Gemini API, कोड को चलाने वाला टूल उपलब्ध कराता है. इसकी मदद से मॉडल, Python कोड जनरेट कर सकता है और उसे चला सकता है. इसके बाद, मॉडल कोड को बार-बार एक्ज़ीक्यूट करके, उसके नतीजों से सीख सकता है. ऐसा तब तक किया जाता है, जब तक उसे सही जवाब नहीं मिल जाता. कोड एग्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करके, ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन बनाए जा सकते हैं जिनमें कोड के आधार पर तर्क करने की सुविधा काम करती है. उदाहरण के लिए, समीकरणों को हल करने या टेक्स्ट को प्रोसेस करने के लिए, कोड लागू करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. ज़्यादा खास टास्क पूरे करने के लिए, कोड को लागू करने वाले एनवायरमेंट में शामिल लाइब्रेरी का भी इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
Gemini सिर्फ़ Python में कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट कर सकता है. Gemini से अब भी किसी दूसरी भाषा में कोड जनरेट करने के लिए कहा जा सकता है. हालाँकि, मॉडल इस कोड को चलाने के लिए, कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन टूल का इस्तेमाल नहीं कर सकता.
कोड चलाने की सुविधा चालू करना
कोड चलाने की सुविधा चालू करने के लिए, मॉडल पर कोड चलाने की सुविधा कॉन्फ़िगर करें. इससे मॉडल को कोड जनरेट करने और उसे चलाने की अनुमति मिलती है.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
const parts = response?.candidates?.[0]?.content?.parts || [];
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode && part.executableCode.code) {
console.log(part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult && part.codeExecutionResult.output) {
console.log(part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
});
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
genai.Text("What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."),
config,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d ' {"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": {
"parts":
{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}
},
}'
आउटपुट कुछ ऐसा दिख सकता है. इसे पढ़ने में आसानी हो, इसलिए फ़ॉर्मैट किया गया है:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
इस आउटपुट में, कॉन्टेंट के कई ऐसे हिस्से शामिल होते हैं जिन्हें कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करते समय मॉडल दिखाता है:
text: मॉडल से जनरेट किया गया इनलाइन टेक्स्टexecutableCode: मॉडल से जनरेट किया गया कोड, जिसे एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जाना हैcodeExecutionResult: एक्ज़ीक्यूटेबल कोड का नतीजा
इन हिस्सों के नाम रखने के नियम, प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा के हिसाब से अलग-अलग होते हैं.
इमेज के साथ कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूट करना (Gemini 3)
Gemini 3 Flash मॉडल, अब Python कोड लिख सकता है और उसे एक्ज़ीक्यूट कर सकता है. इससे वह इमेज में बदलाव कर सकता है और उनकी जाँच कर सकता है.
इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण
- ज़ूम करना और बारीकी से देखना: मॉडल अपने-आप यह पता लगाता है कि जानकारी बहुत छोटी कब है.उदाहरण के लिए, दूर से गेज को पढ़ना. इसके बाद, यह उस हिस्से को क्रॉप करने और ज़्यादा रिज़ॉल्यूशन पर फिर से जांच करने के लिए कोड लिखता है.
- विज़ुअल मैथ: मॉडल, कोड का इस्तेमाल करके कई चरणों में हिसाब-किताब कर सकता है. जैसे, रसीद पर मौजूद लाइन आइटम को जोड़ना.
- इमेज एनोटेशन: मॉडल, सवालों के जवाब देने के लिए इमेज को एनोटेट कर सकता है. जैसे, संबंधों को दिखाने के लिए ऐरो बनाना.
इमेज के साथ कोड चलाने की सुविधा चालू करना
Gemini 3 Flash में, इमेज के साथ कोड को आधिकारिक तौर पर इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इस सुविधा को चालू करने के लिए, टूल के तौर पर कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन और सोचने की क्षमता, दोनों को चालू करें.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
from PIL import Image
import io
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
image = types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes, mime_type="image/jpeg"
)
# Ensure you have your API key set
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[image, "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
if part.as_image() is not None:
# display() is a standard function in Jupyter/Colab notebooks
display(Image.open(io.BytesIO(part.as_image().image_bytes)))
JavaScript
async function main() {
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({ });
// 1. Prepare Image Data
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
// 2. Call the API with Code Execution enabled
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
},
{ text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?" }
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
// 3. Process the response (Text, Code, and Execution Results)
const candidates = result.candidates;
if (candidates && candidates[0].content.parts) {
for (const part of candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.text) {
console.log("Text:", part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(`\nGenerated Code (${part.executableCode.language}):\n`, part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(`\nExecution Output (${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}):\n`, part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
}
}
}
main();
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initialize Client (Reads GEMINI_API_KEY from env)
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 1. Download the image
imageResp, err := http.Get("https://goo.gle/instrument-img")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer imageResp.Body.Close()
imageBytes, err := io.ReadAll(imageResp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 2. Configure Code Execution Tool
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
// 3. Generate Content
result, err := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
[]*genai.Content{
{
Parts: []*genai.Part{
{InlineData: &genai.Blob{MIMEType: "image/jpeg", Data: imageBytes}},
{Text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"},
},
Role: "user",
},
},
config,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 4. Parse Response (Text, Code, Output)
for _, cand := range result.Candidates {
for _, part := range cand.Content.Parts {
if part.Text != "" {
fmt.Println("Text:", part.Text)
}
if part.ExecutableCode != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nGenerated Code (%s):\n%s\n",
part.ExecutableCode.Language,
part.ExecutableCode.Code)
}
if part.CodeExecutionResult != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nExecution Output (%s):\n%s\n",
part.CodeExecutionResult.Outcome,
part.CodeExecutionResult.Output)
}
}
}
}
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MODEL="gemini-3-flash-preview"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/$MODEL:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{
"inline_data": {
"mime_type":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
},
{"text": "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"}
]
}],
"tools": [
{
"code_execution": {}
}
]
}'
चैट में कोड चलाने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना
चैट के दौरान भी कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जा सकता है.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
chat = client.chats.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
response = chat.send_message("I have a math question for you.")
print(response.text)
response = chat.send_message(
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import {GoogleGenAI} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
history: [
{
role: "user",
parts: [{ text: "I have a math question for you:" }],
},
{
role: "model",
parts: [{ text: "Great! I'm ready for your math question. Please ask away." }],
},
],
config: {
tools: [{codeExecution:{}}],
}
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({
message: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
});
console.log("Chat response:", response.text);
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
chat, _ := client.Chats.Create(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
config,
nil,
)
result, _ := chat.SendMessage(
ctx,
genai.Part{Text: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and " +
"make sure you get all 50.",
},
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "Can you print \"Hello world!\"?"
}]
},{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": ""
},
{
"executable_code": {
"language": "PYTHON",
"code": "\nprint(\"hello world!\")\n"
}
},
{
"code_execution_result": {
"outcome": "OUTCOME_OK",
"output": "hello world!\n"
}
},
{
"text": "I have printed \"hello world!\" using the provided python code block. \n"
}
],
},{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}]
}
]
}'
इनपुट/आउटपुट (I/O)
Gemini 2.0 Flash से शुरू करके, कोड को चलाने की सुविधा में फ़ाइल इनपुट और ग्राफ़ आउटपुट का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इनपुट और आउटपुट की इन सुविधाओं का इस्तेमाल करके, CSV और टेक्स्ट फ़ाइलें अपलोड की जा सकती हैं. साथ ही, फ़ाइलों के बारे में सवाल पूछे जा सकते हैं. इसके अलावा, जवाब के तौर पर Matplotlib ग्राफ़ जनरेट किए जा सकते हैं. आउटपुट फ़ाइलें, जवाब में इनलाइन इमेज के तौर पर दिखती हैं.
I/O की कीमत
कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन I/O का इस्तेमाल करने पर, आपसे इनपुट टोकन और आउटपुट टोकन के लिए शुल्क लिया जाता है:
इनपुट टोकन:
- उपयोगकर्ता का प्रॉम्प्ट
आउटपुट टोकन:
- मॉडल से जनरेट किया गया कोड
- कोड एनवायरमेंट में कोड चलाने का आउटपुट
- सोचने वाले टोकन
- मॉडल से जनरेट की गई खास जानकारी
I/O की जानकारी
कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन I/O के साथ काम करते समय, यहां दी गई तकनीकी जानकारी का ध्यान रखें:
- कोड एनवायरमेंट का ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा रनटाइम 30 सेकंड होता है.
- अगर कोड एनवायरमेंट में कोई गड़बड़ी होती है, तो मॉडल कोड आउटपुट को फिर से जनरेट करने का फ़ैसला ले सकता है. ऐसा पांच बार तक किया जा सकता है.
- फ़ाइल के इनपुट का ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा साइज़, मॉडल के टोकन विंडो के हिसाब से तय होता है. AI Studio में, Gemini Flash 2.0 का इस्तेमाल करके, इनपुट फ़ाइल का साइज़ ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 10 लाख टोकन हो सकता है. यह साइज़, इनपुट के तौर पर इस्तेमाल की जा सकने वाली टेक्स्ट फ़ाइलों के लिए करीब 2 एमबी होता है. अगर आपने बहुत बड़ी फ़ाइल अपलोड की है, तो AI Studio उसे भेजने की अनुमति नहीं देगा.
- कोड को टेक्स्ट और CSV फ़ाइलों के साथ सबसे अच्छे तरीके से एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जा सकता है.
- इनपुट फ़ाइल को
part.inlineDataयाpart.fileData(Files API के ज़रिए अपलोड की गई) में पास किया जा सकता है. साथ ही, आउटपुट फ़ाइल हमेशाpart.inlineDataके तौर पर दिखाई जाती है.
बिलिंग
Gemini API से कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन की सुविधा चालू करने के लिए, कोई अतिरिक्त शुल्क नहीं लिया जाता. आपसे इनपुट और आउटपुट टोकन के लिए, Gemini मॉडल की मौजूदा दर के हिसाब से शुल्क लिया जाएगा.
कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूट करने के लिए बिलिंग के बारे में यहां कुछ और बातें बताई गई हैं:
- मॉडल को दिए गए इनपुट टोकन के लिए, आपसे सिर्फ़ एक बार शुल्क लिया जाता है. साथ ही, मॉडल से मिले फ़ाइनल आउटपुट टोकन के लिए, आपसे शुल्क लिया जाता है.
- जनरेट किए गए कोड को दिखाने वाले टोकन, आउटपुट टोकन के तौर पर गिने जाते हैं. जनरेट किए गए कोड में टेक्स्ट और इमेज जैसे मल्टीमॉडल आउटपुट शामिल हो सकते हैं.
- कोड को चलाने के नतीजों को भी आउटपुट टोकन के तौर पर गिना जाता है.
बिलिंग मॉडल को इस डायग्राम में दिखाया गया है:
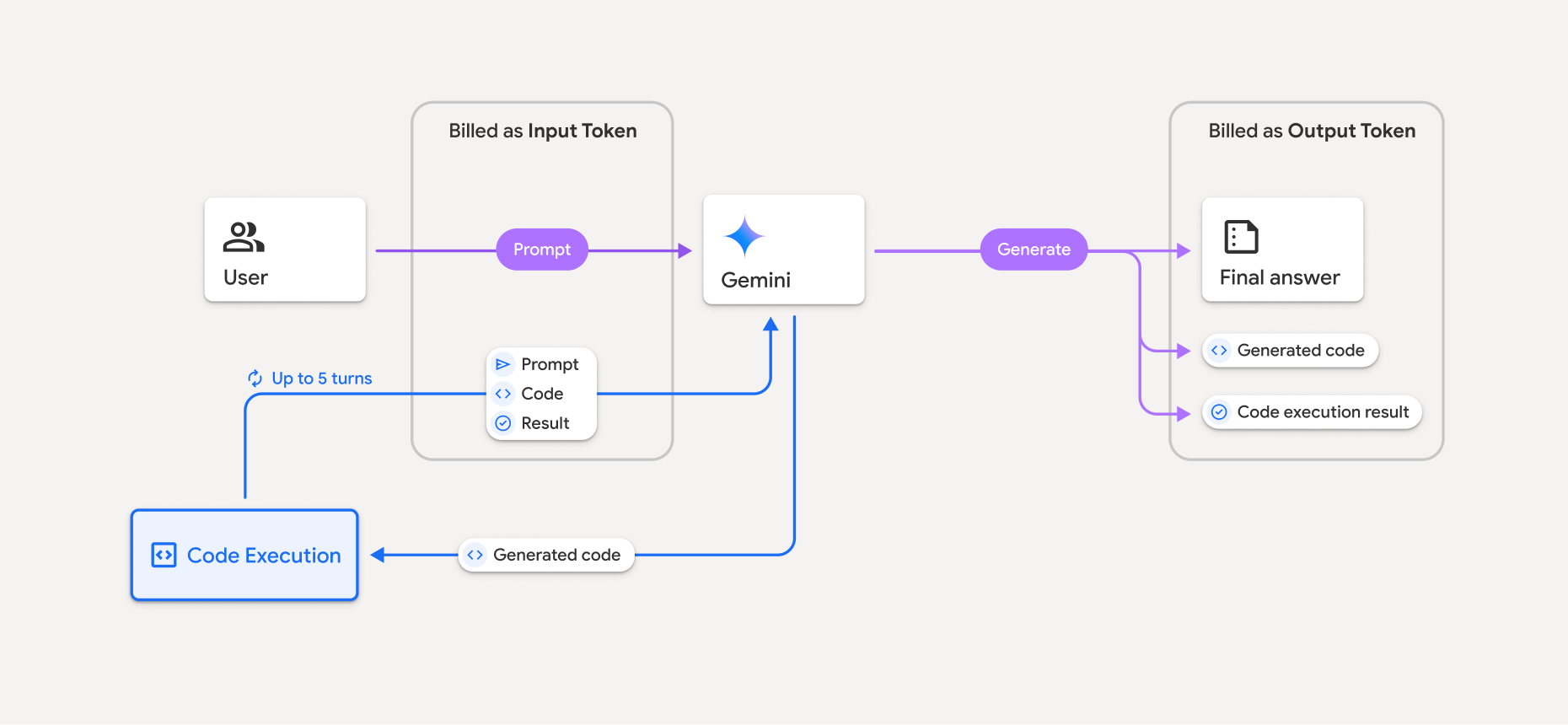
- आपसे इनपुट और आउटपुट टोकन के लिए, Gemini मॉडल के मौजूदा रेट के हिसाब से शुल्क लिया जाता है.
- अगर Gemini, जवाब जनरेट करते समय कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो ओरिजनल प्रॉम्प्ट, जनरेट किया गया कोड, और एक्ज़ीक्यूट किए गए कोड के नतीजे को इंटरमीडिएट टोकन के तौर पर लेबल किया जाता है. साथ ही, इनका बिल इनपुट टोकन के तौर पर भेजा जाता है.
- इसके बाद, Gemini एक खास जानकारी जनरेट करता है. साथ ही, जनरेट किया गया कोड, कोड को चलाने का नतीजा, और खास जानकारी दिखाता है. इनके लिए, आउटपुट टोकन के तौर पर बिल भेजा जाता है.
- Gemini API, एपीआई रिस्पॉन्स में इंटरमीडिएट टोकन की संख्या शामिल करता है, ताकि आपको पता चल सके कि आपको अपने शुरुआती प्रॉम्प्ट के अलावा अतिरिक्त इनपुट टोकन क्यों मिल रहे हैं.
सीमाएं
- यह मॉडल सिर्फ़ कोड जनरेट और एक्ज़ीक्यूट कर सकता है. यह मीडिया फ़ाइलों जैसे अन्य आर्टफ़ैक्ट वापस नहीं ला सकता.
- कुछ मामलों में, कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन की सुविधा चालू करने से, मॉडल के आउटपुट के अन्य हिस्सों में रिग्रेशन हो सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, कहानी लिखना.
- अलग-अलग मॉडल, कोड को सही तरीके से लागू करने की क्षमता में कुछ अंतर होता है.
इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले टूल कॉम्बिनेशन
ज़्यादा पेचीदा इस्तेमाल के मामलों के लिए, कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन टूल को Google Search से मिली जानकारी का इस्तेमाल करने की सुविधा के साथ जोड़ा जा सकता है.
इनके साथ काम करने वाली लाइब्रेरी
कोड को चलाने वाले एनवायरमेंट में ये लाइब्रेरी शामिल हैं:
- attrs
- शतरंज
- contourpy
- fpdf
- geopandas
- imageio
- jinja2
- joblib
- jsonschema
- jsonschema-specifications
- lxml
- matplotlib
- mpmath
- numpy
- opencv-python
- openpyxl
- पैकेजिंग
- पांडा
- तकिया
- protobuf
- pylatex
- pyparsing
- PyPDF2
- python-dateutil
- python-docx
- python-pptx
- reportlab
- scikit-learn
- scipy
- seaborn
- छह
- striprtf
- sympy
- टेबल में व्यवस्थित करना
- tensorflow
- toolz
- xlrd
अपनी लाइब्रेरी इंस्टॉल नहीं की जा सकतीं.
आगे क्या करना है
- कोड लागू करने की सुविधा वाले Colab को आज़माएं.
- Gemini API के अन्य टूल के बारे में जानें:
