Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 është një model i gjuhës së vizionit (VLM) që sjell aftësitë agjentike të Gemini në robotikë. Është projektuar për arsyetim të avancuar në botën fizike, duke u lejuar robotëve të interpretojnë të dhëna komplekse vizuale, të kryejnë arsyetim hapësinor dhe të planifikojnë veprime nga komandat e gjuhës natyrore.
Karakteristikat dhe përfitimet kryesore:
- Autonomi e përmirësuar: Robotët mund të arsyetojnë, të përshtaten dhe t'u përgjigjen ndryshimeve në mjedise të hapura.
- Ndërveprimi në gjuhën natyrore: I bën robotët më të lehtë për t’u përdorur duke mundësuar caktimin e detyrave komplekse duke përdorur gjuhën natyrore.
- Orkestrimi i detyrave: Dekonstrukton komandat e gjuhës natyrore në nëndetyra dhe integrohet me kontrolluesit dhe sjelljet ekzistuese të robotëve për të përfunduar detyra me horizont të gjatë.
- Aftësi të gjithanshme: Lokalizon dhe identifikon objektet, kupton marrëdhëniet midis objekteve, planifikon kapjet dhe trajektore, dhe interpreton skena dinamike.
Ky dokument përshkruan se çfarë bën modeli dhe ju çon nëpër disa shembuj që nxjerrin në pah aftësitë agjentike të modelit.
Nëse doni të filloni menjëherë, mund ta provoni modelin në Google AI Studio.
Siguria
Ndërsa Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 u ndërtua duke pasur parasysh sigurinë, është përgjegjësia juaj të ruani një mjedis të sigurt rreth robotit. Modelet gjeneruese të IA-së mund të bëjnë gabime dhe robotët fizikë mund të shkaktojnë dëme. Siguria është një përparësi dhe siguria e modeleve gjeneruese të IA-së kur përdoren me robotikën e botës reale është një fushë aktive dhe kritike e kërkimit tonë. Për të mësuar më shumë, vizitoni faqen e sigurisë së robotikës në Google DeepMind .
Fillimi: Gjetja e objekteve në një skenë
Shembulli i mëposhtëm demonstron një rast të zakonshëm përdorimi në robotikë. Ai tregon se si t'i kalohet një imazh dhe një mesazh teksti modelit duke përdorur metodën generateContent për të marrë një listë të objekteve të identifikuara me pikat e tyre përkatëse 2D. Modeli kthen pika për artikujt që identifikoi në një imazh, duke kthyer koordinatat dhe etiketat e tyre të normalizuara 2D.
Mund ta përdorni këtë rezultat me një API robotike ose të thirrni një model veprimi me gjuhë-vizioni (VLA) ose çdo funksion tjetër të përcaktuar nga përdoruesi të palës së tretë për të gjeneruar veprime që një robot duhet të kryejë.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
PROMPT = """
Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned
should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format
normalized to 0-1000.
"""
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image
with open("my-image.png", 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/png',
),
PROMPT
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
PUSHTIM
# First, ensure you have the image file locally.
# Encode the image to base64
IMAGE_BASE64=$(base64 -w 0 my-image.png)
curl -X POST \
"https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview:generateContent \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"mimeType": "image/png",
"data": "'"${IMAGE_BASE64}"'"
}
},
{
"text": "Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected. The answer should follow the json format: [{\"point\": [y, x], \"label\": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."
}
]
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"temperature": 0.5,
"thinkingConfig": {
"thinkingBudget": 0
}
}
}'
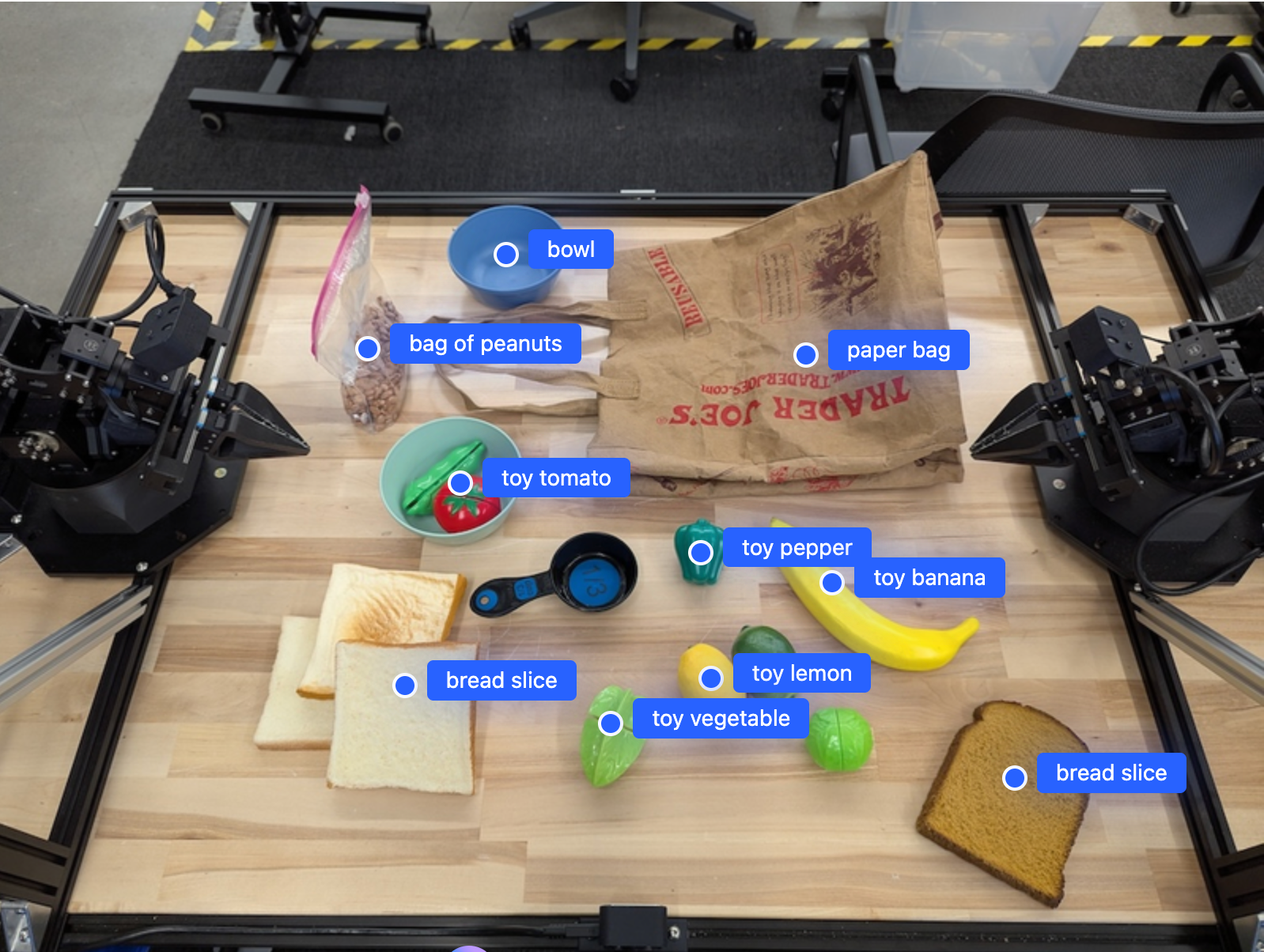
Rezultati do të jetë një varg JSON që përmban objekte, secila me një point (koordinatat e normalizuara [y, x] ) dhe një label që identifikon objektin.
JSON
[
{"point": [376, 508], "label": "small banana"},
{"point": [287, 609], "label": "larger banana"},
{"point": [223, 303], "label": "pink starfruit"},
{"point": [435, 172], "label": "paper bag"},
{"point": [270, 786], "label": "green plastic bowl"},
{"point": [488, 775], "label": "metal measuring cup"},
{"point": [673, 580], "label": "dark blue bowl"},
{"point": [471, 353], "label": "light blue bowl"},
{"point": [492, 497], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [525, 429], "label": "lime"}
]
Imazhi i mëposhtëm është një shembull se si mund të shfaqen këto pika:

Si funksionon
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 u lejon robotëve tuaj të kontekstualizojnë dhe të punojnë në botën fizike duke përdorur kuptimin hapësinor. Ai përdor imazhe/video/audio dhe udhëzime të gjuhës natyrore për të:
- Kuptimi i objekteve dhe kontekstit të skenës : Identifikon objektet dhe arsyet rreth marrëdhënies së tyre me skenën, duke përfshirë edhe mundësitë e tyre.
- Kupton udhëzimet e detyrave : Interpreton detyrat e dhëna në gjuhë natyrore, si "gjej bananen".
- Arsyetoni në mënyrë hapësinore dhe kohore : Kuptoni sekuencat e veprimeve dhe se si objektet bashkëveprojnë me një skenë me kalimin e kohës.
- Jep një rezultat të strukturuar : Kthen koordinatat (pikat ose kutitë kufizuese) që përfaqësojnë vendndodhjet e objekteve.
Kjo i mundëson robotëve të "shohin" dhe "kuptojnë" mjedisin e tyre në mënyrë programore.
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 është gjithashtu agjent, që do të thotë se mund të ndajë detyra komplekse (si "vendos mollën në tas") në nën-detyra për të orkestruar detyra me horizont të gjatë:
- Renditja e nëndetyrave : Zbërthen komandat në një sekuencë logjike hapash.
- Thirrjet e funksioneve/Ekzekutimi i kodit : Ekzekuton hapat duke thirrur funksionet/mjetet ekzistuese të robotit ose duke ekzekutuar kodin e gjeneruar.
Lexoni më shumë rreth asaj se si funksionon thirrja e funksioneve me Gemini në faqen e Thirrjes së Funksioneve .
Përdorimi i buxhetit të të menduarit me Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 ka një buxhet fleksibël të të menduarit që ju jep kontroll mbi kompromiset midis latencës dhe saktësisë. Për detyrat e të kuptuarit hapësinor si zbulimi i objekteve, modeli mund të arrijë performancë të lartë me një buxhet të vogël të të menduarit. Detyrat më komplekse të arsyetimit si numërimi dhe vlerësimi i peshës përfitojnë nga një buxhet më i madh i të menduarit. Kjo ju lejon të balanconi nevojën për përgjigje me latencë të ulët me rezultate me saktësi të lartë për detyra më sfiduese.
Për të mësuar më shumë rreth buxheteve të të menduarit, shihni faqen e aftësive kryesore të të menduarit .
Aftësitë agjentike për robotikën
Ky seksion shqyrton aftësi të ndryshme të Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5, duke demonstruar se si të përdoret modeli për perceptimin, arsyetimin dhe aplikimet e planifikimit robotik.
Shembujt në këtë seksion demonstrojnë aftësi nga drejtimi dhe gjetja e objekteve në një imazh deri te planifikimi i trajektoreve dhe orkestrimi i detyrave me horizont të gjatë. Për thjeshtësi, fragmentet e kodit janë reduktuar për të treguar njoftimin dhe thirrjen për generate_content API. Kodi i plotë i ekzekutueshëm, si dhe shembuj shtesë, mund të gjenden në librin e gatimit të Robotics .
Duke treguar objekte
Tregimi dhe gjetja e objekteve në imazhe ose kuadro video është një rast përdorimi i zakonshëm për modelet e shikimit dhe gjuhës (VLM) në robotikë. Shembulli i mëposhtëm i kërkon modelit të gjejë objekte specifike brenda një imazhi dhe të kthejë koordinatat e tyre në një imazh.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
queries = [
"bread",
"starfruit",
"banana",
]
prompt = f"""
Get all points matching the following objects: {', '.join(queries)}. The
label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Rezultati do të ishte i ngjashëm me shembullin e fillimit, një JSON që përmban koordinatat e objekteve të gjetura dhe etiketat e tyre.
[
{"point": [671, 317], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [738, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [702, 237], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [629, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [833, 800], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [609, 663], "label": "banana"},
{"point": [770, 483], "label": "starfruit"}
]
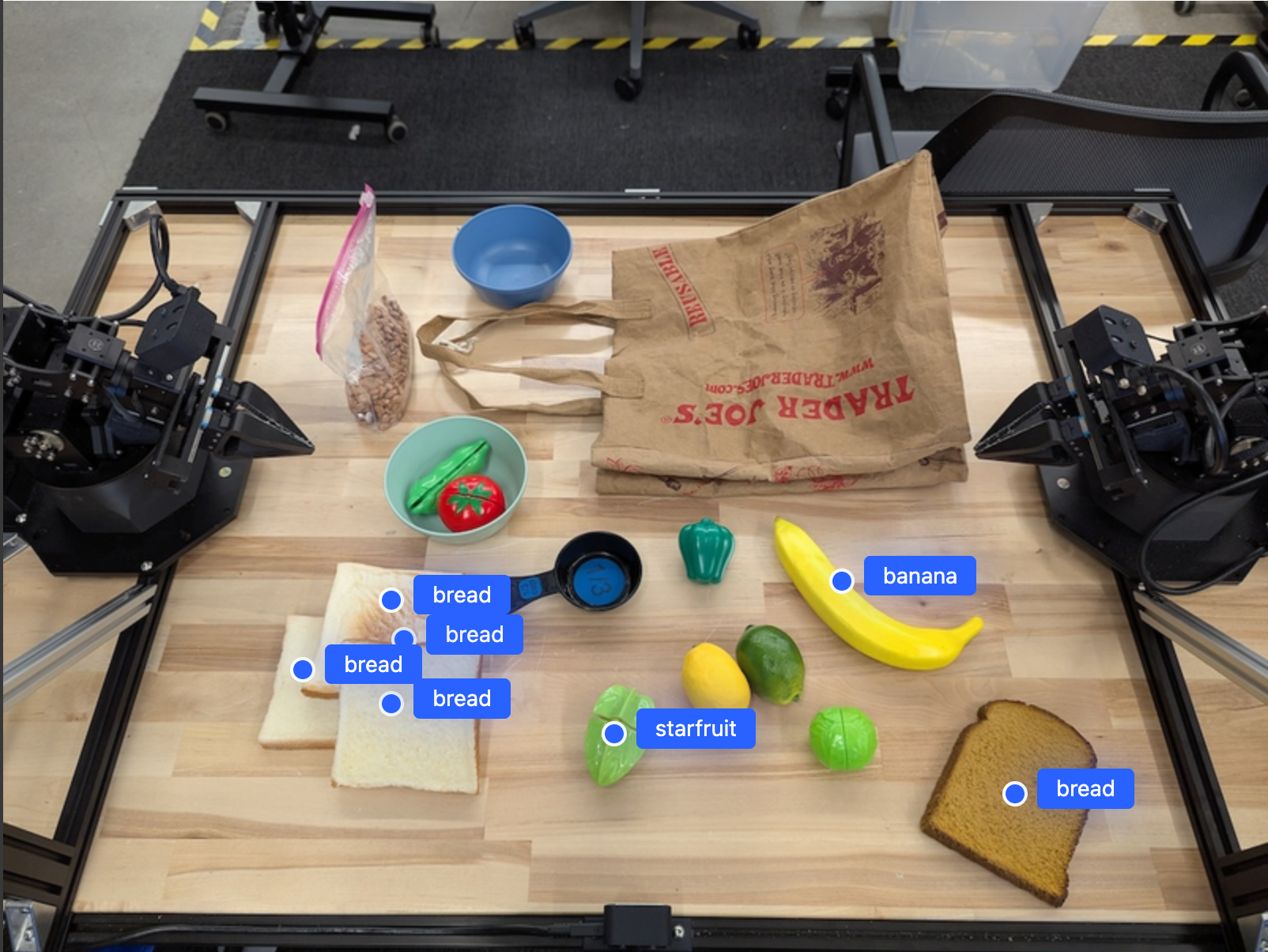

Përdorni komandën e mëposhtme për t'i kërkuar modelit të interpretojë kategoritë abstrakte si "fruta" në vend të objekteve specifike dhe të gjejë të gjitha rastet në imazh.
Python
prompt = f"""
Get all points for fruit. The label returned should be an identifying
name for the object detected.
""" + """The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."""
Vizitoni faqen e të kuptuarit të imazhit për teknika të tjera të përpunimit të imazhit.
Ndjekja e objekteve në një video
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 mund të analizojë gjithashtu kuadro video për të ndjekur objektet me kalimin e kohës. Shihni Hyrjet Video për një listë të formateve të mbështetura të videos.
Më poshtë është kërkesa bazë e përdorur për të gjetur objekte specifike në secilën kornizë që modeli analizon:
Python
# Define the objects to find
queries = [
"pen (on desk)",
"pen (in robot hand)",
"laptop (opened)",
"laptop (closed)",
]
base_prompt = f"""
Point to the following objects in the provided image: {', '.join(queries)}.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
If no objects are found, return an empty JSON list [].
"""
Rezultati tregon një stilolaps dhe një laptop që gjurmohen nëpër kuadrot e videos.
![]()
Për kodin e plotë të ekzekutueshëm, shihni librin e gatimit të Robotics .
Kutitë e zbulimit dhe kufizimit të objekteve
Përtej pikave të vetme, modeli mund të kthejë edhe kuti kufizuese 2D, duke siguruar një rajon drejtkëndor që rrethon një objekt.
Ky shembull kërkon kuti kufizuese 2D për objekte të identifikueshme në një tabelë. Modeli udhëzohet të kufizojë rezultatin në 25 objekte dhe të emërtojë në mënyrë unike shumë raste.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Return bounding boxes as a JSON array with labels. Never return masks
or code fencing. Limit to 25 objects. Include as many objects as you
can identify on the table.
If an object is present multiple times, name them according to their
unique characteristic (colors, size, position, unique characteristics, etc..).
The format should be as follows: [{"box_2d": [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax],
"label": <label for the object>}] normalized to 0-1000. The values in
box_2d must only be integers
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Më poshtë shfaqen kutitë e kthyera nga modeli.
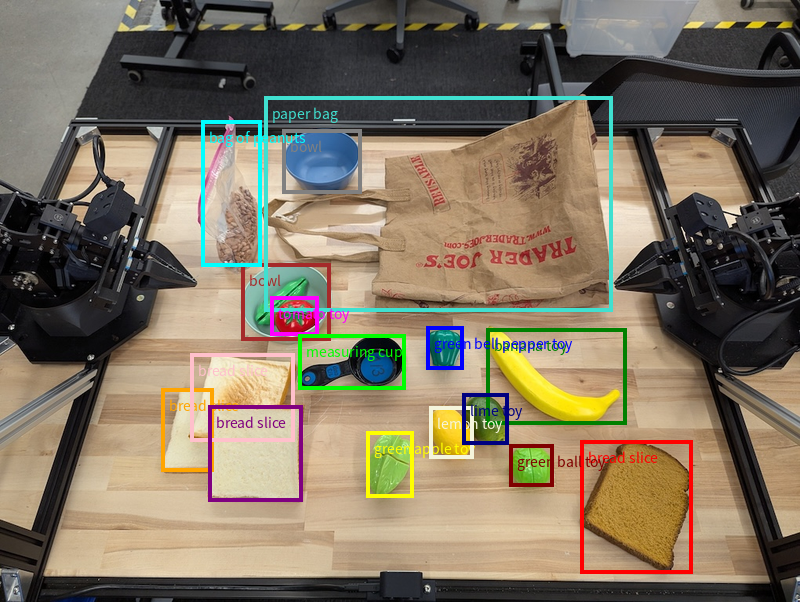
Për kodin e plotë të ekzekutueshëm, shihni librin e gatimit të Robotics . Faqja e të kuptuarit të imazhit ka gjithashtu shembuj shtesë të detyrave vizuale si segmentimi dhe zbulimi i objekteve.
Shembuj të tjerë të kutive kufizuese mund të gjenden në faqen Kuptimi i imazhit .
Trajektoret
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 mund të gjenerojë sekuenca pikash që përcaktojnë një trajektore, e dobishme për udhëzimin e lëvizjes së robotit.
Ky shembull kërkon një trajektore për të lëvizur një stilolaps të kuq në një organizues, duke përfshirë pikën e fillimit dhe një seri pikash të ndërmjetme.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
points_data = []
prompt = """
Place a point on the red pen, then 15 points for the trajectory of
moving the red pen to the top of the organizer on the left.
The points should be labeled by order of the trajectory, from '0'
(start point at left hand) to <n> (final point)
The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Përgjigja është një bashkësi koordinatash që përshkruajnë trajektoren e shtegut që duhet të ndjekë stilolapsi i kuq për të përfunduar detyrën e zhvendosjes së tij sipër organizuesit:
[
{"point": [550, 610], "label": "0"},
{"point": [500, 600], "label": "1"},
{"point": [450, 590], "label": "2"},
{"point": [400, 580], "label": "3"},
{"point": [350, 550], "label": "4"},
{"point": [300, 520], "label": "5"},
{"point": [250, 490], "label": "6"},
{"point": [200, 460], "label": "7"},
{"point": [180, 430], "label": "8"},
{"point": [160, 400], "label": "9"},
{"point": [140, 370], "label": "10"},
{"point": [120, 340], "label": "11"},
{"point": [110, 320], "label": "12"},
{"point": [105, 310], "label": "13"},
{"point": [100, 305], "label": "14"},
{"point": [100, 300], "label": "15"}
]
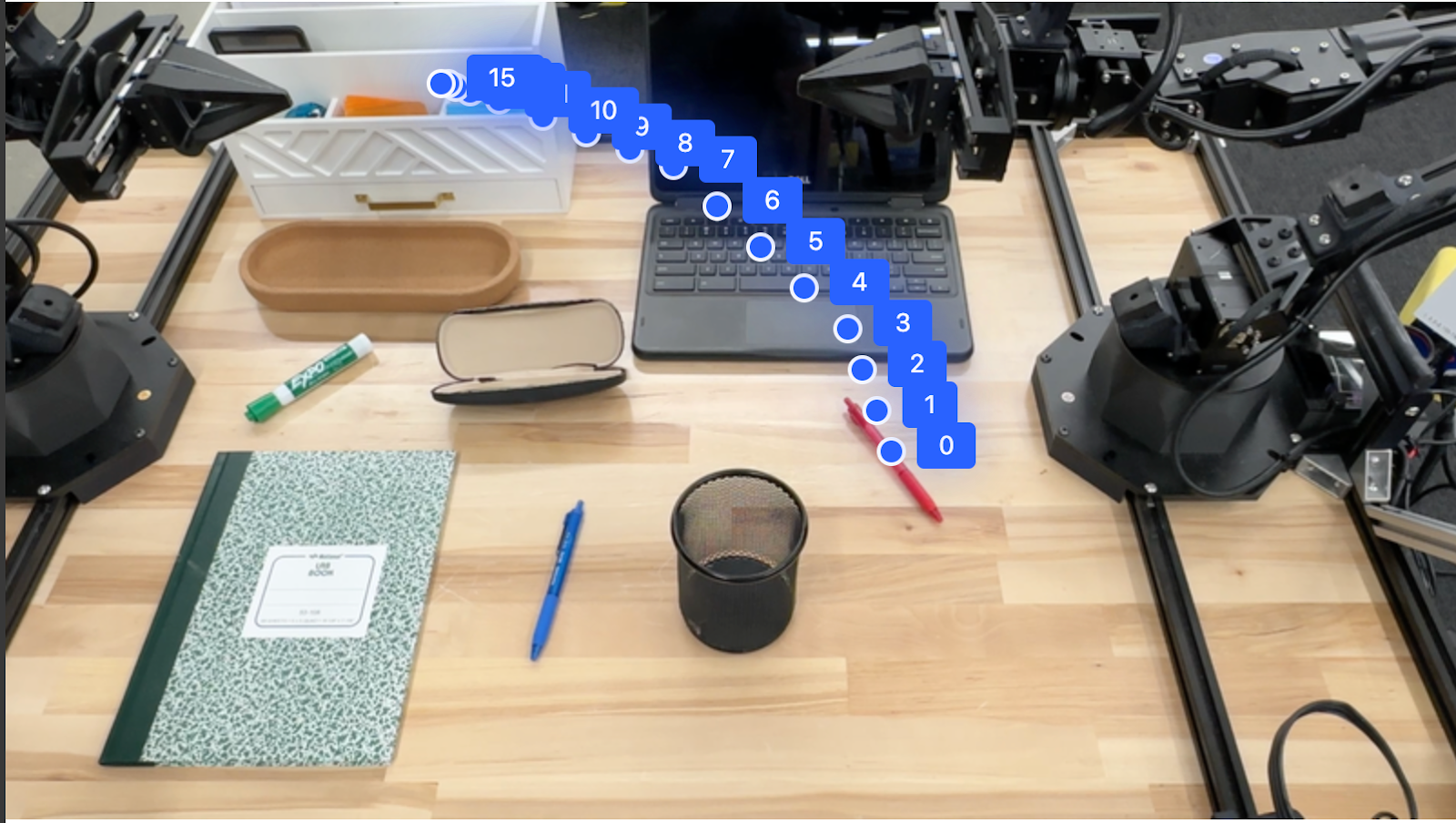

Orkestrim
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 mund të kryejë arsyetim hapësinor të nivelit të lartë, duke nxjerrë përfundime për veprime ose duke identifikuar vendndodhje optimale bazuar në të kuptuarit kontekstual.
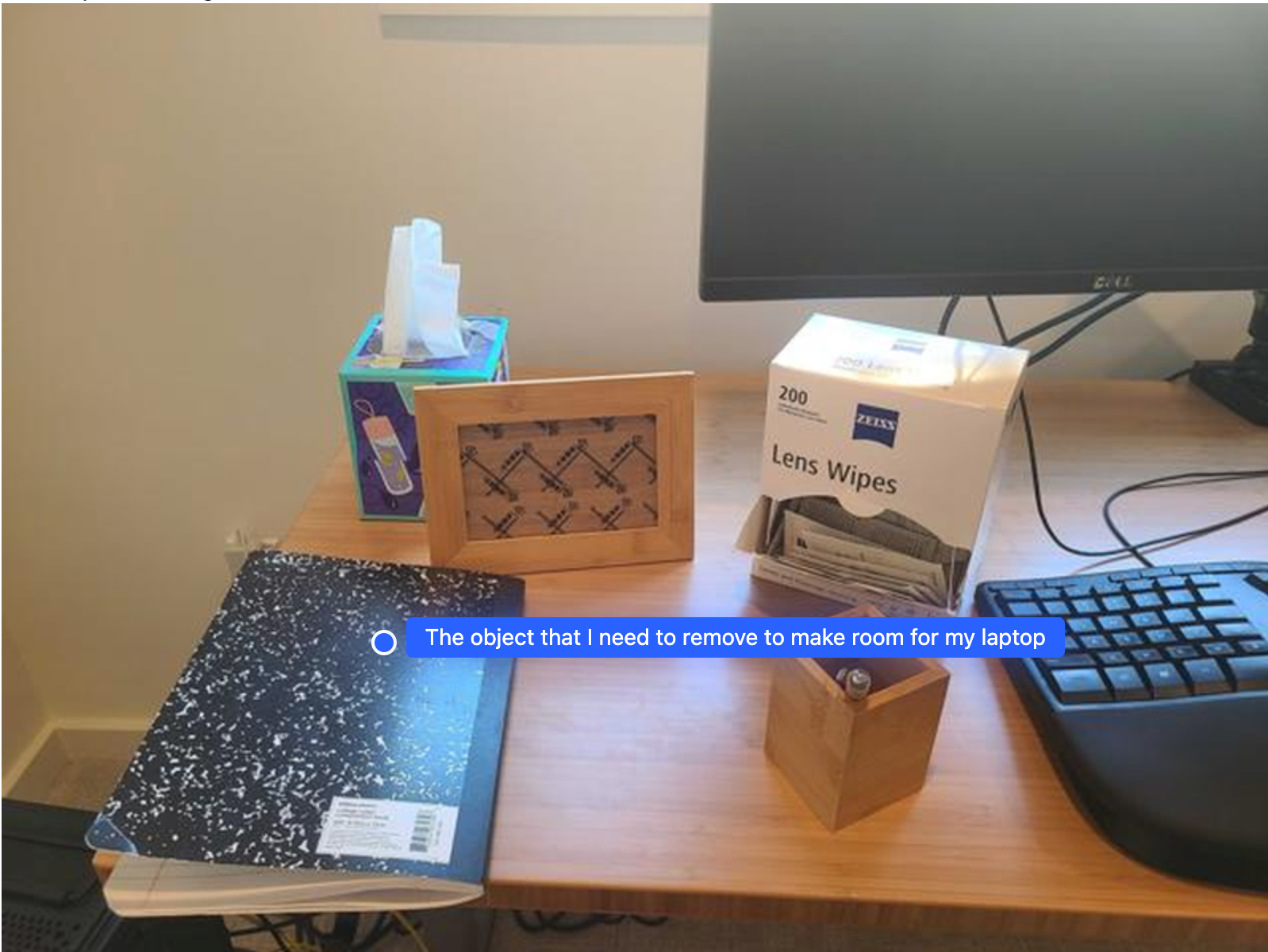
Bërja e një hapësire për një laptop
Ky shembull tregon se si Gemini Robotics-ER mund të arsyetojë rreth një hapësire. Kërkesa i kërkon modelit të identifikojë se cili objekt duhet të zhvendoset për të krijuar hapësirë për një artikull tjetër.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Point to the object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Përgjigja përmban një koordinatë 2D të objektit që i përgjigjet pyetjes së përdoruesit, në këtë rast, objektit që duhet të lëvizë për të bërë vend për një laptop.
[
{"point": [672, 301], "label": "The object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop"}
]

Paketimi i një dreke
Modeli gjithashtu mund të ofrojë udhëzime për detyra me shumë hapa dhe të tregojë objektet përkatëse për secilin hap. Ky shembull tregon se si modeli planifikon një seri hapash për të paketuar një çantë dreke.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-lunch.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Explain how to pack the lunch box and lunch bag. Point to each
object that you refer to. Each point should be in the format:
[{"point": [y, x], "label": }], where the coordinates are
normalized between 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Përgjigja e kësaj pyetjeje është një sërë udhëzimesh hap pas hapi se si të paketoni një çantë dreke nga të dhënat e imazhit.
Fut imazhin
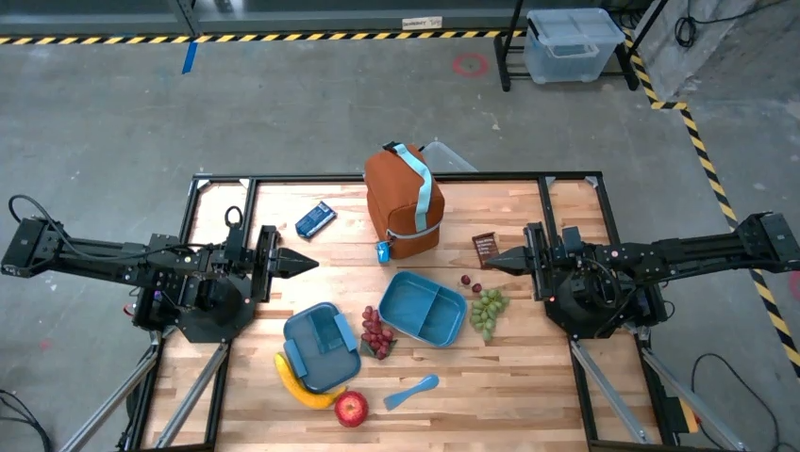
Prodhimi i modelit
Based on the image, here is a plan to pack the lunch box and lunch bag:
1. **Pack the fruit into the lunch box.** Place the [apple](apple), [banana](banana), [red grapes](red grapes), and [green grapes](green grapes) into the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
2. **Add the spoon to the lunch box.** Put the [blue spoon](blue spoon) inside the lunch box as well.
3. **Close the lunch box.** Secure the lid on the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
4. **Place the lunch box inside the lunch bag.** Put the closed [blue lunch box](blue lunch box) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
5. **Pack the remaining items into the lunch bag.** Place the [blue snack bar](blue snack bar) and the [brown snack bar](brown snack bar) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
Here is the list of objects and their locations:
* [{"point": [899, 440], "label": "apple"}]
* [{"point": [814, 363], "label": "banana"}]
* [{"point": [727, 470], "label": "red grapes"}]
* [{"point": [675, 608], "label": "green grapes"}]
* [{"point": [706, 529], "label": "blue lunch box"}]
* [{"point": [864, 517], "label": "blue spoon"}]
* [{"point": [499, 401], "label": "blue snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [614, 705], "label": "brown snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [448, 501], "label": "brown lunch bag"}]
Thirrja e një API-je roboti të personalizuar
Ky shembull demonstron orkestrimin e detyrave me një API të personalizuar për robotët. Ai prezanton një API të improvizuar të projektuar për një operacion marrjeje dhe vendosjeje. Detyra është të marrësh një bllok blu dhe ta vendosësh atë në një tas portokalli:
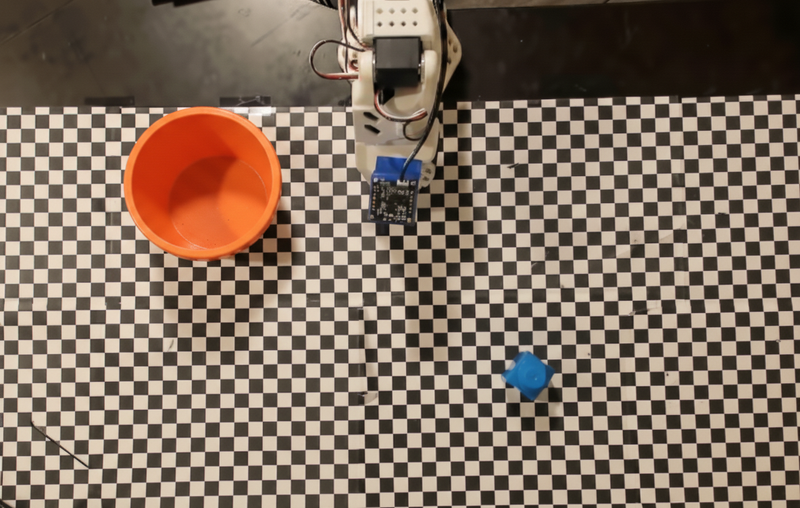
Ngjashëm me shembujt e tjerë në këtë faqe, kodi i plotë i ekzekutueshëm është i disponueshëm në librin e gatimit të Robotics .
Hapi i parë është të gjeni të dy artikujt me anë të komandës së mëposhtme:
Python
prompt = """
Locate and point to the blue block and the orange bowl. The label
returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
Përgjigja e modelit përfshin koordinatat e normalizuara të bllokut dhe tasit:
[
{"point": [389, 252], "label": "orange bowl"},
{"point": [727, 659], "label": "blue block"}
]
Ky shembull përdor API-n e mëposhtme të robotit simulues:
Python
def move(x, y, high):
print(f"moving to coordinates: {x}, {y}, {15 if high else 5}")
def setGripperState(opened):
print("Opening gripper" if opened else "Closing gripper")
def returnToOrigin():
print("Returning to origin pose")
Hapi tjetër është thirrja e një sekuence funksionesh API me logjikën e nevojshme për të ekzekutuar veprimin. Kërkesa e mëposhtme përfshin një përshkrim të API-t të robotit që modeli duhet të përdorë kur orkestron këtë detyrë.
Python
prompt = f"""
You are a robotic arm with six degrees-of-freedom. You have the
following functions available to you:
def move(x, y, high):
# moves the arm to the given coordinates. The boolean value 'high' set
to True means the robot arm should be lifted above the scene for
avoiding obstacles during motion. 'high' set to False means the robot
arm should have the gripper placed on the surface for interacting with
objects.
def setGripperState(opened):
# Opens the gripper if opened set to true, otherwise closes the gripper
def returnToOrigin():
# Returns the robot to an initial state. Should be called as a cleanup
operation.
The origin point for calculating the moves is at normalized point
y={robot_origin_y}, x={robot_origin_x}. Use this as the new (0,0) for
calculating moves, allowing x and y to be negative.
Perform a pick and place operation where you pick up the blue block at
normalized coordinates ({block_x}, {block_y}) (relative coordinates:
{block_relative_x}, {block_relative_y}) and place it into the orange
bowl at normalized coordinates ({bowl_x}, {bowl_y})
(relative coordinates: {bowl_relative_x}, {bowl_relative_y}).
Provide the sequence of function calls as a JSON list of objects, where
each object has a "function" key (the function name) and an "args" key
(a list of arguments for the function).
Also, include your reasoning before the JSON output.
For example:
Reasoning: To pick up the block, I will first move the arm to a high
position above the block, open the gripper, move down to the block,
close the gripper, lift the arm, move to a high position above the bowl,
move down to the bowl, open the gripper, and then lift the arm back to
a high position.
"""
Më poshtë tregohet një rezultat i mundshëm i modelit bazuar në prompt dhe API-n e robotit simulues. Rezultati përfshin procesin e të menduarit mbi modelin dhe detyrat që ai planifikoi si rezultat. Gjithashtu tregon rezultatin e thirrjeve të funksioneve të robotit që modeli i renditi së bashku.
Reasoning: To perform the pick and place operation, I will first move the
robotic arm to a high position above the blue block to ensure clearance. Then, I
will open the gripper in preparation for grasping. Next, I will lower the arm to
the surface level to position the gripper around the block and close the gripper
to secure it. After picking up the block, I will lift the arm to clear the
surface and move towards the orange bowl, maintaining a high position to avoid
collisions. Once positioned above the bowl, I will lower the arm to place the
block inside. I will then open the gripper to release the block. Finally, I will
lift the arm out of the bowl and call `returnToOrigin` to reset the robot's
state.
[
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
false
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "returnToOrigin",
"args": []
}
]
Executing Function Calls:
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 5
Closing gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 5
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
Returning to origin pose
Ekzekutimi i kodit
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 mund të sugjerojë dhe ekzekutojë kod Python për të kryer detyra që kërkojnë veprime dinamike, të tilla si zmadhimi në një rajon imazhi për detaje më të mira.
Ky shembull demonstron se si modeli mund të sugjerojë përdorimin e mjetit të ekzekutimit të kodit për të "zmadhuar" një zonë specifike të një imazhi, gjë që më pas e kryen për t'iu përgjigjur pyetjes së përdoruesit.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-object.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
What is the air quality reading? Using the code execution feature,
zoom in on the image to take a closer look.
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
)
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
Më poshtë tregohet një përgjigje e mundshme e modelit për këtë detyrë. Rezultati tregon kodin që gjeneron modelin për zmadhimin e imazhit për ta lexuar më mirë ekranin. Gjithashtu tregon procesin e të menduarit rreth rregullimeve që i bëri prerjes. Për rezultatin e plotë të mostrës, shihni librin e gatimit të Robotics .
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
# Based on visual inspection, the display is roughly centered around [430, 430] to [500, 500] in a 1000x1000 scale.
# Let's try to zoom in on the display area.
# Bounding box for display: [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax] in pixels.
# From visual inspection of the original image (size 90489 bytes, resolution
unknown but let's assume a standard aspect ratio and roughly 1000x1000 for
relative positioning),
# the display is located at approximately y=380-480, x=410-540.
# Let's define a larger area around it for context.
# Let's say we want to crop from y=350 to y=550 and x=350 to x=650.
...
thought
The crop was too tight and only captured part of the display. Let's adjust the bounding box.
The previous crop was `img.crop((400, 350, 600, 500))`. This means xmin=400, ymin=350, xmax=600, ymax=500.
The display is centered around x=480, y=430.
The previous crop captured the left side of the display.
Let's expand the x range to the right and y range to cover the whole circle.
New bounding box estimate: ymin=370, xmin=400, ymax=500, xmax=600.
Let's try again with a wider crop.
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
…
The reading of 14 falls into the "Moderate" category.
The prompt asks for the "air quality reading", which can be interpreted as
either the numerical value or the categorical description. Given the numerical
value is explicitly displayed, it's the primary reading.
Let's provide the numerical value as the reading.
The reading is 014.
Based on the display on the air purifier, the air quality reading is **014**.
Praktikat më të mira
Për të optimizuar performancën dhe saktësinë e aplikacioneve tuaja të robotikës, është thelbësore të kuptoni se si të bashkëveproni në mënyrë efektive me modelin Gemini. Ky seksion përshkruan praktikat më të mira dhe strategjitë kryesore për hartimin e kërkesave, trajtimin e të dhënave vizuale dhe strukturimin e detyrave për të arritur rezultatet më të besueshme.
Përdorni gjuhë të qartë dhe të thjeshtë.
Përqafojeni gjuhën natyrale : Modeli Gemini është projektuar për të kuptuar gjuhën natyrale, bisedore. Strukturoni sugjerimet tuaja në një mënyrë që është semantikisht e qartë dhe pasqyron mënyrën se si një person do të jepte udhëzime natyrshëm.
Përdorni terminologji të përditshme : Zgjidhni gjuhë të zakonshme, të përditshme në vend të zhargonit teknik ose të specializuar. Nëse modeli nuk i përgjigjet siç pritet një termi të caktuar, provoni ta riformuloni atë me një sinonim më të zakonshëm.
Optimizoni të dhënat vizuale.
Zmadho për detaje : Kur merreni me objekte që janë të vogla ose të vështira për t'u dalluar në një pamje më të gjerë, përdorni një funksion kutie kufizuese për të izoluar objektin e interesit. Pastaj mund ta prisni imazhin në këtë përzgjedhje dhe t'ia dërgoni imazhin e ri, të fokusuar, modelit për një analizë më të detajuar.
Eksperimentoni me ndriçimin dhe ngjyrën : Perceptimi i modelit mund të ndikohet nga kushtet e vështira të ndriçimit dhe kontrasti i dobët i ngjyrave.
Ndani problemet komplekse në hapa më të vegjël. Duke trajtuar secilin hap më të vogël individualisht, mund ta orientoni modelin drejt një rezultati më të saktë dhe të suksesshëm.
Përmirësoni saktësinë përmes konsensusit. Për detyrat që kërkojnë një shkallë të lartë precizioni, mund ta pyetni modelin disa herë me të njëjtën kërkesë. Duke mesatarizuar rezultatet e kthyera, mund të arrini në një "konsensus" që shpesh është më i saktë dhe i besueshëm.
Kufizime
Merrni parasysh kufizimet e mëposhtme kur zhvilloni me Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5:
- Statusi i pamjes paraprake: Modeli është aktualisht në pamje paraprake . API-të dhe aftësitë mund të ndryshojnë dhe mund të mos jetë i përshtatshëm për aplikacionet kritike të prodhimit pa testime të hollësishme.
- Vonesa: Pyetjet komplekse, të dhënat hyrëse me rezolucion të lartë ose buxheti i gjerë
thinking_budgetmund të çojnë në rritje të kohës së përpunimit. - Halucinacione: Ashtu si të gjitha modelet e mëdha gjuhësore, Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 mund të "halucinojë" herë pas here ose të japë informacion të pasaktë, veçanërisht për kërkesa të paqarta ose të dhëna hyrëse jashtë shpërndarjes.
- Varësia nga cilësia e informacionit të shpejtë: Cilësia e rezultatit të modelit varet shumë nga qartësia dhe specifikimi i informacionit të shpejtë. Informacionet e paqarta ose të strukturuara dobët mund të çojnë në rezultate jo optimale.
- Kostoja llogaritëse: Ekzekutimi i modelit, veçanërisht me hyrje video ose
thinking_budgettë lartë, konsumon burime llogaritëse dhe shkakton kosto. Shihni faqen e të menduarit për më shumë detaje. - Llojet e të dhënave hyrëse: Shihni temat e mëposhtme për detaje mbi kufizimet për secilin modalitet.
Njoftim për Privatësinë
Ju pranoni që modelet e referuara në këtë dokument ("Modelet e Robotikës") shfrytëzojnë të dhënat video dhe audio për të operuar dhe lëvizur harduerin tuaj në përputhje me udhëzimet tuaja. Prandaj, ju mund të operoni Modelet e Robotikës në mënyrë që të dhënat nga persona të identifikueshëm, siç janë zëri, imazhet dhe të dhënat e ngjashmërisë ("Të Dhënat Personale"), të mblidhen nga Modelet e Robotikës. Nëse zgjidhni të operoni Modelet e Robotikës në një mënyrë që mbledh të Dhëna Personale, ju pranoni se nuk do të lejoni asnjë person të identifikueshëm të bashkëveprojë me ose të jetë i pranishëm në zonën përreth Modeleve të Robotikës, përveç nëse dhe derisa këta persona të identifikueshëm të jenë njoftuar mjaftueshëm dhe të kenë dhënë pëlqimin për faktin se të Dhënat e tyre Personale mund t'i ofrohen dhe të përdoren nga Google, siç përshkruhet në Kushtet Shtesë të Shërbimit të Gemini API që gjenden në https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/terms ("Kushtet"), duke përfshirë edhe në përputhje me seksionin e titulluar "Si i Përdor Google të Dhënat Tuaja". Ju do të siguroheni që një njoftim i tillë lejon mbledhjen dhe përdorimin e të Dhënave Personale siç përcaktohet në Kushte, dhe do të bëni përpjekje të arsyeshme komerciale për të minimizuar mbledhjen dhe shpërndarjen e të Dhënave Personale duke përdorur teknika të tilla si mjegullimi i fytyrës dhe operimi i Modeleve Robotike në zona që nuk përmbajnë persona të identifikueshëm në masën e praktikueshme.
Çmimet
Për informacion të detajuar mbi çmimet dhe rajonet e disponueshme, referojuni faqes së çmimeve .
Versionet e modelit
| Pronë | Përshkrimi |
|---|---|
| Kodi i modelit të | gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview |
| llojet e të dhënave të mbështetura | Të dhënat hyrëse Tekst, imazhe, video, audio Prodhimi Tekst |
| Limitet e token [*] | Limiti i tokenit të hyrjes 1,048,576 Limiti i tokenit të daljes 65,536 |
| Aftësitë e | Gjenerimi i audios Nuk mbështetet API-ja e grupeve Nuk mbështetet Ruajtja në memorje Nuk mbështetet Ekzekutimi i kodit Mbështetur Thirrja e funksionit Mbështetur Tokëzimi me Google Maps Nuk mbështetet Gjenerimi i imazhit Nuk mbështetet API i drejtpërdrejtë Nuk mbështetet Kërkimi në tokë Mbështetur Rezultatet e strukturuara Mbështetur Të menduarit Mbështetur Konteksti i URL-së Mbështetur |
| Versione |
|
| Përditësimi më i fundit | Shtator 2025 |
| i njohurive | Janar 2025 |
Hapat e ardhshëm
- Eksploroni aftësi të tjera dhe vazhdoni të eksperimentoni me kërkesa dhe të dhëna të ndryshme për të zbuluar më shumë zbatime për Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5. Shihni librin e gatimit të Robotics për më shumë shembuj.
- Mësoni se si u ndërtuan modelet e Gemini Robotics duke pasur parasysh sigurinë, vizitoni faqen e sigurisë së robotikës në Google DeepMind .
- Lexoni rreth përditësimeve më të fundit mbi modelet e Gemini Robotics në faqen kryesore të Gemini Robotics .

