函式呼叫功能可讓您將模型連結至外部工具和 API。 模型不會生成文字回覆,而是判斷何時該呼叫特定函式,並提供執行實際動作所需的參數。這項技術可讓模型成為自然語言與現實世界動作和資料之間的橋梁。函式呼叫功能有 3 個主要用途:
- 擴增知識:存取資料庫、API 和知識庫等外部來源的資訊。
- 擴充功能:使用外部工具執行運算,並擴充模型限制,例如使用計算機或建立圖表。
- 採取行動:使用 API 與外部系統互動,例如安排預約、建立發票、傳送電子郵件或控制智慧住宅裝置。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function declaration for the model
schedule_meeting_function = {
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting.",
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')",
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')",
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting.",
},
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"],
},
}
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[schedule_meeting_function])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/14/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.",
config=config,
)
# Check for a function call
if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call:
function_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
print(f"Function to call: {function_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {function_call.args}")
# In a real app, you would call your function here:
# result = schedule_meeting(**function_call.args)
else:
print("No function call found in the response.")
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define the function declaration for the model
const scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'schedule_meeting',
description: 'Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
attendees: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
items: { type: Type.STRING },
description: 'List of people attending the meeting.',
},
date: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Date of the meeting (e.g., "2024-07-29")',
},
time: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Time of the meeting (e.g., "15:00")',
},
topic: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'The subject or topic of the meeting.',
},
},
required: ['attendees', 'date', 'time', 'topic'],
},
};
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: 'Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.',
config: {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration]
}],
},
});
// Check for function calls in the response
if (response.functionCalls && response.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = response.functionCalls[0]; // Assuming one function call
console.log(`Function to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
console.log(`Arguments: ${JSON.stringify(functionCall.args)}`);
// In a real app, you would call your actual function here:
// const result = await scheduleMeeting(functionCall.args);
} else {
console.log("No function call found in the response.");
console.log(response.text);
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting."
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')"
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')"
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting."
}
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
函式呼叫的運作方式
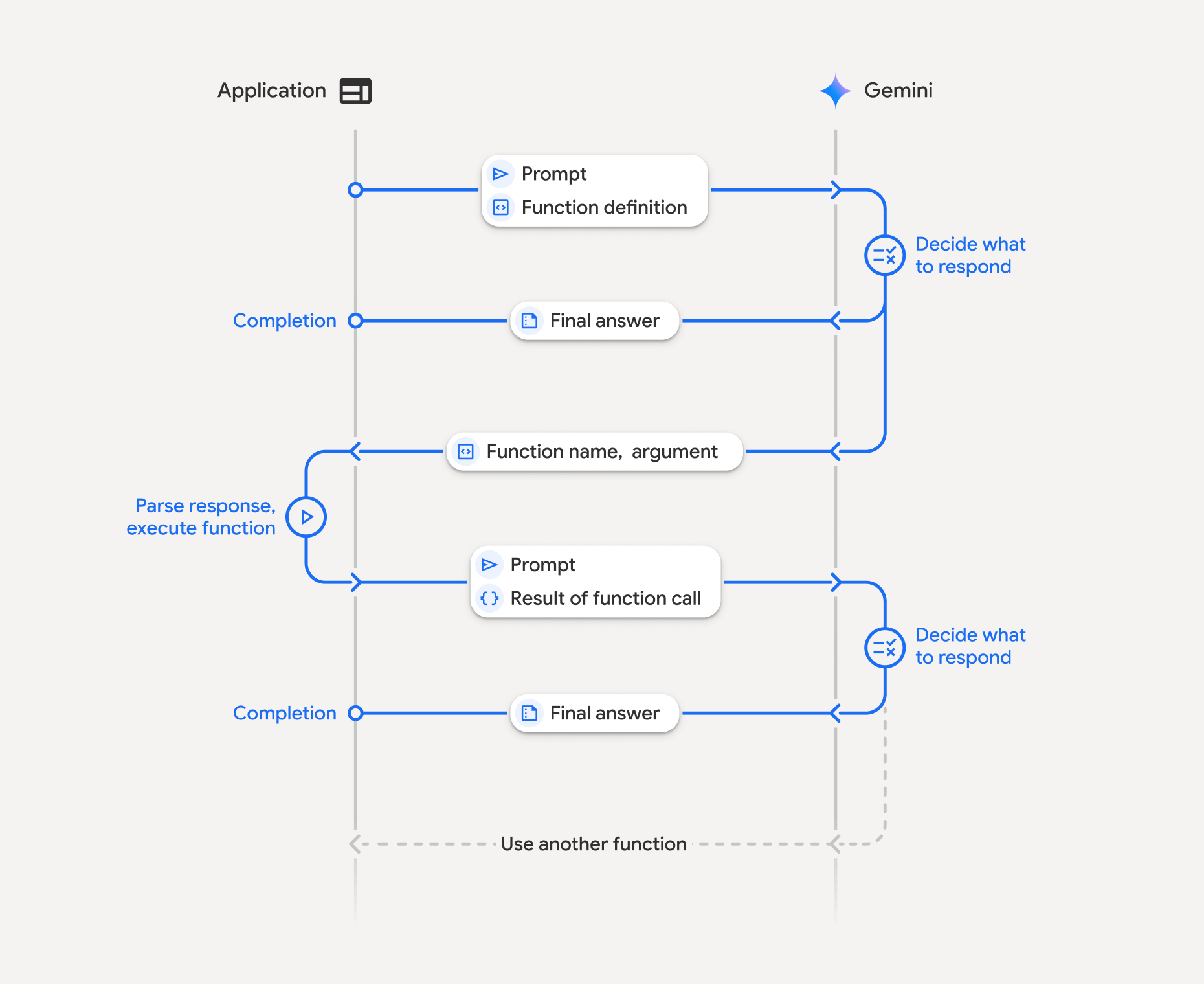
函式呼叫是指應用程式、模型和外部函式之間的結構化互動。以下說明程序中的各個環節:
- 定義函式宣告:在應用程式程式碼中定義函式宣告。函式宣告會向模型說明函式的名稱、參數和用途。
- 使用函式宣告呼叫 LLM:將使用者提示連同函式宣告傳送至模型。這項功能會分析要求,判斷呼叫函式是否有幫助。如果可以,模型會以結構化 JSON 物件回應。
- 執行函式程式碼 (您的責任):模型不會自行執行函式,應用程式有責任處理回應,並檢查是否有函式呼叫。如果
- 是:擷取函式的名稱和引數,並在應用程式中執行對應的函式。
- 否:模型已直接以文字回應提示 (範例中較少強調這個流程,但這是可能結果)。
- 建立友善的回覆:如果執行了函式,請擷取結果,並在後續的對話輪次中傳回模型。並根據結果生成最終回覆,其中會納入函式呼叫中的資訊,方便使用者閱讀。
這個程序可以重複多輪,實現複雜的互動和工作流程。模型也支援在單一回合中呼叫多個函式 (平行函式呼叫),以及依序呼叫 (組合函式呼叫)。
步驟 1:定義函式宣告
在應用程式程式碼中定義函式及其宣告,讓使用者設定燈光值並發出 API 要求。這個函式可能會呼叫外部服務或 API。
Python
# Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
set_light_values_declaration = {
"name": "set_light_values",
"description": "Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness",
},
"color_temp": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"],
"description": "Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.",
},
},
"required": ["brightness", "color_temp"],
},
}
# This is the actual function that would be called based on the model's suggestion
def set_light_values(brightness: int, color_temp: str) -> dict[str, int | str]:
"""Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API).
Args:
brightness: Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
color_temp: Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness, "colorTemperature": color_temp}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
// Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
const setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'set_light_values',
description: 'Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness',
},
color_temp: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm'],
description: 'Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.',
},
},
required: ['brightness', 'color_temp'],
},
};
/**
* Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API)
* @param {number} brightness - Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
* @param {string} color_temp - Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
* @return {Object} A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
*/
function setLightValues(brightness, color_temp) {
return {
brightness: brightness,
colorTemperature: color_temp
};
}
步驟 2:使用函式宣告呼叫模型
定義函式宣告後,您可以提示模型使用這些函式。這項功能會分析提示和函式宣告,然後決定直接回覆或呼叫函式。如果呼叫函式,回應物件會包含函式呼叫建議。
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[set_light_values_declaration])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Define user prompt
contents = [
types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="Turn the lights down to a romantic level")]
)
]
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=contents,
config=config,
)
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Generation config with function declaration
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration]
}]
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define user prompt
const contents = [
{
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: 'Turn the lights down to a romantic level' }]
}
];
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(response.functionCalls[0]);
接著,模型會在與 OpenAPI 相容的結構定義中傳回 functionCall 物件,指定如何呼叫一或多個已宣告的函式,以回覆使用者的問題。
Python
id=None args={'color_temp': 'warm', 'brightness': 25} name='set_light_values'
JavaScript
{
name: 'set_light_values',
args: { brightness: 25, color_temp: 'warm' }
}
步驟 3:執行 set_light_values 函式程式碼
從模型的回應中擷取函式呼叫詳細資料、剖析引數,然後執行 set_light_values 函式。
Python
# Extract tool call details, it may not be in the first part.
tool_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
if tool_call.name == "set_light_values":
result = set_light_values(**tool_call.args)
print(f"Function execution result: {result}")
JavaScript
// Extract tool call details
const tool_call = response.functionCalls[0]
let result;
if (tool_call.name === 'set_light_values') {
result = setLightValues(tool_call.args.brightness, tool_call.args.color_temp);
console.log(`Function execution result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
步驟 4:使用函式結果建立易於理解的回覆,然後再次呼叫模型
最後,將函式執行結果傳回模型,模型就能將這項資訊納入最終回應,傳送給使用者。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Create a function response part
function_response_part = types.Part.from_function_response(
name=tool_call.name,
response={"result": result},
)
# Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.append(response.candidates[0].content) # Append the content from the model's response.
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
client = genai.Client()
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
JavaScript
// Create a function response part
const function_response_part = {
name: tool_call.name,
response: { result }
}
// Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.push(response.candidates[0].content);
contents.push({ role: 'user', parts: [{ functionResponse: function_response_part }] });
// Get the final response from the model
const final_response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(final_response.text);
函式呼叫流程就大功告成。模型已成功使用 set_light_values 函式,執行使用者的要求動作。
函式宣告
在提示中導入函式呼叫時,您會建立 tools 物件,其中包含一或多個 function declarations。您可以使用 JSON 定義函式,具體來說,就是使用 OpenAPI 結構定義格式的選取子集。單一函式宣告可包含下列參數:
name(字串):函式的專屬名稱 (get_weather_forecast、send_email)。請使用不含空格或特殊字元的描述性名稱 (使用底線或駝峰式大小寫)。description(字串):清楚詳細說明函式的用途和功能。這對模型瞭解何時使用函式至關重要。請盡量詳細說明,並視需要提供範例 (「根據地點尋找電影院,並可選擇目前正在電影院上映的電影。」)。parameters(物件):定義函式預期的輸入參數。type(字串):指定整體資料類型,例如object。properties(物件):列出個別參數,每個參數都包含:type(字串):參數的資料類型,例如string、integer、boolean, array。description(字串):參數用途和格式的說明。提供範例和限制 (例如「城市和州別,「加州舊金山」或郵遞區號 (例如 '95616'」。enum(陣列,選用):如果參數值來自固定集合,請使用「enum」列出允許的值,而不是只在說明中描述這些值。這可提升準確度 ("enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"])。
required(陣列):字串陣列,列出函式運作時必須提供的參數名稱。
您也可以使用 types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(client=client, callable=your_function),直接從 Python 函式建構 FunctionDeclarations。
使用思考模型呼叫函式
Gemini 3 和 2.5 系列模型會使用內部「思考」程序來推論要求。這項功能可大幅提升函式呼叫效能,讓模型更準確地判斷何時呼叫函式,以及要使用哪些參數。由於 Gemini API 是無狀態的,模型會使用想法簽章,在多輪對話中維持背景資訊。
本節說明如何進階管理思維簽章,只有在手動建構 API 要求 (例如透過 REST) 或操控對話記錄時,才需要瞭解這項資訊。
如果您使用 Google GenAI SDK (我們的官方程式庫),就不需要管理這個程序。SDK 會自動處理必要步驟,如先前的範例所示。
手動管理對話記錄
如果手動修改對話記錄,而非傳送完整的先前回覆,則必須正確處理模型回合中包含的 thought_signature。
請遵守下列規則,確保模型保留情境:
- 請務必將
thought_signature放回模型內,並放回原始Part。 - 請勿將含有簽章的
Part與不含簽章的Part合併。這會破壞想法的位置脈絡。 - 請勿合併兩個都含有簽章的
Parts,因為簽章字串無法合併。
Gemini 3 思考簽章
在 Gemini 3 中,模型回覆的任何 Part 可能包含想法簽章。一般來說,我們建議從所有 Part 型別傳回簽章,但函式呼叫必須傳回想法簽章。除非您手動操控對話記錄,否則 Google GenAI SDK 會自動處理想法簽章。
如果手動操作對話記錄,請參閱「想法簽章」頁面,取得 Gemini 3 想法簽章的完整處理指南和詳細資料。
檢查想法簽章
雖然實作時不一定需要檢查回應,但您可以檢查回應,以進行偵錯或教育用途。thought_signature
Python
import base64
# After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
# response = client.models.generate_content(...)
# The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0]
if part.thought_signature:
print(base64.b64encode(part.thought_signature).decode("utf-8"))
JavaScript
// After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
// const response = await ai.models.generateContent(...)
// The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
const part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0];
if (part.thoughtSignature) {
console.log(part.thoughtSignature);
}
如要進一步瞭解思維簽章的限制和用途,以及一般思維模型,請參閱「思維」頁面。
平行函式呼叫
除了單次函式呼叫,您也可以一次呼叫多個函式。平行函式呼叫可讓您一次執行多個函式,適用於函式彼此不相依的情況。這在許多情況下都很有用,例如從多個獨立來源收集資料、從不同資料庫擷取客戶詳細資料,或檢查各倉庫的庫存量,以及執行多項動作,例如將公寓改造成迪斯可舞廳。
Python
power_disco_ball = {
"name": "power_disco_ball",
"description": "Powers the spinning disco ball.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"power": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.",
}
},
"required": ["power"],
},
}
start_music = {
"name": "start_music",
"description": "Play some music matching the specified parameters.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"energetic": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is energetic or not.",
},
"loud": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is loud or not.",
},
},
"required": ["energetic", "loud"],
},
}
dim_lights = {
"name": "dim_lights",
"description": "Dim the lights.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.",
}
},
"required": ["brightness"],
},
}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
const powerDiscoBall = {
name: 'power_disco_ball',
description: 'Powers the spinning disco ball.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
power: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.'
}
},
required: ['power']
}
};
const startMusic = {
name: 'start_music',
description: 'Play some music matching the specified parameters.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
energetic: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is energetic or not.'
},
loud: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is loud or not.'
}
},
required: ['energetic', 'loud']
}
};
const dimLights = {
name: 'dim_lights',
description: 'Dim the lights.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.'
}
},
required: ['brightness']
}
};
設定函式呼叫模式,允許使用所有指定的工具。 如要瞭解詳情,請參閱設定函式呼叫。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
house_tools = [
types.Tool(function_declarations=[power_disco_ball, start_music, dim_lights])
]
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=house_tools,
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
disable=True
),
# Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
tool_config=types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(mode='ANY')
),
)
chat = client.chats.create(model="gemini-3-flash-preview", config=config)
response = chat.send_message("Turn this place into a party!")
# Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
print("Example 1: Forced function calling")
for fn in response.function_calls:
args = ", ".join(f"{key}={val}" for key, val in fn.args.items())
print(f"{fn.name}({args})")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Set up function declarations
const houseFns = [powerDiscoBall, startMusic, dimLights];
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: houseFns
}],
// Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
toolConfig: {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: 'any'
}
}
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Create a chat session
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
config: config
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({message: 'Turn this place into a party!'});
// Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
console.log("Example 1: Forced function calling");
for (const fn of response.functionCalls) {
const args = Object.entries(fn.args)
.map(([key, val]) => `${key}=${val}`)
.join(', ');
console.log(`${fn.name}(${args})`);
}
每個列印結果都反映了模型要求的單一函式呼叫。如要傳回結果,請按照要求順序加入回應。
Python SDK 支援自動呼叫函式,可自動將 Python 函式轉換為宣告,並為您處理函式呼叫執行和回應週期。以下是迪斯可用途的範例。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Actual function implementations
def power_disco_ball_impl(power: bool) -> dict:
"""Powers the spinning disco ball.
Args:
power: Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.
Returns:
A status dictionary indicating the current state.
"""
return {"status": f"Disco ball powered {'on' if power else 'off'}"}
def start_music_impl(energetic: bool, loud: bool) -> dict:
"""Play some music matching the specified parameters.
Args:
energetic: Whether the music is energetic or not.
loud: Whether the music is loud or not.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the music settings.
"""
music_type = "energetic" if energetic else "chill"
volume = "loud" if loud else "quiet"
return {"music_type": music_type, "volume": volume}
def dim_lights_impl(brightness: float) -> dict:
"""Dim the lights.
Args:
brightness: The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the new brightness setting.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[power_disco_ball_impl, start_music_impl, dim_lights_impl]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Do everything you need to this place into party!",
config=config,
)
print("\nExample 2: Automatic function calling")
print(response.text)
# I've turned on the disco ball, started playing loud and energetic music, and dimmed the lights to 50% brightness. Let's get this party started!
組合式函式呼叫
組合或循序函式呼叫可讓 Gemini 將多個函式呼叫串連在一起,以完成複雜要求。舉例來說,如要回答「我目前所在位置的溫度」,Gemini API 可能會先叫用 get_current_location() 函式,然後叫用 get_weather() 函式,並將位置資訊做為參數。
以下範例說明如何使用 Python SDK 和自動函式呼叫,實作組合函式呼叫。
Python
本範例使用 google-genai Python SDK 的自動函式呼叫功能。SDK 會自動將 Python 函式轉換為所需結構定義,在模型要求時執行函式呼叫,並將結果傳回模型以完成工作。
import os
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Example Functions
def get_weather_forecast(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current weather temperature for a given location."""
print(f"Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location={location})")
# TODO: Make API call
print("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}")
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "celsius"} # Dummy response
def set_thermostat_temperature(temperature: int) -> dict:
"""Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature."""
print(f"Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature={temperature})")
# TODO: Interact with a thermostat API
print("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configure the client and model
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_weather_forecast, set_thermostat_temperature]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
config=config,
)
# Print the final, user-facing response
print(response.text)
預期輸出內容
執行程式碼時,您會看到 SDK 協調函式呼叫。模型會先呼叫 get_weather_forecast,接收溫度,然後根據提示中的邏輯,以正確值呼叫 set_thermostat_temperature。
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
JavaScript
這個範例說明如何使用 JavaScript/TypeScript SDK,透過手動執行迴圈執行組合函式呼叫。
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from "@google/genai";
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Example Functions
function get_weather_forecast({ location }) {
console.log(`Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=${location})`);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}");
return { temperature: 25, unit: "celsius" };
}
function set_thermostat_temperature({ temperature }) {
console.log(
`Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=${temperature})`,
);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}");
return { status: "success" };
}
const toolFunctions = {
get_weather_forecast,
set_thermostat_temperature,
};
const tools = [
{
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "get_weather_forecast",
description:
"Gets the current weather temperature for a given location.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
location: {
type: Type.STRING,
},
},
required: ["location"],
},
},
{
name: "set_thermostat_temperature",
description: "Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
temperature: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
},
},
required: ["temperature"],
},
},
],
},
];
// Prompt for the model
let contents = [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
},
],
},
];
// Loop until the model has no more function calls to make
while (true) {
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
config: { tools },
});
if (result.functionCalls && result.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = result.functionCalls[0];
const { name, args } = functionCall;
if (!toolFunctions[name]) {
throw new Error(`Unknown function call: ${name}`);
}
// Call the function and get the response.
const toolResponse = toolFunctions[name](args);
const functionResponsePart = {
name: functionCall.name,
response: {
result: toolResponse,
},
};
// Send the function response back to the model.
contents.push({
role: "model",
parts: [
{
functionCall: functionCall,
},
],
});
contents.push({
role: "user",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: functionResponsePart,
},
],
});
} else {
// No more function calls, break the loop.
console.log(result.text);
break;
}
}
預期輸出內容
執行程式碼時,您會看到 SDK 協調函式呼叫。模型會先呼叫 get_weather_forecast,接收溫度,然後根據提示中的邏輯,以正確值呼叫 set_thermostat_temperature。
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. It's 25°C in London, so I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
組合式函式呼叫是 Live API 的原生功能。也就是說,Live API 可以處理函式呼叫,與 Python SDK 類似。
Python
# Light control schemas
turn_on_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_on_the_lights'}
turn_off_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_off_the_lights'}
prompt = """
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
"""
tools = [
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]}
]
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Light control schemas
const turnOnTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_on_the_lights' };
const turnOffTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_off_the_lights' };
const prompt = `
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
`;
const tools = [
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] }
];
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
函式呼叫模式
您可透過 Gemini API 控制模型使用所提供工具 (函式宣告) 的方式。具體來說,您可以在 function_calling_config 中設定模式。
AUTO (Default):模型會根據提示和情境,決定要生成自然語言回應,還是建議呼叫函式。這是最彈性的模式,建議在大多數情況下使用。ANY:模型一律會預測函式呼叫,並保證符合函式結構定義。如果未指定allowed_function_names,模型可以從任何提供的函式宣告中選擇。 如果allowed_function_names是以清單形式提供,模型只能從該清單中的函式選擇。如果需要每則提示 (如適用) 的函式呼叫回應,請使用這個模式。NONE:禁止模型呼叫函式。這相當於傳送要求,但不含任何函式宣告。您可以使用這項功能暫時停用函式呼叫,不必移除工具定義。VALIDATED(預先發布版):模型只能預測函式呼叫或自然語言,並確保符合函式結構定義。如果未提供allowed_function_names,模型會從所有可用的函式宣告中挑選。如果提供allowed_function_names,模型會從允許的函式集中挑選。
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure function calling mode
tool_config = types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(
mode="ANY", allowed_function_names=["get_current_temperature"]
)
)
# Create the generation config
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tools], # not defined here.
tool_config=tool_config,
)
JavaScript
import { FunctionCallingConfigMode } from '@google/genai';
// Configure function calling mode
const toolConfig = {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: FunctionCallingConfigMode.ANY,
allowedFunctionNames: ['get_current_temperature']
}
};
// Create the generation config
const config = {
tools: tools, // not defined here.
toolConfig: toolConfig,
};
自動呼叫函式 (僅限 Python)
使用 Python SDK 時,您可以直接提供 Python 函式做為工具。SDK 會將這些函式轉換為宣告、管理函式呼叫執行作業,並為您處理回應週期。使用型別提示和說明字串定義函式。為獲得最佳結果,建議使用Google 樣式的 docstring。SDK 隨後會自動執行下列操作:
- 偵測模型傳回的函式呼叫回應。
- 在程式碼中呼叫對應的 Python 函式。
- 將函式的回覆傳回模型。
- 傳回模型的最終文字回覆。
SDK 目前不會將引數說明剖析至所產生函式宣告的屬性說明位置。而是將整個 docstring 做為頂層函式說明傳送。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function with type hints and docstring
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current temperature for a given location.
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
Returns:
A dictionary containing the temperature and unit.
"""
# ... (implementation) ...
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "Celsius"}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature]
) # Pass the function itself
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What's the temperature in Boston?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text) # The SDK handles the function call and returns the final text
您可以使用下列程式碼停用自動函式呼叫:
Python
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature],
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(disable=True)
)
自動函式結構定義宣告
這項 API 可說明下列任一類型。只要定義的欄位也由允許的型別組成,即可使用 Pydantic 型別。系統不太支援 Dict 類型 (例如 dict[str: int]),請勿使用。
Python
AllowedType = (
int | float | bool | str | list['AllowedType'] | pydantic.BaseModel)
如要查看推論的結構定義,可以使用 from_callable 進行轉換:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
"""Returns a * b."""
return a * b
client = genai.Client()
fn_decl = types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(callable=multiply, client=client)
# to_json_dict() provides a clean JSON representation.
print(fn_decl.to_json_dict())
使用多種工具:結合原生工具與函式呼叫
您可以同時啟用多項工具,將原生工具與函式呼叫功能結合使用。以下範例說明如何使用 Live API,在要求中啟用「以 Google 搜尋為基礎」和「程式碼執行」這兩項工具。
Python
# Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
prompt = """
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
"""
tools = [
{'google_search': {}},
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]} # not defined here.
]
# Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
const prompt = `
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
`;
const tools = [
{ googleSearch: {} },
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] } // not defined here.
];
// Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, {tools: tools, modality: "AUDIO"});
Python 開發人員可以在 Live API Tool Use 筆記本中試用這項功能。
多模態函式回應
如果是 Gemini 3 系列模型,您可以在傳送給模型的回覆部分中加入多模態內容。模型可以在下一個回合處理這類多模態內容,進而生成更實用的回覆。函式回應中的多模態內容支援下列 MIME 類型:
- 圖片:
image/png、image/jpeg、image/webp - 文件:
application/pdf、text/plain
如要在函式回覆中加入多模態資料,請將資料做為一或多個部分,巢狀內嵌在 functionResponse 部分中。每個多模態部分都必須包含 inlineData。如果您從結構化 response 欄位中參照多模態部分,該欄位必須包含不重複的 displayName。
您也可以使用 JSON 參照格式 {"$ref": "<displayName>"},從 functionResponse 部分的結構化 response 欄位中參照多模態部分。模型會在處理回覆時,以多模態內容取代參照。每個 displayName 在結構化 response 欄位中只能參照一次。
以下範例顯示的訊息包含名為 get_image 的函式 functionResponse,以及包含圖片資料和 displayName: "instrument.jpg" 的巢狀部分。functionResponse's response 欄位會參照這個圖片部分:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
client = genai.Client()
# This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
# 1. Define the function tool
get_image_declaration = types.FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_image",
description="Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"item_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument')."
}
},
"required": ["item_name"],
},
)
tool_config = types.Tool(function_declarations=[get_image_declaration])
# 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
prompt = "Show me the instrument I ordered last month."
response_1 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
)
)
# 3. Handle the function call
function_call = response_1.function_calls[0]
requested_item = function_call.args["item_name"]
print(f"Model wants to call: {function_call.name}")
# Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
# (This is a mock response for the example)
print(f"Calling external tool for: {requested_item}")
function_response_data = {
"image_ref": {"$ref": "instrument.jpg"},
}
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
function_response_multimodal_data = types.FunctionResponsePart(
inline_data=types.FunctionResponseBlob(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
display_name="instrument.jpg",
data=image_bytes,
)
)
# 4. Send the tool's result back
# Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
history = [
types.Content(role="user", parts=[types.Part(text=prompt)]),
response_1.candidates[0].content,
types.Content(
role="tool",
parts=[
types.Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response=function_response_data,
parts=[function_response_multimodal_data]
)
],
)
]
response_2 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=history,
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(include_thoughts=True)
),
)
print(f"\nFinal model response: {response_2.text}")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
const client = new GoogleGenAI({ apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY });
// This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
// 1. Define the function tool
const getImageDeclaration = {
name: 'get_image',
description: 'Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
item_name: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument').",
},
},
required: ['item_name'],
},
};
const toolConfig = {
functionDeclarations: [getImageDeclaration],
};
// 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
const prompt = 'Show me the instrument I ordered last month.';
const response1 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: prompt,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
},
});
// 3. Handle the function call
const functionCall = response1.functionCalls[0];
const requestedItem = functionCall.args.item_name;
console.log(`Model wants to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
// Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
// (This is a mock response for the example)
console.log(`Calling external tool for: ${requestedItem}`);
const functionResponseData = {
image_ref: { $ref: 'instrument.jpg' },
};
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
const functionResponseMultimodalData = {
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
displayName: 'instrument.jpg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
};
// 4. Send the tool's result back
// Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
const history = [
{ role: 'user', parts: [{ text: prompt }] },
response1.candidates[0].content,
{
role: 'tool',
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: functionResponseData,
parts: [functionResponseMultimodalData],
},
},
],
},
];
const response2 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: history,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
thinkingConfig: { includeThoughts: true },
},
});
console.log(`\nFinal model response: ${response2.text}`);
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
# Check for macOS
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
...,
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_image",
"response": {
"image_ref": {
"$ref": "instrument.jpg"
}
},
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"displayName": "instrument.jpg",
"mimeType":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
使用結構化輸出內容進行函式呼叫
對於 Gemini 3 系列模型,您可以搭配結構化輸出內容使用函式呼叫功能。這可讓模型預測符合特定結構定義的函式呼叫或輸出內容。因此,模型未產生函式呼叫時,您會收到格式一致的回覆。
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 是一項開放標準,可將 AI 應用程式連結至外部工具和資料。MCP 提供通用協定,供模型存取脈絡,例如函式 (工具)、資料來源 (資源) 或預先定義的提示。
Gemini SDK 內建 MCP 支援功能,可減少樣板程式碼,並為 MCP 工具提供自動工具呼叫功能。模型產生 MCP 工具呼叫時,Python 和 JavaScript 用戶端 SDK 會自動執行 MCP 工具,並在後續要求中將回應傳回模型,持續這個迴圈,直到模型不再進行工具呼叫為止。
您可以在這裡找到如何搭配使用本機 MCP 伺服器與 Gemini 和 mcp SDK 的範例。
Python
請確認您已在所選平台上安裝最新版 mcp SDK。
pip install mcp
import os
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
# Create server parameters for stdio connection
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="npx", # Executable
args=["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"], # MCP Server
env=None, # Optional environment variables
)
async def run():
async with stdio_client(server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read, write) as session:
# Prompt to get the weather for the current day in London.
prompt = f"What is the weather in London in {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}?"
# Initialize the connection between client and server
await session.initialize()
# Send request to the model with MCP function declarations
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=prompt,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0,
tools=[session], # uses the session, will automatically call the tool
# Uncomment if you **don't** want the SDK to automatically call the tool
# automatic_function_calling=genai.types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
# disable=True
# ),
),
)
print(response.text)
# Start the asyncio event loop and run the main function
asyncio.run(run())
JavaScript
請確認您已在所選平台上安裝最新版 mcp SDK。
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StdioClientTransport({
command: "npx", // Executable
args: ["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"] // MCP Server
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection
await client.close();
內建 MCP 支援的限制
SDK 內建的 MCP 支援是實驗性功能,有下列限制:
- 僅支援工具,不支援資源或提示
- 適用於 Python 和 JavaScript/TypeScript SDK。
- 未來版本可能會出現重大變更。
如果這些限制會影響您建構的內容,您隨時可以手動整合 MCP 伺服器。
支援的模型
本節列出模型及其函式呼叫功能。不含實驗模型。如需完整的功能總覽,請參閱模型總覽頁面。
| 型號 | 函式呼叫 | 平行函式呼叫 | 組合式函式呼叫 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite | X | X | X |
最佳做法
- 函式和參數說明:說明內容務必清楚明確。模型會根據這些資訊選擇正確的函式,並提供適當的引數。
- 命名:使用描述性函式名稱 (不含空格、句點或破折號)。
- 嚴格型別:為參數使用特定型別 (整數、字串、列舉),以減少錯誤。如果參數的有效值有限,請使用列舉。
- 工具選取:模型可使用任意數量的工具,但如果提供過多工具,選取錯誤或次佳工具的風險就會增加。為獲得最佳結果,請盡量只提供與情境或工作相關的工具,最好將有效工具組維持在最多 10 到 20 個。如果工具總數較多,請考慮根據對話內容動態選取工具。
- 提示工程:
- 提供脈絡:告知模型其角色 (例如「你是實用的天氣助理。」)。
- 提供指示:指定函式的使用方式和時機 (例如 「請勿猜測日期,預測時一律使用未來日期。」)。
- 鼓勵釐清:視需要指示模型提出問題釐清狀況。
- 如要進一步瞭解如何設計這些提示,請參閱「Agentic workflows」。以下是經過測試的系統指令範例。
溫度:使用低溫 (例如 0),確保函式呼叫作業更具決定性且可靠。
驗證:如果函式呼叫會造成重大後果 (例如下單),請先向使用者驗證呼叫,再執行呼叫。
檢查完成原因:請務必檢查模型回覆中的
finishReason,處理模型無法產生有效函式呼叫的情況。錯誤處理:在函式中導入完善的錯誤處理機制,以便妥善處理非預期的輸入內容或 API 失敗情形。回傳資訊豐富的錯誤訊息,供模型用來生成對使用者有幫助的回覆。
安全性:呼叫外部 API 時,請注意安全性。使用適當的驗證和授權機制。避免在函式呼叫中公開機密資料。
權杖限制:函式說明和參數會計入輸入權杖限制。如果達到權杖上限,請考慮限制函式數量或說明長度,並將複雜工作分解為較小、更專注的函式集。
注意事項和限制
- 系統僅支援部分 OpenAPI 架構。
- 如果是
ANY模式,API 可能會拒絕過大或深度巢狀結構的結構定義。如果發生錯誤,請縮短屬性名稱、減少巢狀結構或限制函式宣告數量,簡化函式參數和回應結構定義。 - Python 支援的參數類型有限。
- 自動函式呼叫功能僅適用於 Python SDK。
