توفّر Gemini API أداة لتنفيذ الرموز البرمجية تتيح للنموذج إنشاء رموز Python البرمجية وتشغيلها. يمكن للنموذج بعد ذلك أن يتعلّم بشكل متكرّر من نتائج تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي إلى أن يصل إلى الناتج النهائي. يمكنك استخدام تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية لإنشاء تطبيقات تستفيد من الاستدلال المستند إلى التعليمات البرمجية. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك استخدام ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز" لحل المعادلات أو معالجة النصوص. يمكنك أيضًا استخدام المكتبات المضمّنة في بيئة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي لتنفيذ مهام أكثر تخصصًا.
يمكن لـ Gemini تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي بلغة Python فقط. سيظل بإمكانك أن تطلب من Gemini إنشاء رمز بلغة أخرى، ولكن لن يتمكّن النموذج من استخدام أداة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي لتشغيله.
تفعيل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية
لتفعيل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية، عليك ضبط أداة تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية على النموذج. يتيح ذلك للنموذج إنشاء الرموز البرمجية وتشغيلها.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
const parts = response?.candidates?.[0]?.content?.parts || [];
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode && part.executableCode.code) {
console.log(part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult && part.codeExecutionResult.output) {
console.log(part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
});
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
genai.Text("What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."),
config,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d ' {"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": {
"parts":
{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}
},
}'
قد يبدو الناتج على النحو التالي، وقد تم تنسيقه لتسهيل قراءته:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
يجمع هذا الناتج عدة أجزاء من المحتوى يعرضها النموذج عند استخدام تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي:
-
text: نص مضمّن تم إنشاؤه بواسطة النموذج -
executableCode: الرمز الذي أنشأه النموذج والمخصّص للتنفيذ -
codeExecutionResult: نتيجة الرمز القابل للتنفيذ
تختلف اصطلاحات التسمية لهذه الأجزاء حسب لغة البرمجة.
تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية باستخدام الصور (Gemini 3)
يمكن الآن لنموذج Gemini 3 Flash كتابة رموز Python البرمجية وتنفيذها لمعالجة الصور وفحصها بشكل نشط.
حالات الاستخدام
- التكبير والفحص: يرصد النموذج تلقائيًا عندما تكون التفاصيل صغيرة جدًا (مثل قراءة مقياس بعيد)، ويكتب رمزًا برمجيًا لاقتصاص المنطقة وإعادة فحصها بدقة أعلى.
- الرياضيات المرئية: يمكن للنموذج إجراء عمليات حسابية متعددة الخطوات باستخدام الرموز البرمجية (مثل جمع بنود الإيصال).
- التعليق التوضيحي على الصور: يمكن للنموذج إضافة تعليقات توضيحية إلى الصور للإجابة عن أسئلة، مثل رسم أسهم لإظهار العلاقات.
تفعيل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية باستخدام الصور
تتيح Gemini 3 Flash رسميًا تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية باستخدام الصور. يمكنك تفعيل هذا السلوك من خلال تفعيل كلّ من "الاستخدام كأداة تنفيذ رموز برمجية" و"التفكير".
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
from PIL import Image
import io
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
image = types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes, mime_type="image/jpeg"
)
# Ensure you have your API key set
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[image, "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
if part.as_image() is not None:
# display() is a standard function in Jupyter/Colab notebooks
display(Image.open(io.BytesIO(part.as_image().image_bytes)))
JavaScript
async function main() {
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({ });
// 1. Prepare Image Data
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
// 2. Call the API with Code Execution enabled
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
},
{ text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?" }
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
// 3. Process the response (Text, Code, and Execution Results)
const candidates = result.candidates;
if (candidates && candidates[0].content.parts) {
for (const part of candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.text) {
console.log("Text:", part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(`\nGenerated Code (${part.executableCode.language}):\n`, part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(`\nExecution Output (${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}):\n`, part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
}
}
}
main();
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initialize Client (Reads GEMINI_API_KEY from env)
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 1. Download the image
imageResp, err := http.Get("https://goo.gle/instrument-img")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer imageResp.Body.Close()
imageBytes, err := io.ReadAll(imageResp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 2. Configure Code Execution Tool
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
// 3. Generate Content
result, err := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
[]*genai.Content{
{
Parts: []*genai.Part{
{InlineData: &genai.Blob{MIMEType: "image/jpeg", Data: imageBytes}},
{Text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"},
},
Role: "user",
},
},
config,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 4. Parse Response (Text, Code, Output)
for _, cand := range result.Candidates {
for _, part := range cand.Content.Parts {
if part.Text != "" {
fmt.Println("Text:", part.Text)
}
if part.ExecutableCode != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nGenerated Code (%s):\n%s\n",
part.ExecutableCode.Language,
part.ExecutableCode.Code)
}
if part.CodeExecutionResult != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nExecution Output (%s):\n%s\n",
part.CodeExecutionResult.Outcome,
part.CodeExecutionResult.Output)
}
}
}
}
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MODEL="gemini-3-flash-preview"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/$MODEL:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{
"inline_data": {
"mime_type":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
},
{"text": "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"}
]
}],
"tools": [
{
"code_execution": {}
}
]
}'
استخدام ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي" في المحادثة
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية كجزء من محادثة.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
chat = client.chats.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
response = chat.send_message("I have a math question for you.")
print(response.text)
response = chat.send_message(
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import {GoogleGenAI} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
history: [
{
role: "user",
parts: [{ text: "I have a math question for you:" }],
},
{
role: "model",
parts: [{ text: "Great! I'm ready for your math question. Please ask away." }],
},
],
config: {
tools: [{codeExecution:{}}],
}
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({
message: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
});
console.log("Chat response:", response.text);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
chat, _ := client.Chats.Create(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
config,
nil,
)
result, _ := chat.SendMessage(
ctx,
genai.Part{Text: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and " +
"make sure you get all 50.",
},
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "Can you print \"Hello world!\"?"
}]
},{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": ""
},
{
"executable_code": {
"language": "PYTHON",
"code": "\nprint(\"hello world!\")\n"
}
},
{
"code_execution_result": {
"outcome": "OUTCOME_OK",
"output": "hello world!\n"
}
},
{
"text": "I have printed \"hello world!\" using the provided python code block. \n"
}
],
},{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}]
}
]
}'
الإدخال/الإخراج
بدءًا من Gemini 2.0 Flash، تتيح ميزة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي إدخال الملفات وإخراج الرسوم البيانية. باستخدام إمكانات الإدخال والإخراج هذه، يمكنك تحميل ملفات CSV وملفات نصية وطرح أسئلة حول الملفات، كما يمكنك إنشاء رسومات بيانية باستخدام Matplotlib كجزء من الرد. يتم عرض ملفات الإخراج كصور مضمّنة في الردّ.
أسعار مؤتمر I/O
عند استخدام عمليات الإدخال والإخراج لتنفيذ الرمز، يتم تحصيل رسوم منك مقابل الرموز المميزة للإدخال والإخراج:
الرموز المميزة للإدخال:
- طلب المستخدم
الرموز المميزة للناتج:
- الرمز الذي أنشأه النموذج
- ناتج تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي في بيئة الرمز البرمجي
- رموز التفكير
- ملخّص من إنشاء النموذج
تفاصيل مؤتمر I/O
عند العمل على عمليات الإدخال والإخراج لتنفيذ الرمز، يجب الانتباه إلى التفاصيل الفنية التالية:
- الحدّ الأقصى لوقت تشغيل بيئة الرمز هو 30 ثانية.
- إذا أدّى تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي إلى حدوث خطأ، قد يقرّر النموذج إعادة إنشاء مخرجات الرمز البرمجي. يمكن أن يحدث ذلك 5 مرات كحد أقصى.
- يتم تحديد الحد الأقصى لحجم الملفات المُدخَلة من خلال نافذة الرموز المميزة الخاصة بالنموذج. في AI Studio، باستخدام Gemini Flash 2.0، يبلغ الحد الأقصى لحجم ملف الإدخال مليون رمز مميّز (أي حوالي 2 ميغابايت لملفات النصوص من أنواع الإدخال المتوافقة). إذا حمّلت ملفًا كبيرًا جدًا، لن يسمح لك AI Studio بإرساله.
- يعمل تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي على النحو الأمثل مع ملفات النصوص وملفات CSV.
- يمكن تمرير ملف الإدخال في
part.inlineDataأوpart.fileData(يتم تحميله عبر Files API)، ويتم دائمًا عرض ملف الإخراج بتنسيقpart.inlineData.
| انعطاف واحد | ثنائية الاتجاه (واجهة Multimodal Live API) | |
|---|---|---|
| الطُرز المتوافقة | جميع نماذج Gemini 2.0 و2.5 | نماذج Flash التجريبية فقط |
| أنواع إدخال الملفات المتوافقة | .png و.jpeg و.csv و.xml و.cpp و.java و.py و.js و.ts | .png و.jpeg و.csv و.xml و.cpp و.java و.py و.js و.ts |
| مكتبات الرسومات البيانية المتوافقة | مكتبة مات بلوت ليب ومكتبة سيبورن | مكتبة مات بلوت ليب ومكتبة سيبورن |
| استخدام أدوات متعددة | نعم (تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي والتأكد من صحة المعلومات فقط) | نعم |
الفوترة
لن يتم تحصيل أي رسوم إضافية مقابل تفعيل تنفيذ الرمز من خلال Gemini API. سيتم تحصيل الرسوم منك بالسعر الحالي لرموز الإدخال والإخراج استنادًا إلى نموذج Gemini الذي تستخدمه.
في ما يلي بعض المعلومات الأخرى التي يجب معرفتها حول الفوترة مقابل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية:
- يتم تحصيل الرسوم منك مرة واحدة فقط مقابل الرموز المميزة التي يتم إدخالها إلى النموذج، ويتم تحصيل الرسوم منك مقابل الرموز المميزة للناتج النهائي التي يعرضها النموذج.
- يتم احتساب الرموز المميزة التي تمثّل الرمز الذي تم إنشاؤه كرموز مميزة للناتج. يمكن أن يتضمّن الرمز البرمجي الذي تم إنشاؤه نصًا وإخراجًا متعدّد الوسائط، مثل الصور.
- يتم أيضًا احتساب نتائج تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي كرموز مميّزة للناتج.
يظهر نموذج الفوترة في الرسم البياني التالي:
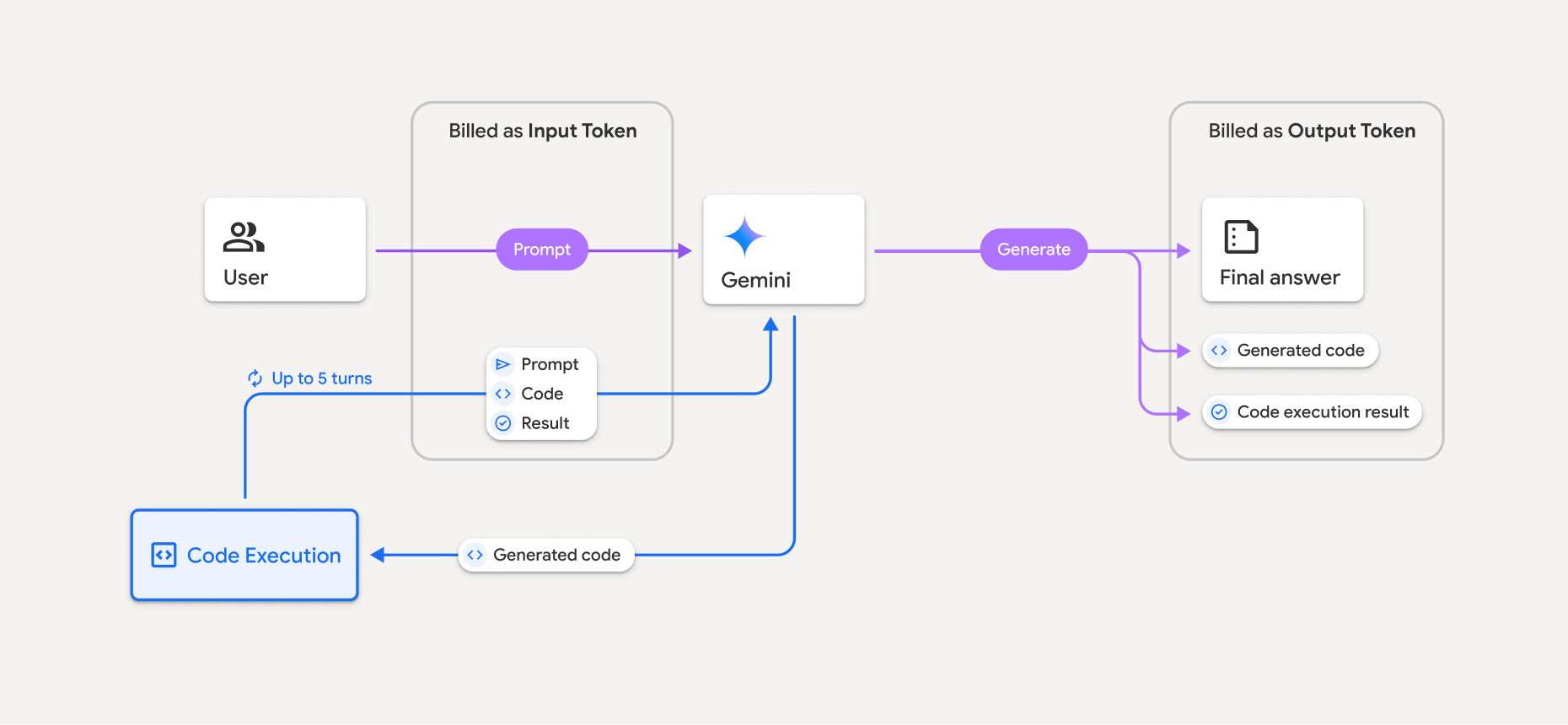
- يتم تحصيل الرسوم منك بالسعر الحالي للرموز المميزة للإدخال والإخراج استنادًا إلى نموذج Gemini الذي تستخدمه.
- إذا استخدم Gemini تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي عند إنشاء ردّك، سيتم تصنيف الطلب الأصلي والرمز البرمجي الذي تم إنشاؤه ونتيجة الرمز البرمجي الذي تم تنفيذه على أنّها رموز مميّزة وسيطة، وسيتم تحصيل الرسوم منها باعتبارها رموزًا مميّزة للإدخال.
- بعد ذلك، ينشئ Gemini ملخّصًا ويعرض الرمز البرمجي الذي تم إنشاؤه ونتيجة الرمز البرمجي الذي تم تنفيذه والملخّص النهائي. تتم فوترة هذه الرموز المميزة على أنّها رموز مميزة للناتج.
- يتضمّن Gemini API عددًا وسيطًا من الرموز المميزة في الردّ من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات، ما يتيح لك معرفة سبب تلقّيك رموزًا مميزة إضافية تتجاوز طلبك الأولي.
القيود
- يمكن للنموذج إنشاء الرموز البرمجية وتنفيذها فقط. ولا يمكنه عرض نتائج أخرى مثل ملفات الوسائط.
- في بعض الحالات، يمكن أن يؤدي تفعيل تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية إلى تراجع في مجالات أخرى من ناتج النموذج (على سبيل المثال، كتابة قصة).
- تتفاوت النماذج المختلفة في قدرتها على تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية بنجاح.
مجموعات الأدوات المتوافقة
يمكن دمج أداة تنفيذ الرمز مع الاستناد إلى "بحث Google" لتعزيز حالات الاستخدام الأكثر تعقيدًا.
المكتبات المتوافقة
تتضمّن بيئة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي المكتبات التالية:
- attrs
- شطرنج
- contourpy
- fpdf
- geopandas
- imageio
- jinja2
- joblib
- jsonschema
- jsonschema-specifications
- lxml
- matplotlib
- mpmath
- numpy
- opencv-python
- openpyxl
- حزمة محتوى التطبيق
- باندا
- وسادة
- protobuf
- pylatex
- pyparsing
- PyPDF2
- python-dateutil
- python-docx
- python-pptx
- reportlab
- scikit-learn
- scipy
- seaborn
- ستة
- striprtf
- sympy
- جدولة
- tensorflow
- toolz
- xlrd
لا يمكنك تثبيت مكتباتك الخاصة.
الخطوات التالية
- جرِّب تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي في Colab.
- مزيد من المعلومات حول أدوات Gemini API الأخرى:
