The Gemini API enables Retrieval Augmented Generation ("RAG") through the File Search tool. File Search imports, chunks, and indexes your data to enable fast retrieval of relevant information based on a provided prompt. This information is then used as context for the model, allowing the model to provide more accurate and relevant answers.
To make File Search simple and affordable for developers, we're making file storage and embedding generation at query time free of charge. You only pay for creating embeddings when you first index your files (at the applicable embedding model cost) and the normal Gemini model input / output tokens cost. This new billing paradigm makes the File Search Tool both easier and more cost-effective to build and scale with.
Directly upload to File Search store
This examples shows how to directly upload a file to the file search store:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file='sample.txt',
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
config={
'display_name' : 'display-file-name',
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
Check the API reference for uploadToFileSearchStore for more information.
Importing files
Alternatively, you can upload an existing file and import it to your file search store:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
sample_file = client.files.upload(file='sample.txt', config={'name': 'display_file_name'})
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const sampleFile = await ai.files.upload({
file: 'sample.txt',
config: { name: 'file-name' }
});
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation: operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
Check the API reference for importFile for more information.
Chunking configuration
When you import a file into a File Search store, it's automatically broken down
into chunks, embedded, indexed, and uploaded to your File Search store. If you
need more control over the chunking strategy, you can specify a
chunking_config setting
to set a maximum number of tokens per chunk and maximum number of overlapping
tokens.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
config={
'chunking_config': {
'white_space_config': {
'max_tokens_per_chunk': 200,
'max_overlap_tokens': 20
}
}
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
print("Custom chunking complete.")
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
chunkingConfig: {
whiteSpaceConfig: {
maxTokensPerChunk: 200,
maxOverlapTokens: 20
}
}
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
console.log("Custom chunking complete.");
To use your File Search store, pass it as a tool to the generateContent
method, as shown in the Upload and Import examples.
How it works
File Search uses a technique called semantic search to find information relevant to the user prompt. Unlike standard keyword-based search, semantic search understands the meaning and context of your query.
When you import a file, it's converted into numerical representations called embeddings, which capture the semantic meaning of the text. These embeddings are stored in a specialized File Search database. When you make a query, it's also converted into an embedding. Then the system performs a File Search to find the most similar and relevant document chunks from the File Search store.
There is no Time To Live (TTL) for embeddings and files; they persist until manually deleted, or when the model is deprecated.
Here's a breakdown of the process for using the File Search
uploadToFileSearchStore API:
Create a File Search store: A File Search store contains the processed data from your files. It's the persistent container for the embeddings that the semantic search will operate on.
Upload a file and import into a File Search store: Simultaneously upload a file and import the results into your File Search store. This creates a temporary
Fileobject, which is a reference to your raw document. That data is then chunked, converted into File Search embeddings, and indexed. TheFileobject gets deleted after 48 hours, while the data imported into the File Search store will be stored indefinitely until you choose to delete it.Query with File Search: Finally, you use the
FileSearchtool in agenerateContentcall. In the tool configuration, you specify aFileSearchRetrievalResource, which points to theFileSearchStoreyou want to search. This tells the model to perform a semantic search on that specific File Search store to find relevant information to ground its response.
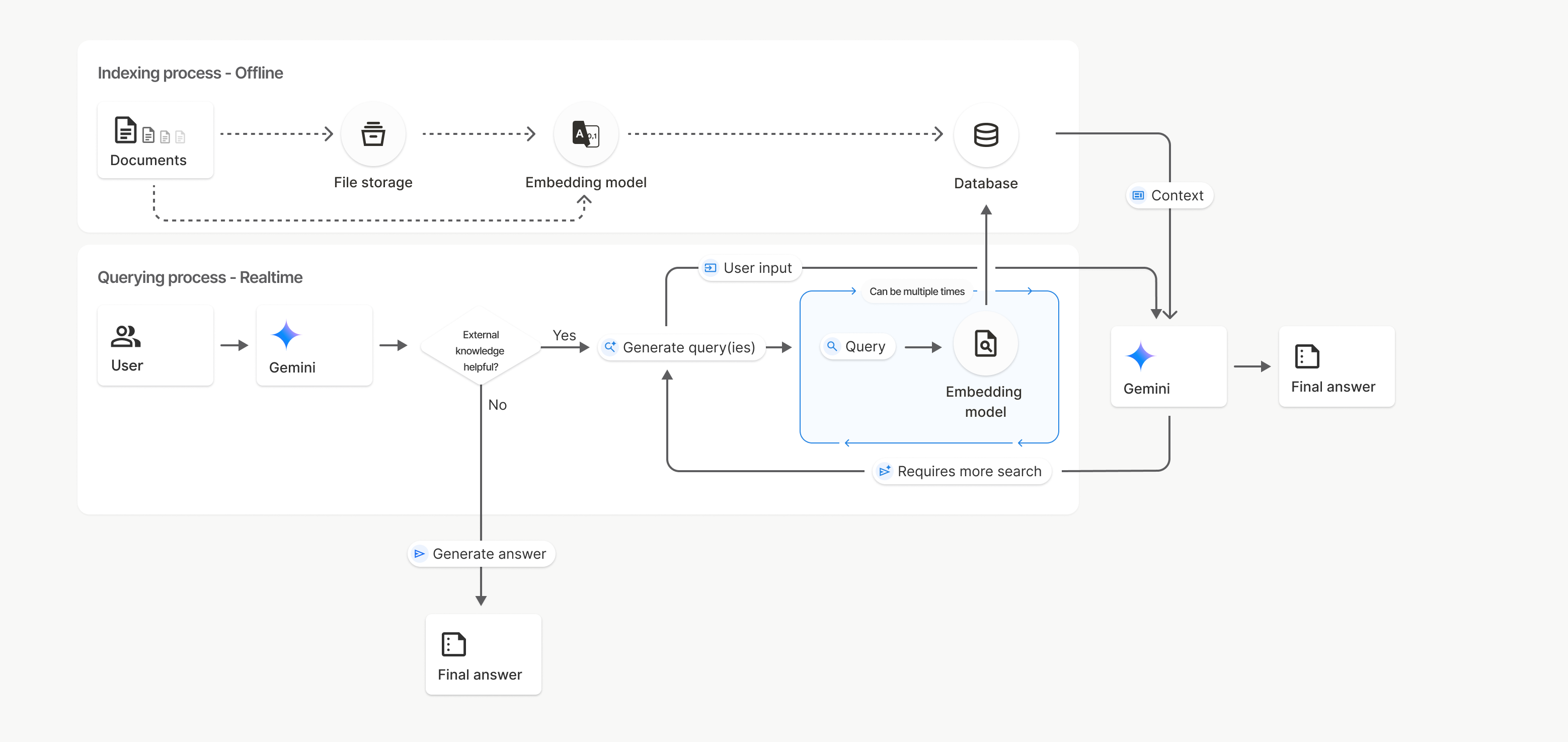
In this diagram, the dotted line from from Documents to Embedding model
(using gemini-embedding-001)
represents the uploadToFileSearchStore API (bypassing File storage).
Otherwise, using the Files API to separately create
and then import files moves the indexing process from Documents to
File storage and then to Embedding model.
File Search stores
A File Search store is a container for your document embeddings. While raw files
uploaded through the File API are deleted after 48 hours, the data imported into
a File Search store is stored indefinitely until you manually delete it. You can
create multiple File Search stores to organize your documents. The
FileSearchStore API lets you create, list, get, and delete to manage your file
search stores. File Search store names are globally scoped.
Here are some examples of how to manage your File Search stores:
Python
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'my-file_search-store-123'})
for file_search_store in client.file_search_stores.list():
print(file_search_store)
my_file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123')
client.file_search_stores.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123', config={'force': True})
JavaScript
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'my-file_search-store-123' }
});
const fileSearchStores = await ai.fileSearchStores.list();
for await (const store of fileSearchStores) {
console.log(store);
}
const myFileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123',
config: { force: true }
});
REST
curl -X POST "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{ "displayName": "My Store" }'
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
File search documents
You can manage individual documents in your file stores with the
File Search Documents API to list each document
in a file search store, get information about a document, and delete a
document by name.
Python
for document_in_store in client.file_search_stores.documents.list(parent='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'):
print(document_in_store)
file_search_document = client.file_search_stores.documents.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
print(file_search_document)
client.file_search_stores.documents.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
JavaScript
const documents = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.list({
parent: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
for await (const doc of documents) {
console.log(doc);
}
const fileSearchDocument = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
File metadata
You can add custom metadata to your files to help filter them or provide additional context. Metadata is a set of key-value pairs.
Python
op = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
custom_metadata=[
{"key": "author", "string_value": "Robert Graves"},
{"key": "year", "numeric_value": 1934}
]
)
JavaScript
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name,
config: {
customMetadata: [
{ key: "author", stringValue: "Robert Graves" },
{ key: "year", numericValue: 1934 }
]
}
});
This is useful when you have multiple documents in a File Search store and want to search only a subset of them.
Python
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name],
metadata_filter="author=Robert Graves",
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name],
metadataFilter: 'author="Robert Graves"',
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[{"text": "Tell me about the book I, Claudius"}]
}],
"tools": [{
"file_search": {
"file_search_store_names":["'$STORE_NAME'"],
"metadata_filter": "author = \"Robert Graves\""
}
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
Guidance on implementing list filter syntax for metadata_filter can be found
at google.aip.dev/160
Citations
When you use File Search, the model's response may include citations that specify which parts of your uploaded documents were used to generate the answer. This helps with fact-checking and verification.
You can access citation information through the grounding_metadata attribute
of the response.
Python
print(response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata)
JavaScript
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.candidates?.[0]?.groundingMetadata, null, 2));
Structured output
Starting with Gemini 3 models, you can combine file search tool with structured outputs.
Python
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Money(BaseModel):
amount: str = Field(description="The numerical part of the amount.")
currency: str = Field(description="The currency of amount.")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
],
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=Money.model_json_schema()
)
)
result = Money.model_validate_json(response.text)
print(result)
JavaScript
import { z } from "zod";
const moneySchema = z.object({
amount: z.string().describe("The numerical part of the amount."),
currency: z.string().describe("The currency of amount."),
});
async function run() {
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [file_search_store.name],
},
},
],
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseJsonSchema: z.toJSONSchema(moneySchema),
},
});
const result = moneySchema.parse(JSON.parse(response.text));
console.log(result);
}
run();
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts": [{"text": "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?"}]
}],
"tools": [
{
"fileSearch": {
"fileSearchStoreNames": ["$FILE_SEARCH_STORE_NAME"]
}
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"responseMimeType": "application/json",
"responseJsonSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "string", "description": "The numerical part of the amount."},
"currency": {"type": "string", "description": "The currency of amount."}
},
"required": ["amount", "currency"]
}
}
}'
Supported models
The following models support File Search:
Supported file types
File Search supports a wide range of file formats, listed in the following sections.
Application file types
application/dartapplication/ecmascriptapplication/jsonapplication/ms-javaapplication/mswordapplication/pdfapplication/sqlapplication/typescriptapplication/vnd.curlapplication/vnd.dartapplication/vnd.ibm.secure-containerapplication/vnd.jupyterapplication/vnd.ms-excelapplication/vnd.oasis.opendocument.textapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentationapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheetapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.documentapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.templateapplication/x-cshapplication/x-hwpapplication/x-hwp-v5application/x-latexapplication/x-phpapplication/x-powershellapplication/x-shapplication/x-shellscriptapplication/x-texapplication/x-zshapplication/xmlapplication/zip
Text file types
text/1d-interleaved-parityfectext/REDtext/SGMLtext/cache-manifesttext/calendartext/cqltext/cql-extensiontext/cql-identifiertext/csstext/csvtext/csv-schematext/dnstext/encaprtptext/enrichedtext/exampletext/fhirpathtext/flexfectext/fwdredtext/gff3text/grammar-ref-listtext/hl7v2text/htmltext/javascripttext/jcr-cndtext/jsxtext/markdowntext/mizartext/n3text/parameterstext/parityfectext/phptext/plaintext/provenance-notationtext/prs.fallenstein.rsttext/prs.lines.tagtext/prs.prop.logictext/raptorfectext/rfc822-headerstext/rtftext/rtp-enc-aescm128text/rtploopbacktext/rtxtext/sgmltext/shaclctext/shextext/spdxtext/stringstext/t140text/tab-separated-valuestext/texmacstext/trofftext/tsvtext/tsxtext/turtletext/ulpfectext/uri-listtext/vcardtext/vnd.DMClientScripttext/vnd.IPTC.NITFtext/vnd.IPTC.NewsMLtext/vnd.atext/vnd.abctext/vnd.ascii-arttext/vnd.curltext/vnd.debian.copyrighttext/vnd.dvb.subtitletext/vnd.esmertec.theme-descriptortext/vnd.exchangeabletext/vnd.familysearch.gedcomtext/vnd.ficlab.flttext/vnd.flytext/vnd.fmi.flexstortext/vnd.gmltext/vnd.graphviztext/vnd.hanstext/vnd.hgltext/vnd.in3d.3dmltext/vnd.in3d.spottext/vnd.latex-ztext/vnd.motorola.reflextext/vnd.ms-mediapackagetext/vnd.net2phone.commcenter.commandtext/vnd.radisys.msml-basic-layouttext/vnd.senx.warpscripttext/vnd.sositext/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptortext/vnd.trolltech.linguisttext/vnd.wap.sitext/vnd.wap.sltext/vnd.wap.wmltext/vnd.wap.wmlscripttext/vtttext/wgsltext/x-asmtext/x-bibtextext/x-bootext/x-ctext/x-c++hdrtext/x-c++srctext/x-cassandratext/x-chdrtext/x-coffeescripttext/x-componenttext/x-cshtext/x-csharptext/x-csrctext/x-cudatext/x-dtext/x-difftext/x-dsrctext/x-emacs-lisptext/x-erlangtext/x-gff3text/x-gotext/x-haskelltext/x-javatext/x-java-propertiestext/x-java-sourcetext/x-kotlintext/x-lilypondtext/x-lisptext/x-literate-haskelltext/x-luatext/x-moctext/x-objcsrctext/x-pascaltext/x-pcs-gcdtext/x-perltext/x-perl-scripttext/x-pythontext/x-python-scripttext/x-r-markdowntext/x-rsrctext/x-rsttext/x-ruby-scripttext/x-rusttext/x-sasstext/x-scalatext/x-schemetext/x-script.pythontext/x-scsstext/x-setexttext/x-sfvtext/x-shtext/x-siestatext/x-sostext/x-sqltext/x-swifttext/x-tcltext/x-textext/x-vbasictext/x-vcalendartext/xmltext/xml-dtdtext/xml-external-parsed-entitytext/yaml
Limitations
- Live API: File Search is not supported in the Live API.
- Tool incompatibility: File Search cannot be combined with other tools like Grounding with Google Search, URL Context, etc. at this time.
Rate limits
The File Search API has the following limits to enforce service stability:
- Maximum file size / per document limit: 100 MB
- Total size of project File Search stores (based on user tier):
- Free: 1 GB
- Tier 1: 10 GB
- Tier 2: 100 GB
- Tier 3: 1 TB
- Recommendation: Limit the size of each File Search store to under 20 GB to ensure optimal retrieval latencies.
Pricing
- Developers are charged for embeddings at indexing time based on existing embeddings pricing ($0.15 per 1M tokens).
- Storage is free of charge.
- Query time embeddings are free of charge.
- Retrieved document tokens are charged as regular context tokens.
What's next
- Visit the API reference for File Search Stores and File Search Documents.
