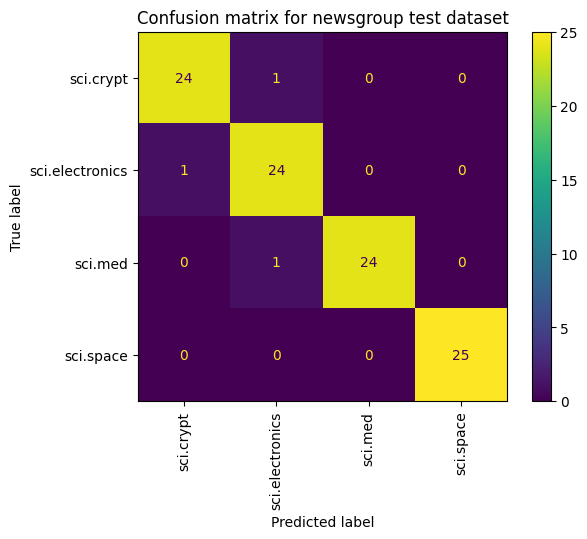
דרך נוספת להציג את ביצועי המודל, מעבר למדידת אובדן ודיוק היא להשתמש במטריצה של בלבול. מטריצת הבלבול מאפשרת להעריך את הביצועים של מודל הסיווג מעבר לדיוק. אתם יכולים לראות אילו נקודות מסווגות באופן שגוי. כדי לבנות מטריצת הבלבול לבעיה של סיווג מרובה-סיווגים, צריך לקבל את הערכים בפועל בקבוצת הבדיקה ואת הערכים החזויים.
מתחילים ביצירת המחלקה החזויה לכל דוגמה בקבוצת האימות באמצעות Model.predict().
y_hat = classifier.predict(x=x_val)
y_hat = np.argmax(y_hat, axis=1)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step
labels_dict = dict(zip(df_test['Class Name'], df_test['Encoded Label']))
labels_dict
{'sci.crypt': 0, 'sci.electronics': 1, 'sci.med': 2, 'sci.space': 3}
cm = skmetrics.confusion_matrix(y_val, y_hat)
disp = skmetrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm,
display_labels=labels_dict.keys())
disp.plot(xticks_rotation='vertical')
plt.title('Confusion matrix for newsgroup test dataset');
plt.grid(False)
השלבים הבאים
כדי ללמוד איך להשתמש בהטמעות, אפשר לעיין במדריכים הבאים:

