|
|
 Google Colab で実行 Google Colab で実行
|
 GitHub のソースを表示 GitHub のソースを表示
|
概要
このノートブックでは、Gemini API によって生成されたエンベディングを使用して、トピックに基づいてさまざまな種類のニュースグループの投稿を分類できるモデルをトレーニングする方法を学習します。
このチュートリアルでは、ニュースグループの投稿がどのクラスに属するかを予測する分類器をトレーニングします。
前提条件
このクイックスタートは Google Colab で実行できます。
このクイックスタートを独自の開発環境で完了するには、環境が次の要件を満たしていることを確認してください。
- Python 3.9 以降
- ノートブックを実行するための
jupyterのインストール。
セットアップ
まず、Gemini API Python ライブラリをダウンロードしてインストールします。
pip install -U -q google.generativeai
import re
import tqdm
import keras
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import google.generativeai as genai
# Used to securely store your API key
from google.colab import userdata
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras import layers
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
import sklearn.metrics as skmetrics
API キーを取得
Gemini API を使用するには、まず API キーを取得する必要があります。キーをまだ作成していない場合は、Google AI Studio でワンクリックで作成できます。
Colab で、左側のパネルの「↩」の下にあるシークレット マネージャーにキーを追加します。API_KEY という名前を付けます。
API キーを取得したら、SDK に渡します。作成する方法は次の 2 つです。
- 鍵を
GOOGLE_API_KEY環境変数に設定します(SDK はそこから自動的に取得します)。 - 鍵を
genai.configure(api_key=...)に渡す
# Or use `os.getenv('API_KEY')` to fetch an environment variable.
API_KEY=userdata.get('API_KEY')
genai.configure(api_key=API_KEY)
for m in genai.list_models():
if 'embedContent' in m.supported_generation_methods:
print(m.name)
models/embedding-001 models/embedding-001
データセット
20 Newsgroups Text Dataset は、トレーニング セットとテストセットに分かれており、20 のトピックに関する 18,000 件のニュースグループ投稿が含まれています。トレーニング データセットとテスト データセットの分割は、特定の日付の前後に投稿されたメッセージに基づいて行われます。このチュートリアルでは、トレーニング データセットとテスト データセットのサブセットを使用します。データを前処理して Pandas DataFrame に整理します。
newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train')
newsgroups_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test')
# View list of class names for dataset
newsgroups_train.target_names
['alt.atheism', 'comp.graphics', 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc', 'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware', 'comp.sys.mac.hardware', 'comp.windows.x', 'misc.forsale', 'rec.autos', 'rec.motorcycles', 'rec.sport.baseball', 'rec.sport.hockey', 'sci.crypt', 'sci.electronics', 'sci.med', 'sci.space', 'soc.religion.christian', 'talk.politics.guns', 'talk.politics.mideast', 'talk.politics.misc', 'talk.religion.misc']
トレーニング セットのデータポイントはこのように表示されます。
idx = newsgroups_train.data[0].index('Lines')
print(newsgroups_train.data[0][idx:])
Lines: 15 I was wondering if anyone out there could enlighten me on this car I saw the other day. It was a 2-door sports car, looked to be from the late 60s/ early 70s. It was called a Bricklin. The doors were really small. In addition, the front bumper was separate from the rest of the body. This is all I know. If anyone can tellme a model name, engine specs, years of production, where this car is made, history, or whatever info you have on this funky looking car, please e-mail. Thanks, - IL ---- brought to you by your neighborhood Lerxst ----
次に、このチュートリアルで使用するデータの前処理を開始します。名前、メールアドレスなどの機密情報や、"From: " や "\nSubject: " などの不要なテキスト部分を削除します。読みやすくするために、情報を Pandas DataFrame に整理する。
def preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroup_dataset):
# Apply functions to remove names, emails, and extraneous words from data points in newsgroups.data
newsgroup_dataset.data = [re.sub(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', '', d) for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove email
newsgroup_dataset.data = [re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", d) for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove names
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d.replace("From: ", "") for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove "From: "
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d.replace("\nSubject: ", "") for d in newsgroup_dataset.data] # Remove "\nSubject: "
# Cut off each text entry after 5,000 characters
newsgroup_dataset.data = [d[0:5000] if len(d) > 5000 else d for d in newsgroup_dataset.data]
# Put data points into dataframe
df_processed = pd.DataFrame(newsgroup_dataset.data, columns=['Text'])
df_processed['Label'] = newsgroup_dataset.target
# Match label to target name index
df_processed['Class Name'] = ''
for idx, row in df_processed.iterrows():
df_processed.at[idx, 'Class Name'] = newsgroup_dataset.target_names[row['Label']]
return df_processed
# Apply preprocessing function to training and test datasets
df_train = preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroups_train)
df_test = preprocess_newsgroup_data(newsgroups_test)
df_train.head()
次に、このチュートリアルで使用するトレーニング データセット内の 100 個のデータポイントを取得し、いくつかのカテゴリを除外して、一部のデータをサンプリングします。比較する科学のカテゴリを選択してください。
def sample_data(df, num_samples, classes_to_keep):
df = df.groupby('Label', as_index = False).apply(lambda x: x.sample(num_samples)).reset_index(drop=True)
df = df[df['Class Name'].str.contains(classes_to_keep)]
# Reset the encoding of the labels after sampling and dropping certain categories
df['Class Name'] = df['Class Name'].astype('category')
df['Encoded Label'] = df['Class Name'].cat.codes
return df
TRAIN_NUM_SAMPLES = 100
TEST_NUM_SAMPLES = 25
CLASSES_TO_KEEP = 'sci' # Class name should contain 'sci' in it to keep science categories
df_train = sample_data(df_train, TRAIN_NUM_SAMPLES, CLASSES_TO_KEEP)
df_test = sample_data(df_test, TEST_NUM_SAMPLES, CLASSES_TO_KEEP)
df_train.value_counts('Class Name')
Class Name sci.crypt 100 sci.electronics 100 sci.med 100 sci.space 100 dtype: int64
df_test.value_counts('Class Name')
Class Name sci.crypt 25 sci.electronics 25 sci.med 25 sci.space 25 dtype: int64
エンベディングを作成する
このセクションでは、Gemini API のエンベディングを使用してテキストのエンベディングを生成する方法について説明します。エンベディングの詳細については、エンベディング ガイドをご覧ください。
エンベディング embedding-001 の API の変更
新しいエンベディング モデルには、新しいタスクタイプのパラメータとオプションのタイトルがあります(task_type=RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT の場合のみ有効です)。
これらの新しいパラメータは、最新のエンベディング モデルにのみ適用されます。タスクの種類は次のとおりです。
| タスクの種類 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| RETRIEVAL_QUERY | 指定したテキストが検索 / 取得設定のクエリであることを指定します。 |
| RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT | 指定したテキストが検索 / 取得設定のドキュメントであることを指定します。 |
| SEMANTIC_SIMILARITY | 指定したテキストが意味論的テキスト類似性(STS)で使用されることを指定します。 |
| 分類 | エンベディングを分類に使用することを指定します。 |
| クラスタリング | エンベディングをクラスタリングに使用することを指定します。 |
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()
from google.api_core import retry
def make_embed_text_fn(model):
@retry.Retry(timeout=300.0)
def embed_fn(text: str) -> list[float]:
# Set the task_type to CLASSIFICATION.
embedding = genai.embed_content(model=model,
content=text,
task_type="classification")
return embedding['embedding']
return embed_fn
def create_embeddings(model, df):
df['Embeddings'] = df['Text'].progress_apply(make_embed_text_fn(model))
return df
model = 'models/embedding-001'
df_train = create_embeddings(model, df_train)
df_test = create_embeddings(model, df_test)
0%| | 0/400 [00:00<?, ?it/s] 0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
df_train.head()
シンプルな分類モデルを構築する
ここでは、1 つの隠れ層と 1 つのクラス確率出力を持つ単純なモデルを定義します。この予測は、あるテキストが特定のクラスのニュースである確率に対応します。モデルの構築時に、Keras は自動的にデータポイントをシャッフルします。
def build_classification_model(input_size: int, num_classes: int) -> keras.Model:
inputs = x = keras.Input(input_size)
x = layers.Dense(input_size, activation='relu')(x)
x = layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='sigmoid')(x)
return keras.Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=x)
# Derive the embedding size from the first training element.
embedding_size = len(df_train['Embeddings'].iloc[0])
# Give your model a different name, as you have already used the variable name 'model'
classifier = build_classification_model(embedding_size, len(df_train['Class Name'].unique()))
classifier.summary()
classifier.compile(loss = keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001),
metrics=['accuracy'])
Model: "model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 768)] 0
dense (Dense) (None, 768) 590592
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 4) 3076
=================================================================
Total params: 593668 (2.26 MB)
Trainable params: 593668 (2.26 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
embedding_size
768
ニュースグループを分類するようにモデルをトレーニングする
最後に、シンプルなモデルをトレーニングします。過学習を避けるために、少数のエポックを使用します。最初のエポックは、エンべディングを 1 回だけ計算する必要があるため、残りのエポックよりもはるかに時間がかかります。
NUM_EPOCHS = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 32
# Split the x and y components of the train and validation subsets.
y_train = df_train['Encoded Label']
x_train = np.stack(df_train['Embeddings'])
y_val = df_test['Encoded Label']
x_val = np.stack(df_test['Embeddings'])
# Train the model for the desired number of epochs.
callback = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='accuracy', patience=3)
history = classifier.fit(x=x_train,
y=y_train,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
callbacks=[callback],
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS,)
Epoch 1/20 /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/keras/src/backend.py:5729: UserWarning: "`sparse_categorical_crossentropy` received `from_logits=True`, but the `output` argument was produced by a Softmax activation and thus does not represent logits. Was this intended? output, from_logits = _get_logits( 13/13 [==============================] - 1s 30ms/step - loss: 1.2141 - accuracy: 0.6675 - val_loss: 0.9801 - val_accuracy: 0.8800 Epoch 2/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.7580 - accuracy: 0.9400 - val_loss: 0.6061 - val_accuracy: 0.9300 Epoch 3/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.4249 - accuracy: 0.9525 - val_loss: 0.3902 - val_accuracy: 0.9200 Epoch 4/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.2561 - accuracy: 0.9625 - val_loss: 0.2597 - val_accuracy: 0.9400 Epoch 5/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.1693 - accuracy: 0.9700 - val_loss: 0.2145 - val_accuracy: 0.9300 Epoch 6/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.1240 - accuracy: 0.9850 - val_loss: 0.1801 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 7/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0931 - accuracy: 0.9875 - val_loss: 0.1623 - val_accuracy: 0.9400 Epoch 8/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 16ms/step - loss: 0.0736 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.1418 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 9/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0613 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.1315 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 10/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0479 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1235 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 Epoch 11/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0399 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1219 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 12/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0326 - accuracy: 0.9975 - val_loss: 0.1158 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 13/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 19ms/step - loss: 0.0263 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1127 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 14/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 17ms/step - loss: 0.0229 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1123 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 15/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 20ms/step - loss: 0.0195 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1063 - val_accuracy: 0.9700 Epoch 16/20 13/13 [==============================] - 0s 17ms/step - loss: 0.0172 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.1070 - val_accuracy: 0.9700
モデルのパフォーマンスを評価する
Keras Model.evaluate を使用して、テスト データセットの損失と精度を取得します。
classifier.evaluate(x=x_val, y=y_val, return_dict=True)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1070 - accuracy: 0.9700
{'loss': 0.10700511932373047, 'accuracy': 0.9700000286102295}
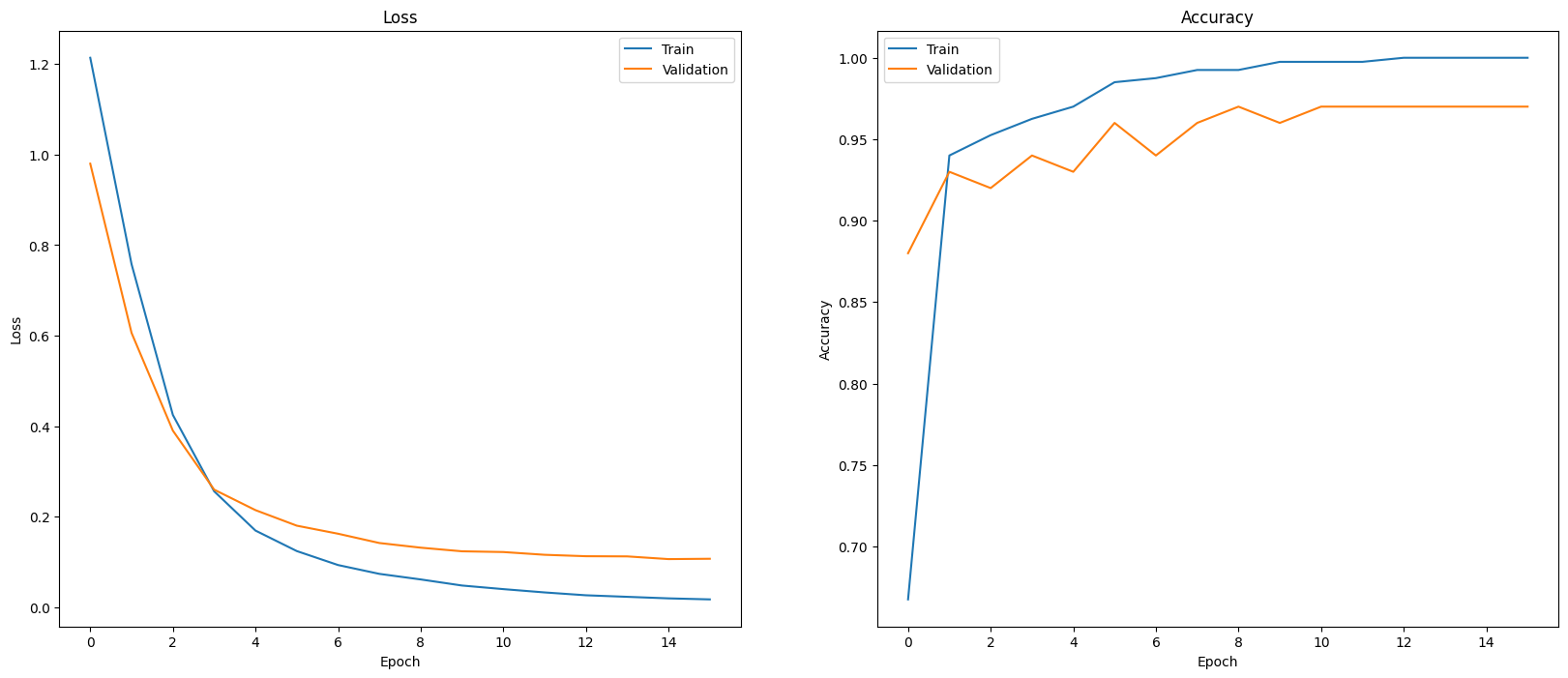
モデルのパフォーマンスを評価する 1 つの方法は、分類器のパフォーマンスを可視化することです。plot_history を使用して、エポックにおける損失と精度の傾向を確認します。
def plot_history(history):
"""
Plotting training and validation learning curves.
Args:
history: model history with all the metric measures
"""
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1,2)
fig.set_size_inches(20, 8)
# Plot loss
ax1.set_title('Loss')
ax1.plot(history.history['loss'], label = 'train')
ax1.plot(history.history['val_loss'], label = 'test')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
# Plot accuracy
ax2.set_title('Accuracy')
ax2.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label = 'train')
ax2.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label = 'test')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.legend(['Train', 'Validation'])
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
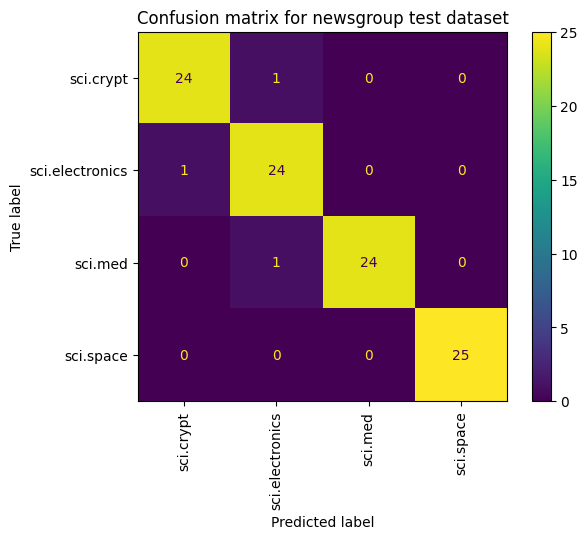
モデルのパフォーマンスを表示するもう 1 つの方法は、損失と精度を測定するだけでなく、混同行列を使用することです。混同行列を使用すると、精度を超えて分類モデルのパフォーマンスを評価できます。誤って分類されたポイントがどのポイントに分類されるかを確認できます。このマルチクラス分類問題用の混同行列を作成するには、テストセットの実際の値と予測値を取得します。
まず、Model.predict() を使用して、検証セット内の各サンプルの予測クラスを生成します。
y_hat = classifier.predict(x=x_val)
y_hat = np.argmax(y_hat, axis=1)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step
labels_dict = dict(zip(df_test['Class Name'], df_test['Encoded Label']))
labels_dict
{'sci.crypt': 0, 'sci.electronics': 1, 'sci.med': 2, 'sci.space': 3}
cm = skmetrics.confusion_matrix(y_val, y_hat)
disp = skmetrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm,
display_labels=labels_dict.keys())
disp.plot(xticks_rotation='vertical')
plt.title('Confusion matrix for newsgroup test dataset');
plt.grid(False)
次のステップ
エンベディングの使用方法について詳しくは、以下のチュートリアルをご覧ください。

