함수 호출을 사용하면 모델을 외부 도구 및 API에 연결할 수 있습니다. 모델은 텍스트 대답을 생성하는 대신 특정 함수를 호출할 시점을 결정하고 실제 작업을 실행하는 데 필요한 파라미터를 제공합니다. 이를 통해 모델은 자연어와 실제 작업 및 데이터 간의 브리지 역할을 할 수 있습니다. 함수 호출에는 3가지 주요 사용 사례가 있습니다.
- 지식 보강: 데이터베이스, API, 기술 자료와 같은 외부 소스의 정보에 액세스합니다.
- 기능 확장: 외부 도구를 사용하여 계산을 수행하고 계산기 사용 또는 차트 생성과 같은 모델의 제한사항을 확장합니다.
- 작업 실행: API를 사용하여 외부 시스템과 상호작용합니다(예: 일정 예약, 인보이스 생성, 이메일 전송, 스마트 홈 기기 제어).
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function declaration for the model
schedule_meeting_function = {
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting.",
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')",
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')",
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting.",
},
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"],
},
}
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[schedule_meeting_function])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/14/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.",
config=config,
)
# Check for a function call
if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call:
function_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
print(f"Function to call: {function_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {function_call.args}")
# In a real app, you would call your function here:
# result = schedule_meeting(**function_call.args)
else:
print("No function call found in the response.")
print(response.text)
자바스크립트
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define the function declaration for the model
const scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'schedule_meeting',
description: 'Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
attendees: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
items: { type: Type.STRING },
description: 'List of people attending the meeting.',
},
date: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Date of the meeting (e.g., "2024-07-29")',
},
time: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Time of the meeting (e.g., "15:00")',
},
topic: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'The subject or topic of the meeting.',
},
},
required: ['attendees', 'date', 'time', 'topic'],
},
};
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: 'Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.',
config: {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration]
}],
},
});
// Check for function calls in the response
if (response.functionCalls && response.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = response.functionCalls[0]; // Assuming one function call
console.log(`Function to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
console.log(`Arguments: ${JSON.stringify(functionCall.args)}`);
// In a real app, you would call your actual function here:
// const result = await scheduleMeeting(functionCall.args);
} else {
console.log("No function call found in the response.");
console.log(response.text);
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting."
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')"
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')"
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting."
}
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
함수 호출 작동 방식
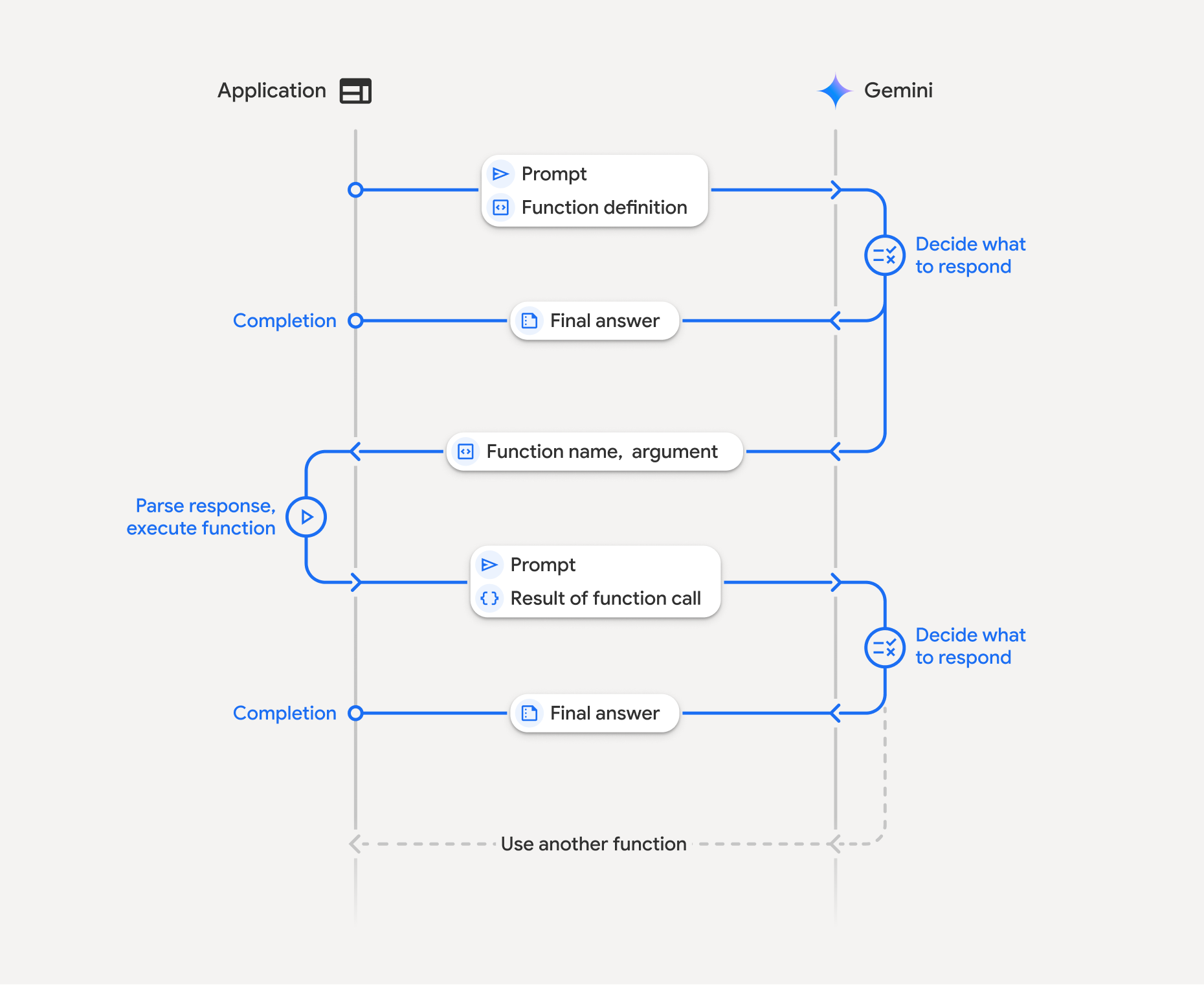
함수 호출은 애플리케이션, 모델, 외부 함수 간의 구조화된 상호작용을 포함합니다. 이 과정은 다음과 같이 세분화할 수 있습니다.
- 함수 선언 정의: 애플리케이션 코드에서 함수 선언을 정의합니다. 함수 선언은 함수의 이름, 매개변수, 목적을 모델에 설명합니다.
- 함수 선언으로 LLM 호출: 사용자 프롬프트와 함수 선언을 모델에 전송합니다. 요청을 분석하고 함수 호출이 유용한지 판단합니다. 그렇다면 구조화된 JSON 객체로 응답합니다.
- 함수 코드 실행 (사용자 책임): 모델은 함수 자체를 실행하지 않습니다.
- 예: 함수의 이름과 인수를 추출하고 애플리케이션에서 해당 함수를 실행합니다.
- 아니요: 모델이 프롬프트에 직접 텍스트 응답을 제공했습니다(이 흐름은 예시에서 덜 강조되지만 가능한 결과임).
- 사용자 친화적인 대답 만들기: 함수가 실행된 경우 결과를 캡처하고 대화의 후속 턴에서 모델에 다시 보냅니다. 이 결과를 사용하여 함수 호출의 정보를 통합하는 최종적이고 사용자 친화적인 대답을 생성합니다.
이 프로세스는 여러 턴에 걸쳐 반복될 수 있으므로 복잡한 상호작용과 워크플로가 가능합니다. 또한 모델은 싱글턴에서 여러 함수를 호출하는 것 (병렬 함수 호출)과 순차적으로 호출하는 것 (컴포지셔널 함수 호출)을 지원합니다.
1단계: 함수 선언 정의
사용자가 조명 값을 설정하고 API 요청을 할 수 있도록 애플리케이션 코드 내에서 함수와 선언을 정의합니다. 이 함수는 외부 서비스나 API를 호출할 수 있습니다.
Python
# Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
set_light_values_declaration = {
"name": "set_light_values",
"description": "Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness",
},
"color_temp": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"],
"description": "Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.",
},
},
"required": ["brightness", "color_temp"],
},
}
# This is the actual function that would be called based on the model's suggestion
def set_light_values(brightness: int, color_temp: str) -> dict[str, int | str]:
"""Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API).
Args:
brightness: Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
color_temp: Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness, "colorTemperature": color_temp}
자바스크립트
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
// Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
const setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'set_light_values',
description: 'Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness',
},
color_temp: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm'],
description: 'Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.',
},
},
required: ['brightness', 'color_temp'],
},
};
/**
* Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API)
* @param {number} brightness - Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
* @param {string} color_temp - Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
* @return {Object} A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
*/
function setLightValues(brightness, color_temp) {
return {
brightness: brightness,
colorTemperature: color_temp
};
}
2단계: 함수 선언으로 모델 호출
함수 선언을 정의한 후 모델에 이를 사용하도록 프롬프트를 표시할 수 있습니다. 프롬프트와 함수 선언을 분석하여 직접 응답할지 함수를 호출할지 결정합니다. 함수가 호출되면 응답 객체에 함수 호출 제안이 포함됩니다.
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[set_light_values_declaration])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Define user prompt
contents = [
types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="Turn the lights down to a romantic level")]
)
]
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=contents,
config=config,
)
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call)
자바스크립트
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Generation config with function declaration
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration]
}]
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define user prompt
const contents = [
{
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: 'Turn the lights down to a romantic level' }]
}
];
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(response.functionCalls[0]);
그런 다음 모델은 사용자의 질문에 답변하기 위해 선언된 함수를 하나 이상 호출하는 방법을 지정하는 OpenAPI 호환 스키마의 functionCall 객체를 반환합니다.
Python
id=None args={'color_temp': 'warm', 'brightness': 25} name='set_light_values'
자바스크립트
{
name: 'set_light_values',
args: { brightness: 25, color_temp: 'warm' }
}
3단계: set_light_values 함수 코드 실행
모델의 대답에서 함수 호출 세부정보를 추출하고, 인수를 파싱하고, set_light_values 함수를 실행합니다.
Python
# Extract tool call details, it may not be in the first part.
tool_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
if tool_call.name == "set_light_values":
result = set_light_values(**tool_call.args)
print(f"Function execution result: {result}")
자바스크립트
// Extract tool call details
const tool_call = response.functionCalls[0]
let result;
if (tool_call.name === 'set_light_values') {
result = setLightValues(tool_call.args.brightness, tool_call.args.color_temp);
console.log(`Function execution result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
4단계: 함수 결과로 사용자 친화적인 응답을 만들고 모델을 다시 호출
마지막으로 함수 실행 결과를 모델에 다시 전송하여 이 정보를 사용자에 대한 최종 대답에 통합할 수 있도록 합니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Create a function response part
function_response_part = types.Part.from_function_response(
name=tool_call.name,
response={"result": result},
)
# Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.append(response.candidates[0].content) # Append the content from the model's response.
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
client = genai.Client()
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
자바스크립트
// Create a function response part
const function_response_part = {
name: tool_call.name,
response: { result }
}
// Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.push(response.candidates[0].content);
contents.push({ role: 'user', parts: [{ functionResponse: function_response_part }] });
// Get the final response from the model
const final_response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(final_response.text);
이로써 함수 호출 흐름이 완료됩니다. 모델이 set_light_values 함수를 사용하여 사용자의 요청 작업을 성공적으로 수행했습니다.
함수 선언
프롬프트에서 함수 호출을 구현할 때 하나 이상의 function declarations이 포함된 tools 객체를 만듭니다. JSON을 사용하여 함수를 정의할 때, 특히 OpenAPI 스키마 형식의 선택된 하위 집합을 사용합니다. 단일 함수 선언에는 다음 파라미터가 포함될 수 있습니다.
name(문자열): 함수의 고유한 이름 (get_weather_forecast,send_email)입니다. 공백이나 특수문자가 없는 설명적인 이름을 사용하세요(밑줄이나 카멜 표기법 사용).description(문자열): 함수의 목적과 기능을 명확하고 자세하게 설명합니다. 이는 모델이 함수를 사용해야 하는 시점을 이해하는 데 중요합니다. 구체적으로 설명하고 도움이 되는 경우 예를 들어 줍니다 ('위치를 기반으로 영화관을 찾고, 선택적으로 현재 영화관에서 상영 중인 영화 제목을 찾습니다.').parameters(객체): 함수에서 예상하는 입력 매개변수를 정의합니다.type(문자열):object과 같은 전체 데이터 유형을 지정합니다.properties(객체): 개별 파라미터를 각각 나열합니다.type(문자열): 매개변수의 데이터 유형입니다(예:string,integer,boolean, array).description(문자열): 매개변수의 목적과 형식을 설명합니다. 예와 제약 조건 ('도시와 주, 예를 들어 'San Francisco, CA' 또는 우편번호(예: '95616').enum(배열, 선택사항): 파라미터 값이 고정된 집합에서 파생된 경우 설명에 값을 설명하는 대신 'enum'을 사용하여 허용된 값을 나열합니다. 이렇게 하면 정확도가 향상됩니다 ('enum': ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm']).
required(배열): 함수가 작동하는 데 필수인 파라미터 이름을 나열하는 문자열 배열입니다.
types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(client=client, callable=your_function)을 사용하여 Python 함수에서 직접 FunctionDeclarations를 구성할 수도 있습니다.
사고 모델을 사용한 함수 호출
Gemini 3 및 2.5 시리즈 모델은 내부 '사고' 프로세스를 사용하여 요청을 추론합니다. 이렇게 하면 함수 호출 성능이 크게 향상되어 모델이 함수를 호출할 시기와 사용할 매개변수를 더 잘 결정할 수 있습니다. Gemini API는 스테이트리스(Stateless)이므로 모델은 생각 서명을 사용하여 멀티턴 대화 전반에서 컨텍스트를 유지합니다.
이 섹션에서는 생각 서명의 고급 관리를 다루며, API 요청을 수동으로 구성하거나 (예: REST를 통해) 대화 기록을 조작하는 경우에만 필요합니다.
Google 생성형 AI SDK (Google의 공식 라이브러리)를 사용하는 경우 이 프로세스를 관리할 필요가 없습니다. SDK는 이전 예에 표시된 대로 필요한 단계를 자동으로 처리합니다.
대화 기록 수동 관리
이전 전체 응답을 보내는 대신 대화 기록을 수동으로 수정하는 경우 모델의 턴에 포함된 thought_signature을 올바르게 처리해야 합니다.
모델의 컨텍스트가 유지되도록 다음 규칙을 따르세요.
- 항상 원래
Part내에서thought_signature를 모델에 다시 전송합니다. - 서명이 포함된
Part를 서명이 포함되지 않은Part와 병합하지 마세요. 이렇게 하면 사고의 위치 컨텍스트가 깨집니다. - 서명이 포함된 두 개의
Parts를 결합하지 마세요. 서명 문자열은 병합할 수 없습니다.
Gemini 3 생각 서명
Gemini 3에서는 모델 응답의 Part에 사고 서명이 포함될 수 있습니다.
일반적으로 모든 Part 유형에서 서명을 반환하는 것이 좋지만, 함수 호출의 경우 생각 서명을 다시 전달해야 합니다. 대화 기록을 수동으로 조작하지 않는 한 Google 생성형 AI SDK에서 생각 서명을 자동으로 처리합니다.
대화 기록을 수동으로 조작하는 경우 생각 서명 페이지에서 Gemini 3의 생각 서명 처리에 관한 전체 안내와 세부정보를 참고하세요.
생각 서명 검사
구현에 필수는 아니지만 디버깅이나 교육 목적으로 응답을 검사하여 thought_signature를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Python
import base64
# After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
# response = client.models.generate_content(...)
# The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0]
if part.thought_signature:
print(base64.b64encode(part.thought_signature).decode("utf-8"))
자바스크립트
// After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
// const response = await ai.models.generateContent(...)
// The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
const part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0];
if (part.thoughtSignature) {
console.log(part.thoughtSignature);
}
생각 페이지에서 생각 서명의 제한사항 및 사용법과 일반적인 생각 모델에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
병렬 함수 호출
단일 턴 함수 호출 외에도 한 번에 여러 함수를 호출할 수 있습니다. 병렬 함수 호출을 사용하면 여러 함수를 한 번에 실행할 수 있으며 함수가 서로 종속되지 않는 경우에 사용됩니다. 이는 여러 독립 소스에서 데이터를 수집하는 시나리오에서 유용합니다. 예를 들어 여러 데이터베이스에서 고객 세부정보를 가져오거나, 다양한 창고에서 재고 수준을 확인하거나, 아파트를 디스코로 변환하는 등 여러 작업을 실행하는 경우에 유용합니다.
Python
power_disco_ball = {
"name": "power_disco_ball",
"description": "Powers the spinning disco ball.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"power": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.",
}
},
"required": ["power"],
},
}
start_music = {
"name": "start_music",
"description": "Play some music matching the specified parameters.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"energetic": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is energetic or not.",
},
"loud": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is loud or not.",
},
},
"required": ["energetic", "loud"],
},
}
dim_lights = {
"name": "dim_lights",
"description": "Dim the lights.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.",
}
},
"required": ["brightness"],
},
}
자바스크립트
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
const powerDiscoBall = {
name: 'power_disco_ball',
description: 'Powers the spinning disco ball.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
power: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.'
}
},
required: ['power']
}
};
const startMusic = {
name: 'start_music',
description: 'Play some music matching the specified parameters.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
energetic: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is energetic or not.'
},
loud: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is loud or not.'
}
},
required: ['energetic', 'loud']
}
};
const dimLights = {
name: 'dim_lights',
description: 'Dim the lights.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.'
}
},
required: ['brightness']
}
};
지정된 모든 도구를 사용할 수 있도록 함수 호출 모드를 구성합니다. 자세한 내용은 함수 호출 구성을 참고하세요.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
house_tools = [
types.Tool(function_declarations=[power_disco_ball, start_music, dim_lights])
]
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=house_tools,
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
disable=True
),
# Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
tool_config=types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(mode='ANY')
),
)
chat = client.chats.create(model="gemini-3-flash-preview", config=config)
response = chat.send_message("Turn this place into a party!")
# Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
print("Example 1: Forced function calling")
for fn in response.function_calls:
args = ", ".join(f"{key}={val}" for key, val in fn.args.items())
print(f"{fn.name}({args})")
자바스크립트
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Set up function declarations
const houseFns = [powerDiscoBall, startMusic, dimLights];
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: houseFns
}],
// Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
toolConfig: {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: 'any'
}
}
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Create a chat session
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
config: config
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({message: 'Turn this place into a party!'});
// Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
console.log("Example 1: Forced function calling");
for (const fn of response.functionCalls) {
const args = Object.entries(fn.args)
.map(([key, val]) => `${key}=${val}`)
.join(', ');
console.log(`${fn.name}(${args})`);
}
인쇄된 각 결과는 모델이 요청한 단일 함수 호출을 반영합니다. 결과를 다시 보내려면 요청된 순서와 동일한 순서로 응답을 포함하세요.
Python SDK는 자동 함수 호출을 지원하며, 이는 Python 함수를 선언으로 자동 변환하고 함수 호출 실행 및 응답 주기를 처리합니다. 다음은 디스코 사용 사례의 예입니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Actual function implementations
def power_disco_ball_impl(power: bool) -> dict:
"""Powers the spinning disco ball.
Args:
power: Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.
Returns:
A status dictionary indicating the current state.
"""
return {"status": f"Disco ball powered {'on' if power else 'off'}"}
def start_music_impl(energetic: bool, loud: bool) -> dict:
"""Play some music matching the specified parameters.
Args:
energetic: Whether the music is energetic or not.
loud: Whether the music is loud or not.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the music settings.
"""
music_type = "energetic" if energetic else "chill"
volume = "loud" if loud else "quiet"
return {"music_type": music_type, "volume": volume}
def dim_lights_impl(brightness: float) -> dict:
"""Dim the lights.
Args:
brightness: The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the new brightness setting.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[power_disco_ball_impl, start_music_impl, dim_lights_impl]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Do everything you need to this place into party!",
config=config,
)
print("\nExample 2: Automatic function calling")
print(response.text)
# I've turned on the disco ball, started playing loud and energetic music, and dimmed the lights to 50% brightness. Let's get this party started!
구성 함수 호출
구성적 또는 순차적 함수 호출을 사용하면 Gemini가 여러 함수 호출을 함께 연결하여 복잡한 요청을 처리할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 '현재 위치의 온도를 알려 줘'라는 질문에 답하기 위해 Gemini API는 먼저 get_current_location() 함수를 호출한 다음 위치를 매개변수로 사용하는 get_weather() 함수를 호출할 수 있습니다.
다음 예에서는 Python SDK와 자동 함수 호출을 사용하여 컴포지셔널 함수 호출을 구현하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
Python
이 예시에서는 google-genai Python SDK의 자동 함수 호출 기능을 사용합니다. SDK는 Python 함수를 필요한 스키마로 자동 변환하고, 모델에서 요청할 때 함수 호출을 실행하고, 작업을 완료하기 위해 결과를 모델에 다시 전송합니다.
import os
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Example Functions
def get_weather_forecast(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current weather temperature for a given location."""
print(f"Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location={location})")
# TODO: Make API call
print("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}")
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "celsius"} # Dummy response
def set_thermostat_temperature(temperature: int) -> dict:
"""Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature."""
print(f"Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature={temperature})")
# TODO: Interact with a thermostat API
print("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configure the client and model
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_weather_forecast, set_thermostat_temperature]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
config=config,
)
# Print the final, user-facing response
print(response.text)
예상 출력:
코드를 실행하면 SDK가 함수 호출을 오케스트레이션하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 모델은 먼저 get_weather_forecast를 호출하고 온도를 수신한 다음 프롬프트의 로직에 따라 올바른 값으로 set_thermostat_temperature를 호출합니다.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
자바스크립트
이 예시에서는 JavaScript/TypeScript SDK를 사용하여 수동 실행 루프를 통해 컴포지션 함수 호출을 실행하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from "@google/genai";
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Example Functions
function get_weather_forecast({ location }) {
console.log(`Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=${location})`);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}");
return { temperature: 25, unit: "celsius" };
}
function set_thermostat_temperature({ temperature }) {
console.log(
`Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=${temperature})`,
);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}");
return { status: "success" };
}
const toolFunctions = {
get_weather_forecast,
set_thermostat_temperature,
};
const tools = [
{
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "get_weather_forecast",
description:
"Gets the current weather temperature for a given location.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
location: {
type: Type.STRING,
},
},
required: ["location"],
},
},
{
name: "set_thermostat_temperature",
description: "Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
temperature: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
},
},
required: ["temperature"],
},
},
],
},
];
// Prompt for the model
let contents = [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
},
],
},
];
// Loop until the model has no more function calls to make
while (true) {
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
config: { tools },
});
if (result.functionCalls && result.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = result.functionCalls[0];
const { name, args } = functionCall;
if (!toolFunctions[name]) {
throw new Error(`Unknown function call: ${name}`);
}
// Call the function and get the response.
const toolResponse = toolFunctions[name](args);
const functionResponsePart = {
name: functionCall.name,
response: {
result: toolResponse,
},
};
// Send the function response back to the model.
contents.push({
role: "model",
parts: [
{
functionCall: functionCall,
},
],
});
contents.push({
role: "user",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: functionResponsePart,
},
],
});
} else {
// No more function calls, break the loop.
console.log(result.text);
break;
}
}
예상 출력:
코드를 실행하면 SDK가 함수 호출을 오케스트레이션하는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다. 모델은 먼저 get_weather_forecast를 호출하고 온도를 수신한 다음 프롬프트의 로직에 따라 올바른 값으로 set_thermostat_temperature를 호출합니다.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. It's 25°C in London, so I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
구성 함수 호출은 네이티브 Live API 기능입니다. 즉, Live API는 Python SDK와 유사하게 함수 호출을 처리할 수 있습니다.
Python
# Light control schemas
turn_on_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_on_the_lights'}
turn_off_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_off_the_lights'}
prompt = """
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
"""
tools = [
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]}
]
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
자바스크립트
// Light control schemas
const turnOnTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_on_the_lights' };
const turnOffTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_off_the_lights' };
const prompt = `
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
`;
const tools = [
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] }
];
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
함수 호출 모드
Gemini API를 사용하면 모델이 제공된 도구(함수 선언)를 사용하는 방식을 제어할 수 있습니다. 특히.function_calling_config 내에서 모드를 설정할 수 있습니다.
AUTO (Default): 모델은 프롬프트와 컨텍스트에 따라 자연어 응답을 생성할지 아니면 함수 호출을 제안할지 결정합니다. 이 모드는 가장 유연한 모드이며 대부분의 시나리오에 권장됩니다.ANY: 모델이 항상 함수 호출을 예측하도록 제한되며 함수 스키마 준수를 보장합니다.allowed_function_names가 지정되지 않은 경우 모델은 제공된 함수 선언 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다.allowed_function_names가 목록으로 제공되면 모델은 해당 목록의 함수 중에서만 선택할 수 있습니다. 모든 프롬프트에 함수 호출 응답이 필요한 경우 이 모드를 사용하세요 (해당하는 경우).NONE: 모델이 함수 호출을 실행하는 것이 금지됩니다. 이는 함수 선언 없이 요청을 전송하는 것과 동일합니다. 이 모드를 사용하면 도구 정의를 삭제하지 않고 함수 호출을 일시적으로 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.VALIDATED(프리뷰): 모델이 함수 호출 또는 자연어를 예측하도록 제한되며 함수 스키마 준수를 보장합니다.allowed_function_names가 제공되지 않았으면 모델이 사용 가능한 모든 함수 선언 중에서 선택합니다.allowed_function_names가 제공되면 모델이 허용된 함수 집합 중에서 선택합니다.
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure function calling mode
tool_config = types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(
mode="ANY", allowed_function_names=["get_current_temperature"]
)
)
# Create the generation config
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tools], # not defined here.
tool_config=tool_config,
)
자바스크립트
import { FunctionCallingConfigMode } from '@google/genai';
// Configure function calling mode
const toolConfig = {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: FunctionCallingConfigMode.ANY,
allowedFunctionNames: ['get_current_temperature']
}
};
// Create the generation config
const config = {
tools: tools, // not defined here.
toolConfig: toolConfig,
};
자동 함수 호출 (Python만 해당)
Python SDK를 사용하는 경우 Python 함수를 도구로 직접 제공할 수 있습니다. SDK는 이러한 함수를 선언으로 변환하고, 함수 호출 실행을 관리하며, 응답 주기를 처리합니다. 타입 힌트와 독스트링을 사용하여 함수를 정의합니다. 최적의 결과를 얻으려면 Google 스타일 docstring을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다. 그러면 SDK가 다음 작업을 자동으로 실행합니다.
- 모델의 함수 호출 응답을 감지합니다.
- 코드에서 해당 Python 함수를 호출합니다.
- 함수의 응답을 모델에 다시 보냅니다.
- 모델의 최종 텍스트 응답을 반환합니다.
SDK는 현재 생성된 함수 선언의 속성 설명 슬롯으로 인자 설명을 파싱하지 않습니다. 대신 전체 docstring을 최상위 함수 설명으로 전송합니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function with type hints and docstring
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current temperature for a given location.
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
Returns:
A dictionary containing the temperature and unit.
"""
# ... (implementation) ...
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "Celsius"}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature]
) # Pass the function itself
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What's the temperature in Boston?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text) # The SDK handles the function call and returns the final text
다음과 같이 자동 함수 호출을 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.
Python
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature],
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(disable=True)
)
자동 함수 스키마 선언
API는 다음 유형을 설명할 수 있습니다. Pydantic 유형은 허용됩니다. 단, 유형에 정의된 필드도 허용된 유형으로 구성되어야 합니다. 여기서는 딕셔너리 유형 (예: dict[str: int])이 잘 지원되지 않으므로 사용하지 마세요.
Python
AllowedType = (
int | float | bool | str | list['AllowedType'] | pydantic.BaseModel)
추론된 스키마가 어떻게 표시되는지 확인하려면 from_callable를 사용하여 변환하면 됩니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
"""Returns a * b."""
return a * b
client = genai.Client()
fn_decl = types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(callable=multiply, client=client)
# to_json_dict() provides a clean JSON representation.
print(fn_decl.to_json_dict())
다중 도구 사용: 네이티브 도구와 함수 호출 결합
기본 도구와 함수 호출을 결합하는 여러 도구를 동시에 사용 설정할 수 있습니다. 다음은 Live API를 사용하는 요청에서 두 도구인 Google 검색을 통한 그라운딩과 코드 실행을 사용 설정하는 예입니다.
Python
# Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
prompt = """
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
"""
tools = [
{'google_search': {}},
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]} # not defined here.
]
# Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
자바스크립트
// Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
const prompt = `
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
`;
const tools = [
{ googleSearch: {} },
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] } // not defined here.
];
// Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, {tools: tools, modality: "AUDIO"});
Python 개발자는 Live API Tool Use 노트북에서 이를 사용해 볼 수 있습니다.
멀티모달 함수 응답
Gemini 3 시리즈 모델의 경우 모델에 전송하는 함수 응답 부분에 멀티모달 콘텐츠를 포함할 수 있습니다. 모델은 다음 차례에 이 멀티모달 콘텐츠를 처리하여 더 많은 정보를 바탕으로 응답을 생성할 수 있습니다. 함수 응답의 멀티모달 콘텐츠에 지원되는 MIME 유형은 다음과 같습니다.
- 이미지:
image/png,image/jpeg,image/webp - 문서:
application/pdf,text/plain
함수 응답에 멀티모달 데이터를 포함하려면 functionResponse 부분 내에 중첩된 하나 이상의 부분으로 포함하세요. 각 멀티모달 부분에는 inlineData가 포함되어야 합니다. 구조화된 response 필드 내에서 멀티모달 부분을 참조하는 경우 고유한 displayName이 포함되어야 합니다.
JSON 참조 형식({"$ref": "<displayName>"})을 사용하여 functionResponse 부분의 구조화된 response 필드 내에서 멀티모달 부분을 참조할 수도 있습니다. 이 모델은 응답을 처리할 때 참조를 멀티모달 콘텐츠로 대체합니다. 각 displayName은 구조화된 response 필드에서 한 번만 참조할 수 있습니다.
다음 예시에서는 get_image라는 함수의 functionResponse를 포함하는 메시지와 displayName: "instrument.jpg" 형식의 이미지 데이터를 포함하는 중첩된 부분을 보여줍니다. functionResponse의 response 필드는 이 이미지 부분을 참조합니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
client = genai.Client()
# This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
# 1. Define the function tool
get_image_declaration = types.FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_image",
description="Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"item_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument')."
}
},
"required": ["item_name"],
},
)
tool_config = types.Tool(function_declarations=[get_image_declaration])
# 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
prompt = "Show me the instrument I ordered last month."
response_1 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
)
)
# 3. Handle the function call
function_call = response_1.function_calls[0]
requested_item = function_call.args["item_name"]
print(f"Model wants to call: {function_call.name}")
# Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
# (This is a mock response for the example)
print(f"Calling external tool for: {requested_item}")
function_response_data = {
"image_ref": {"$ref": "instrument.jpg"},
}
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
function_response_multimodal_data = types.FunctionResponsePart(
inline_data=types.FunctionResponseBlob(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
display_name="instrument.jpg",
data=image_bytes,
)
)
# 4. Send the tool's result back
# Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
history = [
types.Content(role="user", parts=[types.Part(text=prompt)]),
response_1.candidates[0].content,
types.Content(
role="tool",
parts=[
types.Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response=function_response_data,
parts=[function_response_multimodal_data]
)
],
)
]
response_2 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=history,
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(include_thoughts=True)
),
)
print(f"\nFinal model response: {response_2.text}")
자바스크립트
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
const client = new GoogleGenAI({ apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY });
// This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
// 1. Define the function tool
const getImageDeclaration = {
name: 'get_image',
description: 'Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
item_name: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument').",
},
},
required: ['item_name'],
},
};
const toolConfig = {
functionDeclarations: [getImageDeclaration],
};
// 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
const prompt = 'Show me the instrument I ordered last month.';
const response1 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: prompt,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
},
});
// 3. Handle the function call
const functionCall = response1.functionCalls[0];
const requestedItem = functionCall.args.item_name;
console.log(`Model wants to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
// Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
// (This is a mock response for the example)
console.log(`Calling external tool for: ${requestedItem}`);
const functionResponseData = {
image_ref: { $ref: 'instrument.jpg' },
};
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
const functionResponseMultimodalData = {
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
displayName: 'instrument.jpg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
};
// 4. Send the tool's result back
// Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
const history = [
{ role: 'user', parts: [{ text: prompt }] },
response1.candidates[0].content,
{
role: 'tool',
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: functionResponseData,
parts: [functionResponseMultimodalData],
},
},
],
},
];
const response2 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: history,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
thinkingConfig: { includeThoughts: true },
},
});
console.log(`\nFinal model response: ${response2.text}`);
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
# Check for macOS
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
...,
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_image",
"response": {
"image_ref": {
"$ref": "instrument.jpg"
}
},
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"displayName": "instrument.jpg",
"mimeType":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
구조화된 출력을 사용한 함수 호출
Gemini 3 시리즈 모델의 경우 구조화된 출력과 함께 함수 호출을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 모델이 특정 스키마를 준수하는 함수 호출 또는 출력을 예측할 수 있습니다. 따라서 모델이 함수 호출을 생성하지 않을 때 일관된 형식의 응답을 받을 수 있습니다.
모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜 (MCP)
모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜 (MCP)은 AI 애플리케이션을 외부 도구 및 데이터에 연결하기 위한 개방형 표준입니다. MCP는 모델이 함수(도구), 데이터 소스 (리소스), 사전 정의된 프롬프트와 같은 컨텍스트에 액세스할 수 있는 공통 프로토콜을 제공합니다.
Gemini SDK에는 MCP 지원이 내장되어 있어 상용구 코드를 줄이고 MCP 도구의 자동 도구 호출을 제공합니다. 모델이 MCP 도구 호출을 생성하면 Python 및 JavaScript 클라이언트 SDK가 MCP 도구를 자동으로 실행하고 후속 요청에서 모델에 응답을 다시 전송하여 모델에서 더 이상 도구 호출이 이루어지지 않을 때까지 이 루프를 계속할 수 있습니다.
여기에서 Gemini 및 mcp SDK로 로컬 MCP 서버를 사용하는 방법의 예를 확인할 수 있습니다.
Python
선택한 플랫폼에 최신 버전의 mcp SDK가 설치되어 있는지 확인합니다.
pip install mcp
import os
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
# Create server parameters for stdio connection
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="npx", # Executable
args=["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"], # MCP Server
env=None, # Optional environment variables
)
async def run():
async with stdio_client(server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read, write) as session:
# Prompt to get the weather for the current day in London.
prompt = f"What is the weather in London in {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}?"
# Initialize the connection between client and server
await session.initialize()
# Send request to the model with MCP function declarations
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=prompt,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0,
tools=[session], # uses the session, will automatically call the tool
# Uncomment if you **don't** want the SDK to automatically call the tool
# automatic_function_calling=genai.types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
# disable=True
# ),
),
)
print(response.text)
# Start the asyncio event loop and run the main function
asyncio.run(run())
자바스크립트
선택한 플랫폼에 최신 버전의 mcp SDK가 설치되어 있는지 확인합니다.
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StdioClientTransport({
command: "npx", // Executable
args: ["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"] // MCP Server
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection
await client.close();
내장 MCP 지원의 제한사항
기본 제공 MCP 지원은 SDK의 실험적 기능이며 다음과 같은 제한사항이 있습니다.
- 리소스나 프롬프트가 아닌 도구만 지원됩니다.
- Python 및 JavaScript/TypeScript SDK에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 향후 출시에서 호환성이 깨지는 변경사항이 발생할 수 있습니다.
이러한 제한으로 인해 빌드하는 항목이 제한되는 경우 MCP 서버를 수동으로 통합하는 방법도 있습니다.
지원되는 모델
이 섹션에는 모델과 함수 호출 기능이 나와 있습니다. 실험용 모델은 포함되지 않습니다. 모델 개요 페이지에서 포괄적인 기능 개요를 확인할 수 있습니다.
| 모델 | 함수 호출 | 병렬 함수 호출 | 구성 함수 호출 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite | X | X | X |
권장사항
- 함수 및 파라미터 설명: 설명을 매우 명확하고 구체적으로 작성하세요. 모델은 이를 기반으로 올바른 함수를 선택하고 적절한 인수를 제공합니다.
- 이름 지정: 공백, 마침표, 대시 없이 설명이 포함된 함수 이름을 사용합니다.
- 강력한 유형 지정: 오류를 줄이기 위해 매개변수에 특정 유형 (정수, 문자열, enum)을 사용합니다. 매개변수에 유효한 값의 집합이 제한되어 있는 경우 enum을 사용합니다.
- 도구 선택: 모델은 임의의 수의 도구를 사용할 수 있지만 너무 많은 도구를 제공하면 잘못되거나 최적화되지 않은 도구를 선택할 위험이 커집니다. 최상의 결과를 얻으려면 컨텍스트 또는 작업과 관련된 도구만 제공하는 것이 좋습니다. 활성 도구 세트는 최대 10~20개로 유지하는 것이 좋습니다. 총 도구 수가 많은 경우 대화 컨텍스트에 기반한 동적 도구 선택을 고려하세요.
- 프롬프트 엔지니어링:
온도: 낮은 온도 (예: 0)을 사용하여 더 결정적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 함수 호출을 할 수 있습니다.
유효성 검사: 함수 호출에 중대한 결과 (예: 주문)가 있는 경우 이를 실행하기 전에 사용자와 함께 호출 유효성을 검사합니다.
종료 이유 확인: 모델이 유효한 함수 호출을 생성하지 못한 경우를 처리하기 위해 항상 모델의 대답에서
finishReason를 확인합니다.오류 처리: 함수에 강력한 오류 처리를 구현하여 예기치 않은 입력이나 API 오류를 정상적으로 처리합니다. 모델이 유용한 사용자 응답을 생성하는 데 사용할 수 있는 유익한 오류 메시지를 반환합니다.
보안: 외부 API를 호출할 때 보안에 유의하세요. 적절한 인증 및 승인 메커니즘을 사용합니다. 함수 호출에서 민감한 데이터를 노출하지 마세요.
토큰 제한: 함수 설명과 파라미터는 입력 토큰 제한에 포함됩니다. 토큰 한도에 도달하면 함수 수나 설명 길이를 제한하고 복잡한 작업을 더 작고 집중적인 함수 집합으로 나누는 것이 좋습니다.
참고사항 및 제한사항
- OpenAPI 스키마의 하위 집합만 지원됩니다.
ANY모드의 경우 API에서 매우 크거나 깊이 중첩된 스키마를 거부할 수 있습니다. 오류가 발생하면 속성 이름을 줄이거나, 중첩을 줄이거나, 함수 선언 수를 제한하여 함수 매개변수와 응답 스키마를 단순화해 보세요.- Python에서 지원되는 매개변수 유형은 제한적입니다.
- 자동 함수 호출은 Python SDK 기능입니다.
