فراخوانی تابع به شما امکان میدهد مدلها را به ابزارها و APIهای خارجی متصل کنید. به جای تولید پاسخهای متنی، مدل زمان فراخوانی توابع خاص را تعیین میکند و پارامترهای لازم را برای اجرای اقدامات دنیای واقعی فراهم میکند. این امر به مدل اجازه میدهد تا به عنوان پلی بین زبان طبیعی و اقدامات و دادههای دنیای واقعی عمل کند. فراخوانی تابع دارای ۳ مورد استفاده اصلی است:
- افزایش دانش: دسترسی به اطلاعات از منابع خارجی مانند پایگاههای داده، APIها و پایگاههای دانش.
- گسترش قابلیتها: از ابزارهای خارجی برای انجام محاسبات و گسترش محدودیتهای مدل، مانند استفاده از ماشین حساب یا ایجاد نمودار، استفاده کنید.
- اقدامات لازم: با استفاده از APIها با سیستمهای خارجی تعامل داشته باشید، مانند برنامهریزی قرار ملاقاتها، ایجاد فاکتورها، ارسال ایمیل یا کنترل دستگاههای خانه هوشمند.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function declaration for the model
schedule_meeting_function = {
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting.",
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')",
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')",
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting.",
},
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"],
},
}
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[schedule_meeting_function])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/14/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.",
config=config,
)
# Check for a function call
if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call:
function_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
print(f"Function to call: {function_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {function_call.args}")
# In a real app, you would call your function here:
# result = schedule_meeting(**function_call.args)
else:
print("No function call found in the response.")
print(response.text)
جاوا اسکریپت
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define the function declaration for the model
const scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'schedule_meeting',
description: 'Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
attendees: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
items: { type: Type.STRING },
description: 'List of people attending the meeting.',
},
date: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Date of the meeting (e.g., "2024-07-29")',
},
time: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Time of the meeting (e.g., "15:00")',
},
topic: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'The subject or topic of the meeting.',
},
},
required: ['attendees', 'date', 'time', 'topic'],
},
};
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: 'Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.',
config: {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration]
}],
},
});
// Check for function calls in the response
if (response.functionCalls && response.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = response.functionCalls[0]; // Assuming one function call
console.log(`Function to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
console.log(`Arguments: ${JSON.stringify(functionCall.args)}`);
// In a real app, you would call your actual function here:
// const result = await scheduleMeeting(functionCall.args);
} else {
console.log("No function call found in the response.");
console.log(response.text);
}
استراحت
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting."
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')"
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')"
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting."
}
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
نحوه فراخوانی تابع
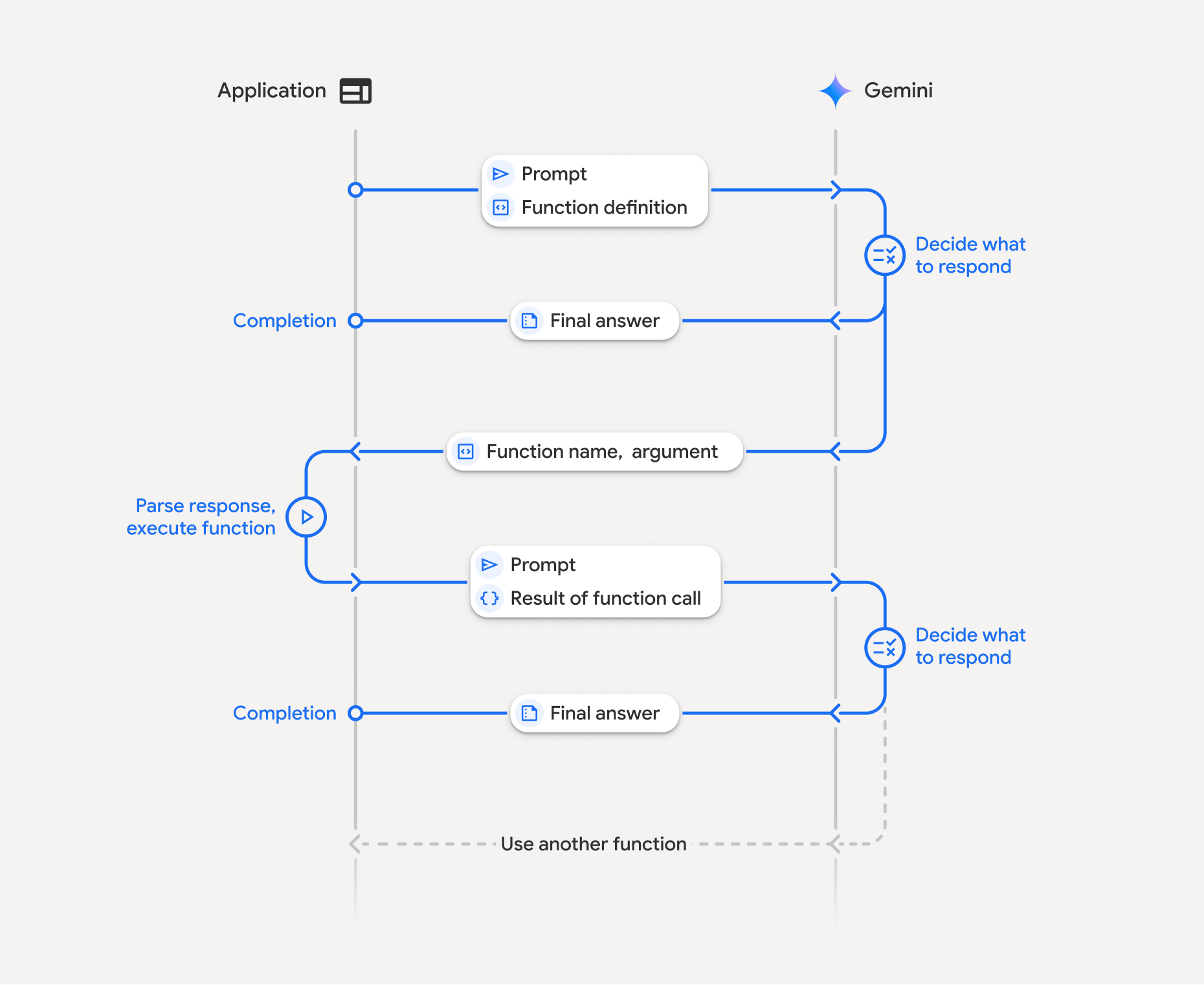
فراخوانی تابع شامل یک تعامل ساختاریافته بین برنامه شما، مدل و توابع خارجی است. در اینجا خلاصهای از این فرآیند آمده است:
- تعریف اعلان تابع: اعلان تابع را در کد برنامه خود تعریف کنید. اعلانهای تابع، نام، پارامترها و هدف تابع را برای مدل توصیف میکنند.
- فراخوانی LLM با اعلان تابع: ارسال اعلان کاربر به همراه اعلان تابع (های) تعریف شده برای مدل. این درخواست را تجزیه و تحلیل میکند و تعیین میکند که آیا فراخوانی تابع مفید خواهد بود یا خیر. در این صورت، با یک شیء JSON ساختار یافته پاسخ میدهد.
- اجرای کد تابع (مسئولیت شما): مدل خود تابع را اجرا نمیکند . این مسئولیت برنامه شماست که پاسخ را پردازش کند و در صورت وجود فراخوانی تابع، آن را بررسی کند.
- بله : نام و آرگومانهای تابع را استخراج کرده و تابع مربوطه را در برنامه خود اجرا کنید.
- خیر: مدل یک پاسخ متنی مستقیم به سوال ارائه داده است (این جریان در مثال کمتر مورد تأکید قرار گرفته است، اما یک نتیجه احتمالی است).
- ایجاد پاسخ کاربرپسند: اگر تابعی اجرا شده باشد، نتیجه را ثبت کرده و در نوبت بعدی مکالمه به مدل ارسال میکند. مدل از نتیجه برای تولید یک پاسخ نهایی و کاربرپسند که شامل اطلاعات حاصل از فراخوانی تابع است، استفاده خواهد کرد.
این فرآیند میتواند در چندین نوبت تکرار شود و امکان تعاملات و گردشهای کاری پیچیده را فراهم کند. این مدل همچنین از فراخوانی چندین تابع در یک نوبت ( فراخوانی تابع موازی ) و به ترتیب ( فراخوانی تابع ترکیبی ) پشتیبانی میکند.
مرحله ۱: تعریف یک تابع
یک تابع و اعلان آن را در کد برنامه خود تعریف کنید که به کاربران اجازه میدهد مقادیر سبک را تنظیم کرده و یک درخواست API ارسال کنند. این تابع میتواند سرویسهای خارجی یا APIها را فراخوانی کند.
پایتون
# Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
set_light_values_declaration = {
"name": "set_light_values",
"description": "Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness",
},
"color_temp": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"],
"description": "Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.",
},
},
"required": ["brightness", "color_temp"],
},
}
# This is the actual function that would be called based on the model's suggestion
def set_light_values(brightness: int, color_temp: str) -> dict[str, int | str]:
"""Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API).
Args:
brightness: Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
color_temp: Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness, "colorTemperature": color_temp}
جاوا اسکریپت
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
// Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
const setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'set_light_values',
description: 'Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness',
},
color_temp: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm'],
description: 'Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.',
},
},
required: ['brightness', 'color_temp'],
},
};
/**
* Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API)
* @param {number} brightness - Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
* @param {string} color_temp - Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
* @return {Object} A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
*/
function setLightValues(brightness, color_temp) {
return {
brightness: brightness,
colorTemperature: color_temp
};
}
مرحله ۲: فراخوانی مدل با اعلان توابع
پس از تعریف اعلانهای تابع، میتوانید مدل را وادار به استفاده از آنها کنید. مدل اعلانها و اعلانهای تابع را تجزیه و تحلیل میکند و تصمیم میگیرد که آیا مستقیماً پاسخ دهد یا یک تابع را فراخوانی کند. اگر تابعی فراخوانی شود، شیء پاسخ شامل یک پیشنهاد فراخوانی تابع خواهد بود.
پایتون
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[set_light_values_declaration])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Define user prompt
contents = [
types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="Turn the lights down to a romantic level")]
)
]
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=contents,
config=config,
)
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call)
جاوا اسکریپت
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Generation config with function declaration
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration]
}]
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define user prompt
const contents = [
{
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: 'Turn the lights down to a romantic level' }]
}
];
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(response.functionCalls[0]);
سپس مدل یک شیء functionCall را در یک طرح سازگار با OpenAPI برمیگرداند که نحوه فراخوانی یک یا چند تابع اعلام شده را برای پاسخ به سوال کاربر مشخص میکند.
پایتون
id=None args={'color_temp': 'warm', 'brightness': 25} name='set_light_values'
جاوا اسکریپت
{
name: 'set_light_values',
args: { brightness: 25, color_temp: 'warm' }
}
مرحله ۳: اجرای کد تابع set_light_values
جزئیات فراخوانی تابع را از پاسخ مدل استخراج کنید، آرگومانها را تجزیه کنید و تابع set_light_values را اجرا کنید.
پایتون
# Extract tool call details, it may not be in the first part.
tool_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
if tool_call.name == "set_light_values":
result = set_light_values(**tool_call.args)
print(f"Function execution result: {result}")
جاوا اسکریپت
// Extract tool call details
const tool_call = response.functionCalls[0]
let result;
if (tool_call.name === 'set_light_values') {
result = setLightValues(tool_call.args.brightness, tool_call.args.color_temp);
console.log(`Function execution result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
مرحله ۴: ایجاد پاسخ کاربرپسند با نتیجه تابع و فراخوانی مجدد مدل
در نهایت، نتیجه اجرای تابع را به مدل ارسال کنید تا بتواند این اطلاعات را در پاسخ نهایی خود به کاربر بگنجاند.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Create a function response part
function_response_part = types.Part.from_function_response(
name=tool_call.name,
response={"result": result},
)
# Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.append(response.candidates[0].content) # Append the content from the model's response.
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
client = genai.Client()
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
جاوا اسکریپت
// Create a function response part
const function_response_part = {
name: tool_call.name,
response: { result }
}
// Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.push(response.candidates[0].content);
contents.push({ role: 'user', parts: [{ functionResponse: function_response_part }] });
// Get the final response from the model
const final_response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(final_response.text);
این، جریان فراخوانی تابع را کامل میکند. مدل با موفقیت از تابع set_light_values برای انجام عمل درخواست کاربر استفاده کرد.
اعلانهای تابع
وقتی فراخوانی تابع را در یک اعلان پیادهسازی میکنید، یک شیء tools ایجاد میکنید که شامل یک یا چند function declarations است. توابع را با استفاده از JSON، به طور خاص با یک زیرمجموعه انتخابی از قالب طرحواره OpenAPI ، تعریف میکنید. یک اعلان تابع واحد میتواند شامل پارامترهای زیر باشد:
-
name(رشته): یک نام منحصر به فرد برای تابع (get_weather_forecast،send_email). از نامهای توصیفی بدون فاصله یا کاراکترهای خاص استفاده کنید (از زیرخط یا camelCase استفاده کنید). -
description(رشته): توضیحی واضح و مفصل از هدف و قابلیتهای تابع. این برای مدل بسیار مهم است که بفهمد چه زمانی از تابع استفاده کند. دقیق باشید و در صورت مفید بودن، مثالهایی ارائه دهید ("سینماها را بر اساس موقعیت مکانی و در صورت تمایل عنوان فیلمی که در حال حاضر در سینماها در حال پخش است، پیدا میکند."). -
parameters(شیء): پارامترهای ورودی مورد انتظار تابع را تعریف میکند.-
type(رشته): نوع داده کلی، مانندobjectرا مشخص میکند. -
properties(شیء): پارامترهای جداگانه را فهرست میکند که هر کدام شامل موارد زیر است:-
type(رشته): نوع داده پارامتر، مانندstring،integer،boolean, array. -
description(رشته): توضیحی در مورد هدف و قالب پارامتر. مثالها و محدودیتها را ارائه دهید ("شهر و ایالت، مثلاً 'سانفرانسیسکو، کالیفرنیا' یا کد پستی، مثلاً '95616'."). -
enum(آرایه، اختیاری): اگر مقادیر پارامترها از یک مجموعه ثابت هستند، به جای اینکه فقط آنها را در توضیحات توضیح دهید، از "enum" برای فهرست کردن مقادیر مجاز استفاده کنید. این کار دقت را بهبود میبخشد ("enum": ["نور روز"، "خنک"، "گرم"]).
-
-
required(آرایه): آرایهای از رشتهها که نام پارامترهایی را که برای عملکرد تابع اجباری هستند، فهرست میکند.
-
شما همچنین میتوانید FunctionDeclarations مستقیماً از توابع پایتون با استفاده types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(client=client, callable=your_function) بسازید.
فراخوانی تابع با مدلهای تفکر
مدلهای سری Gemini 3 و 2.5 از یک فرآیند «تفکر» داخلی برای استدلال از طریق درخواستها استفاده میکنند. این امر به طور قابل توجهی عملکرد فراخوانی تابع را بهبود میبخشد و به مدل اجازه میدهد تا بهتر تعیین کند چه زمانی یک تابع را فراخوانی کند و از کدام پارامترها استفاده کند. از آنجا که API Gemini بدون وضعیت است، مدلها از امضاهای فکری برای حفظ زمینه در مکالمات چند نوبتی استفاده میکنند.
این بخش مدیریت پیشرفته امضاهای فکری را پوشش میدهد و فقط در صورتی ضروری است که شما به صورت دستی درخواستهای API (مثلاً از طریق REST) ایجاد میکنید یا سابقه مکالمه را دستکاری میکنید.
اگر از SDK های Google GenAI (کتابخانه های رسمی ما) استفاده می کنید، نیازی به مدیریت این فرآیند ندارید . SDK ها به طور خودکار مراحل لازم را انجام می دهند، همانطور که در مثال قبلی نشان داده شده است.
مدیریت دستی تاریخچه مکالمات
اگر تاریخچه مکالمه را به صورت دستی تغییر دهید، به جای ارسال پاسخ کامل قبلی، باید به درستی thought_signature موجود در نوبت مدل را مدیریت کنید.
برای اطمینان از حفظ بافت مدل، این قوانین را دنبال کنید:
- همیشه
thought_signatureرا به مدل درونPartاصلی آن برگردانید. -
Partکه حاوی امضا است را با بخشی که امضا ندارد ادغام نکنید. این کار زمینهی مکانیِ فکر را از بین میبرد. - دو
Partsکه هر دو حاوی امضا هستند را با هم ترکیب نکنید، زیرا رشتههای امضا قابل ادغام نیستند.
امضاهای فکری Gemini 3
در Gemini 3، هر Part از پاسخ مدل ممکن است حاوی یک امضای فکری باشد. در حالی که ما معمولاً بازگرداندن امضاها از همه انواع Part را توصیه میکنیم، ارسال امضاهای فکری برای فراخوانی تابع الزامی است. مگر اینکه سابقه مکالمه را به صورت دستی دستکاری کنید، Google GenAI SDK امضاهای فکری را به طور خودکار مدیریت میکند.
اگر تاریخچه مکالمات را به صورت دستی دستکاری میکنید، برای راهنمایی کامل و جزئیات مربوط به مدیریت امضاهای فکری برای Gemini 3 به صفحه امضاهای فکری مراجعه کنید.
بررسی امضاهای فکری
اگرچه برای پیادهسازی ضروری نیست، میتوانید پاسخ را بررسی کنید تا thought_signature را برای اشکالزدایی یا اهداف آموزشی ببینید.
پایتون
import base64
# After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
# response = client.models.generate_content(...)
# The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0]
if part.thought_signature:
print(base64.b64encode(part.thought_signature).decode("utf-8"))
جاوا اسکریپت
// After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
// const response = await ai.models.generateContent(...)
// The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
const part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0];
if (part.thoughtSignature) {
console.log(part.thoughtSignature);
}
برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد محدودیتها و کاربردهای امضاهای فکری، و بهطورکلی در مورد مدلهای تفکر، به صفحه تفکر مراجعه کنید.
فراخوانی موازی توابع
علاوه بر فراخوانی تابع تک نوبتی، میتوانید چندین تابع را نیز به طور همزمان فراخوانی کنید. فراخوانی تابع موازی به شما امکان میدهد چندین تابع را به طور همزمان اجرا کنید و زمانی استفاده میشود که توابع به یکدیگر وابسته نباشند. این در سناریوهایی مانند جمعآوری دادهها از چندین منبع مستقل، مانند بازیابی جزئیات مشتری از پایگاههای داده مختلف یا بررسی سطح موجودی در انبارهای مختلف یا انجام چندین عمل مانند تبدیل آپارتمان خود به یک دیسکو مفید است.
پایتون
power_disco_ball = {
"name": "power_disco_ball",
"description": "Powers the spinning disco ball.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"power": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.",
}
},
"required": ["power"],
},
}
start_music = {
"name": "start_music",
"description": "Play some music matching the specified parameters.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"energetic": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is energetic or not.",
},
"loud": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is loud or not.",
},
},
"required": ["energetic", "loud"],
},
}
dim_lights = {
"name": "dim_lights",
"description": "Dim the lights.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.",
}
},
"required": ["brightness"],
},
}
جاوا اسکریپت
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
const powerDiscoBall = {
name: 'power_disco_ball',
description: 'Powers the spinning disco ball.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
power: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.'
}
},
required: ['power']
}
};
const startMusic = {
name: 'start_music',
description: 'Play some music matching the specified parameters.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
energetic: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is energetic or not.'
},
loud: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is loud or not.'
}
},
required: ['energetic', 'loud']
}
};
const dimLights = {
name: 'dim_lights',
description: 'Dim the lights.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.'
}
},
required: ['brightness']
}
};
حالت فراخوانی تابع را طوری پیکربندی کنید که امکان استفاده از تمام ابزارهای مشخص شده را فراهم کند. برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر، میتوانید درباره پیکربندی فراخوانی تابع مطالعه کنید.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
house_tools = [
types.Tool(function_declarations=[power_disco_ball, start_music, dim_lights])
]
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=house_tools,
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
disable=True
),
# Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
tool_config=types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(mode='ANY')
),
)
chat = client.chats.create(model="gemini-3-flash-preview", config=config)
response = chat.send_message("Turn this place into a party!")
# Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
print("Example 1: Forced function calling")
for fn in response.function_calls:
args = ", ".join(f"{key}={val}" for key, val in fn.args.items())
print(f"{fn.name}({args})")
جاوا اسکریپت
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Set up function declarations
const houseFns = [powerDiscoBall, startMusic, dimLights];
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: houseFns
}],
// Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
toolConfig: {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: 'any'
}
}
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Create a chat session
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
config: config
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({message: 'Turn this place into a party!'});
// Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
console.log("Example 1: Forced function calling");
for (const fn of response.functionCalls) {
const args = Object.entries(fn.args)
.map(([key, val]) => `${key}=${val}`)
.join(', ');
console.log(`${fn.name}(${args})`);
}
هر یک از نتایج چاپ شده، منعکس کننده یک فراخوانی تابع واحد است که مدل درخواست کرده است. برای ارسال مجدد نتایج، پاسخها را به همان ترتیبی که درخواست شدهاند، وارد کنید.
کیت توسعه نرمافزار پایتون (SDK) از فراخوانی خودکار تابع پشتیبانی میکند، که به طور خودکار توابع پایتون را به اعلان تبدیل میکند، اجرای فراخوانی تابع و چرخه پاسخ را برای شما مدیریت میکند. در ادامه مثالی برای مورد استفاده دیسکو آورده شده است.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Actual function implementations
def power_disco_ball_impl(power: bool) -> dict:
"""Powers the spinning disco ball.
Args:
power: Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.
Returns:
A status dictionary indicating the current state.
"""
return {"status": f"Disco ball powered {'on' if power else 'off'}"}
def start_music_impl(energetic: bool, loud: bool) -> dict:
"""Play some music matching the specified parameters.
Args:
energetic: Whether the music is energetic or not.
loud: Whether the music is loud or not.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the music settings.
"""
music_type = "energetic" if energetic else "chill"
volume = "loud" if loud else "quiet"
return {"music_type": music_type, "volume": volume}
def dim_lights_impl(brightness: float) -> dict:
"""Dim the lights.
Args:
brightness: The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the new brightness setting.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[power_disco_ball_impl, start_music_impl, dim_lights_impl]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Do everything you need to this place into party!",
config=config,
)
print("\nExample 2: Automatic function calling")
print(response.text)
# I've turned on the disco ball, started playing loud and energetic music, and dimmed the lights to 50% brightness. Let's get this party started!
فراخوانی تابع ترکیبی
فراخوانی توابع ترکیبی یا ترتیبی به Gemini اجازه میدهد تا چندین تابع را به صورت زنجیرهای فراخوانی کند تا یک درخواست پیچیده را انجام دهد. برای مثال، برای پاسخ به "دریافت دمای مکان فعلی من"، API Gemini ممکن است ابتدا یک تابع get_current_location() و به دنبال آن یک تابع get_weather() را فراخوانی کند که مکان را به عنوان پارامتر میگیرد.
مثال زیر نحوه پیادهسازی فراخوانی توابع ترکیبی با استفاده از SDK پایتون و فراخوانی خودکار توابع را نشان میدهد.
پایتون
این مثال از ویژگی فراخوانی خودکار تابع در SDK پایتون google-genai استفاده میکند. SDK به طور خودکار توابع پایتون را به طرح مورد نیاز تبدیل میکند، فراخوانیهای تابع را در صورت درخواست مدل اجرا میکند و نتایج را برای تکمیل کار به مدل ارسال میکند.
import os
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Example Functions
def get_weather_forecast(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current weather temperature for a given location."""
print(f"Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location={location})")
# TODO: Make API call
print("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}")
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "celsius"} # Dummy response
def set_thermostat_temperature(temperature: int) -> dict:
"""Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature."""
print(f"Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature={temperature})")
# TODO: Interact with a thermostat API
print("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configure the client and model
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_weather_forecast, set_thermostat_temperature]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
config=config,
)
# Print the final, user-facing response
print(response.text)
خروجی مورد انتظار
وقتی کد را اجرا میکنید، خواهید دید که SDK فراخوانیهای تابع را هماهنگ میکند. مدل ابتدا get_weather_forecast را فراخوانی میکند، دما را دریافت میکند و سپس set_thermostat_temperature را با مقدار صحیح بر اساس منطق موجود در اعلان فراخوانی میکند.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
جاوا اسکریپت
این مثال نحوه استفاده از SDK جاوااسکریپت/تایپاسکریپت را برای فراخوانی توابع ترکیبی با استفاده از یک حلقه اجرای دستی نشان میدهد.
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from "@google/genai";
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Example Functions
function get_weather_forecast({ location }) {
console.log(`Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=${location})`);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}");
return { temperature: 25, unit: "celsius" };
}
function set_thermostat_temperature({ temperature }) {
console.log(
`Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=${temperature})`,
);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}");
return { status: "success" };
}
const toolFunctions = {
get_weather_forecast,
set_thermostat_temperature,
};
const tools = [
{
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "get_weather_forecast",
description:
"Gets the current weather temperature for a given location.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
location: {
type: Type.STRING,
},
},
required: ["location"],
},
},
{
name: "set_thermostat_temperature",
description: "Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
temperature: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
},
},
required: ["temperature"],
},
},
],
},
];
// Prompt for the model
let contents = [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
},
],
},
];
// Loop until the model has no more function calls to make
while (true) {
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
config: { tools },
});
if (result.functionCalls && result.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = result.functionCalls[0];
const { name, args } = functionCall;
if (!toolFunctions[name]) {
throw new Error(`Unknown function call: ${name}`);
}
// Call the function and get the response.
const toolResponse = toolFunctions[name](args);
const functionResponsePart = {
name: functionCall.name,
response: {
result: toolResponse,
},
};
// Send the function response back to the model.
contents.push({
role: "model",
parts: [
{
functionCall: functionCall,
},
],
});
contents.push({
role: "user",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: functionResponsePart,
},
],
});
} else {
// No more function calls, break the loop.
console.log(result.text);
break;
}
}
خروجی مورد انتظار
وقتی کد را اجرا میکنید، خواهید دید که SDK فراخوانیهای تابع را هماهنگ میکند. مدل ابتدا get_weather_forecast را فراخوانی میکند، دما را دریافت میکند و سپس set_thermostat_temperature را با مقدار صحیح بر اساس منطق موجود در اعلان فراخوانی میکند.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. It's 25°C in London, so I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
فراخوانی توابع ترکیبی یک ویژگی بومی Live API است. این بدان معناست که Live API میتواند فراخوانی توابع را مشابه SDK پایتون مدیریت کند.
پایتون
# Light control schemas
turn_on_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_on_the_lights'}
turn_off_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_off_the_lights'}
prompt = """
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
"""
tools = [
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]}
]
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
جاوا اسکریپت
// Light control schemas
const turnOnTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_on_the_lights' };
const turnOffTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_off_the_lights' };
const prompt = `
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
`;
const tools = [
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] }
];
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
حالتهای فراخوانی تابع
رابط برنامهنویسی کاربردی Gemini به شما امکان میدهد نحوه استفاده مدل از ابزارهای ارائه شده (اعلانهای تابع) را کنترل کنید. به طور خاص، میتوانید حالت را در فایل function_calling_config تنظیم کنید.
-
AUTO (Default): مدل تصمیم میگیرد که آیا یک پاسخ زبان طبیعی تولید کند یا بر اساس اعلان و متن، فراخوانی تابع را پیشنهاد دهد. این حالت انعطافپذیرترین حالت است و برای اکثر سناریوها توصیه میشود. -
ANY: مدل ملزم به پیشبینی فراخوانی تابع است و پیروی از طرحواره تابع را تضمین میکند. اگرallowed_function_namesمشخص نشده باشد، مدل میتواند از هر یک از اعلانهای تابع ارائه شده انتخاب کند. اگرallowed_function_namesبه عنوان یک لیست ارائه شده باشد، مدل فقط میتواند از توابع موجود در آن لیست انتخاب کند. از این حالت زمانی استفاده کنید که به پاسخ فراخوانی تابع برای هر اعلان (در صورت وجود) نیاز دارید. -
NONE: مدل از فراخوانی توابع منع شده است. این معادل ارسال درخواست بدون تعریف هیچ تابعی است. از این برای غیرفعال کردن موقت فراخوانی توابع بدون حذف تعاریف ابزار خود استفاده کنید. VALIDATED(پیشنمایش): مدل محدود به پیشبینی فراخوانیهای تابع یا زبان طبیعی است و از پایبندی به طرحواره تابع اطمینان حاصل میکند. اگرallowed_function_namesارائه نشده باشد، مدل از تمام اعلانهای تابع موجود انتخاب میکند. اگرallowed_function_namesارائه شده باشد، مدل از مجموعه توابع مجاز انتخاب میکند.
پایتون
from google.genai import types
# Configure function calling mode
tool_config = types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(
mode="ANY", allowed_function_names=["get_current_temperature"]
)
)
# Create the generation config
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tools], # not defined here.
tool_config=tool_config,
)
جاوا اسکریپت
import { FunctionCallingConfigMode } from '@google/genai';
// Configure function calling mode
const toolConfig = {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: FunctionCallingConfigMode.ANY,
allowedFunctionNames: ['get_current_temperature']
}
};
// Create the generation config
const config = {
tools: tools, // not defined here.
toolConfig: toolConfig,
};
فراخوانی خودکار تابع (فقط پایتون)
هنگام استفاده از SDK پایتون، میتوانید توابع پایتون را مستقیماً به عنوان ابزار ارائه دهید. SDK این توابع را به اعلان تبدیل میکند، اجرای فراخوانی تابع را مدیریت میکند و چرخه پاسخ را برای شما مدیریت میکند. تابع خود را با نکات نوع و یک رشته سند تعریف کنید. برای نتایج بهینه، توصیه میشود از رشتههای سند به سبک گوگل استفاده کنید. سپس SDK به طور خودکار:
- پاسخهای فراخوانی تابع را از مدل تشخیص دهید.
- تابع پایتون مربوطه را در کد خود فراخوانی کنید.
- پاسخ تابع را به مدل ارسال کن.
- پاسخ متنی نهایی مدل را برمیگرداند.
SDK در حال حاضر توضیحات آرگومانها را در جایگاههای توضیحات ویژگیِ تعریف تابع تولید شده تجزیه نمیکند. در عوض، کل رشتهی سند (docstring) را به عنوان توضیحات تابع سطح بالا ارسال میکند.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function with type hints and docstring
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current temperature for a given location.
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
Returns:
A dictionary containing the temperature and unit.
"""
# ... (implementation) ...
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "Celsius"}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature]
) # Pass the function itself
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What's the temperature in Boston?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text) # The SDK handles the function call and returns the final text
شما میتوانید فراخوانی خودکار تابع را با دستور زیر غیرفعال کنید:
پایتون
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature],
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(disable=True)
)
اعلان خودکار طرحواره تابع
این API قادر به توصیف هر یک از انواع زیر است. انواع Pydantic مجاز هستند، مادامی که فیلدهای تعریف شده روی آنها نیز از انواع مجاز تشکیل شده باشند. انواع Dict (مانند dict[str: int] ) در اینجا به خوبی پشتیبانی نمیشوند، از آنها استفاده نکنید.
پایتون
AllowedType = (
int | float | bool | str | list['AllowedType'] | pydantic.BaseModel)
برای دیدن اینکه طرحواره استنباط شده چگونه به نظر میرسد، میتوانید آن را با استفاده از from_callable تبدیل کنید:
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
"""Returns a * b."""
return a * b
client = genai.Client()
fn_decl = types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(callable=multiply, client=client)
# to_json_dict() provides a clean JSON representation.
print(fn_decl.to_json_dict())
استفاده چند ابزاری: ابزارهای بومی را با فراخوانی تابع ترکیب کنید
شما میتوانید چندین ابزار را با ترکیب ابزارهای بومی و فراخوانی تابع به طور همزمان فعال کنید. در اینجا مثالی آورده شده است که دو ابزار، Grounding with Google Search و code execution ، را در یک درخواست با استفاده از Live API فعال میکند.
پایتون
# Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
prompt = """
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
"""
tools = [
{'google_search': {}},
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]} # not defined here.
]
# Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
جاوا اسکریپت
// Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
const prompt = `
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
`;
const tools = [
{ googleSearch: {} },
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] } // not defined here.
];
// Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, {tools: tools, modality: "AUDIO"});
توسعهدهندگان پایتون میتوانند این را در دفترچه یادداشت Live API Tool Use امتحان کنند.
پاسخهای تابع چندوجهی
برای مدلهای سری Gemini 3، میتوانید محتوای چندوجهی را در بخشهای پاسخ تابعی که به مدل ارسال میکنید، بگنجانید. مدل میتواند این محتوای چندوجهی را در نوبت بعدی خود پردازش کند تا پاسخی آگاهانهتر تولید کند. انواع MIME زیر برای محتوای چندوجهی در پاسخهای تابع پشتیبانی میشوند:
- تصاویر :
image/png،image/jpeg،image/webp - اسناد :
application/pdf،text/plain
برای گنجاندن دادههای چندوجهی در پاسخ یک تابع، آن را به صورت یک یا چند بخش تو در تو در بخش functionResponse قرار دهید. هر بخش چندوجهی باید شامل inlineData باشد. اگر به یک بخش چندوجهی از درون فیلد response ساختاریافته ارجاع میدهید، باید حاوی یک displayName منحصر به فرد باشد.
همچنین میتوانید با استفاده از قالب ارجاع JSON {"$ref": "<displayName>"} ، از درون فیلد response ساختاریافتهی بخش functionResponse به یک بخش چندوجهی ارجاع دهید. مدل هنگام پردازش پاسخ، ارجاع را با محتوای چندوجهی جایگزین میکند. هر displayName فقط میتواند یک بار در فیلد response ساختاریافته ارجاع داده شود.
مثال زیر پیامی را نشان میدهد که حاوی یک functionResponse برای تابعی به نام get_image و یک بخش تو در تو حاوی دادههای تصویری با displayName: "instrument.jpg" است. فیلد response functionResponse به این بخش تصویر اشاره میکند:
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
client = genai.Client()
# This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
# 1. Define the function tool
get_image_declaration = types.FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_image",
description="Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"item_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument')."
}
},
"required": ["item_name"],
},
)
tool_config = types.Tool(function_declarations=[get_image_declaration])
# 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
prompt = "Show me the instrument I ordered last month."
response_1 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
)
)
# 3. Handle the function call
function_call = response_1.function_calls[0]
requested_item = function_call.args["item_name"]
print(f"Model wants to call: {function_call.name}")
# Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
# (This is a mock response for the example)
print(f"Calling external tool for: {requested_item}")
function_response_data = {
"image_ref": {"$ref": "instrument.jpg"},
}
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
function_response_multimodal_data = types.FunctionResponsePart(
inline_data=types.FunctionResponseBlob(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
display_name="instrument.jpg",
data=image_bytes,
)
)
# 4. Send the tool's result back
# Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
history = [
types.Content(role="user", parts=[types.Part(text=prompt)]),
response_1.candidates[0].content,
types.Content(
role="tool",
parts=[
types.Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response=function_response_data,
parts=[function_response_multimodal_data]
)
],
)
]
response_2 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=history,
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(include_thoughts=True)
),
)
print(f"\nFinal model response: {response_2.text}")
جاوا اسکریپت
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
const client = new GoogleGenAI({ apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY });
// This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
// 1. Define the function tool
const getImageDeclaration = {
name: 'get_image',
description: 'Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
item_name: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument').",
},
},
required: ['item_name'],
},
};
const toolConfig = {
functionDeclarations: [getImageDeclaration],
};
// 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
const prompt = 'Show me the instrument I ordered last month.';
const response1 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: prompt,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
},
});
// 3. Handle the function call
const functionCall = response1.functionCalls[0];
const requestedItem = functionCall.args.item_name;
console.log(`Model wants to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
// Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
// (This is a mock response for the example)
console.log(`Calling external tool for: ${requestedItem}`);
const functionResponseData = {
image_ref: { $ref: 'instrument.jpg' },
};
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
const functionResponseMultimodalData = {
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
displayName: 'instrument.jpg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
};
// 4. Send the tool's result back
// Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
const history = [
{ role: 'user', parts: [{ text: prompt }] },
response1.candidates[0].content,
{
role: 'tool',
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: functionResponseData,
parts: [functionResponseMultimodalData],
},
},
],
},
];
const response2 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: history,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
thinkingConfig: { includeThoughts: true },
},
});
console.log(`\nFinal model response: ${response2.text}`);
استراحت
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
# Check for macOS
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
...,
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_image",
"response": {
"image_ref": {
"$ref": "instrument.jpg"
}
},
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"displayName": "instrument.jpg",
"mimeType":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
فراخوانی تابع با خروجی ساختاریافته
برای مدلهای سری Gemini 3، میتوانید از فراخوانی تابع با خروجی ساختاریافته استفاده کنید. این به مدل اجازه میدهد تا فراخوانیهای تابع یا خروجیهایی را که به یک طرحواره خاص پایبند هستند، پیشبینی کند. در نتیجه، وقتی مدل فراخوانیهای تابع ایجاد نمیکند، پاسخهای با قالببندی ثابتی دریافت میکنید.
پروتکل زمینه مدل (MCP)
پروتکل زمینه مدل (MCP) یک استاندارد باز برای اتصال برنامههای هوش مصنوعی با ابزارها و دادههای خارجی است. MCP یک پروتکل مشترک برای مدلها فراهم میکند تا به زمینه، مانند توابع (ابزارها)، منابع داده (منابع) یا اعلانهای از پیش تعریف شده، دسترسی داشته باشند.
کیتهای توسعه نرمافزار (SDK) جمینی (Gemini) از MCP پشتیبانی داخلی دارند که باعث کاهش کدهای تکراری و ارائه فراخوانی خودکار ابزار برای ابزارهای MCP میشود. هنگامی که مدل یک فراخوانی ابزار MCP ایجاد میکند، SDK کلاینت پایتون و جاوا اسکریپت میتواند به طور خودکار ابزار MCP را اجرا کرده و پاسخ را در درخواست بعدی به مدل ارسال کند و این حلقه را تا زمانی که دیگر هیچ فراخوانی ابزاری توسط مدل انجام نشود، ادامه دهد.
در اینجا میتوانید مثالی از نحوه استفاده از یک سرور محلی MCP با Gemini و mcp SDK را بیابید.
پایتون
مطمئن شوید که آخرین نسخه mcp SDK روی پلتفرم مورد نظر شما نصب شده است.
pip install mcp
import os
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
# Create server parameters for stdio connection
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="npx", # Executable
args=["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"], # MCP Server
env=None, # Optional environment variables
)
async def run():
async with stdio_client(server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read, write) as session:
# Prompt to get the weather for the current day in London.
prompt = f"What is the weather in London in {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}?"
# Initialize the connection between client and server
await session.initialize()
# Send request to the model with MCP function declarations
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=prompt,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0,
tools=[session], # uses the session, will automatically call the tool
# Uncomment if you **don't** want the SDK to automatically call the tool
# automatic_function_calling=genai.types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
# disable=True
# ),
),
)
print(response.text)
# Start the asyncio event loop and run the main function
asyncio.run(run())
جاوا اسکریپت
مطمئن شوید که آخرین نسخه mcp SDK روی پلتفرم مورد نظر شما نصب شده است.
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StdioClientTransport({
command: "npx", // Executable
args: ["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"] // MCP Server
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection
await client.close();
محدودیتهای پشتیبانی داخلی MCP
پشتیبانی داخلی MCP یک ویژگی آزمایشی در SDK های ما است و محدودیتهای زیر را دارد:
- فقط ابزارها پشتیبانی میشوند، نه منابع و نه اعلانها
- این ابزار برای SDK پایتون و جاوا اسکریپت/تایپ اسکریپت در دسترس است.
- ممکن است در نسخههای آینده تغییرات اساسی رخ دهد.
اگر سرورهای MCP ساخت شما را محدود میکنند، ادغام دستی آنها همیشه یک گزینه است.
مدلهای پشتیبانیشده
این بخش مدلها و قابلیتهای فراخوانی تابع آنها را فهرست میکند. مدلهای آزمایشی شامل نمیشوند. میتوانید یک مرور کلی از قابلیتها را در صفحه مرور مدل پیدا کنید.
| مدل | فراخوانی تابع | فراخوانی موازی توابع | فراخوانی توابع ترکیبی |
|---|---|---|---|
| جمینی ۳ پرو | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| فلش جمینی ۳ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| جمینی ۲.۵ پرو | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| فلش جمینی ۲.۵ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| جمینی ۲.۵ فلش-لایت | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| فلش جمینی ۲.۰ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| جمینی ۲.۰ فلش-لایت | ایکس | ایکس | ایکس |
بهترین شیوهها
- توضیحات تابع و پارامتر: در توضیحات خود بسیار واضح و مشخص باشید. مدل برای انتخاب تابع صحیح و ارائه آرگومانهای مناسب به این توضیحات متکی است.
- نامگذاری: از نامهای توصیفی برای توابع استفاده کنید (بدون فاصله، نقطه یا خط تیره).
- تایپ قوی: برای کاهش خطاها از انواع خاص (عدد صحیح، رشته، شمارشی) برای پارامترها استفاده کنید. اگر یک پارامتر مجموعه محدودی از مقادیر معتبر دارد، از شمارشی استفاده کنید.
- انتخاب ابزار: اگرچه مدل میتواند از تعداد دلخواهی ابزار استفاده کند، اما ارائه تعداد زیاد ابزار میتواند خطر انتخاب ابزار نادرست یا غیربهینه را افزایش دهد. برای بهترین نتیجه، سعی کنید فقط ابزارهای مرتبط با زمینه یا وظیفه را ارائه دهید، در حالت ایدهآل، مجموعه فعال را حداکثر ۱۰ تا ۲۰ ابزار نگه دارید. اگر تعداد کل ابزارهای شما زیاد است، انتخاب پویای ابزار را بر اساس زمینه مکالمه در نظر بگیرید.
- مهندسی سریع:
- زمینه را فراهم کنید: نقش مدل را به او بگویید (مثلاً «شما یک دستیار هواشناسی مفید هستید.»).
- دستورالعملها را ارائه دهید: نحوه و زمان استفاده از توابع را مشخص کنید (مثلاً «تاریخها را حدس نزنید؛ همیشه از تاریخ آینده برای پیشبینیها استفاده کنید.»).
- تشویق به شفافسازی: به مدل آموزش دهید که در صورت نیاز، سوالات شفافسازی بپرسد.
- برای استراتژیهای بیشتر در طراحی این دستورالعملها، به گردشهای کاری Agentic مراجعه کنید. در اینجا مثالی از یک دستورالعمل سیستمی آزمایششده آورده شده است.
دما: برای فراخوانی توابع قطعیتر و قابل اعتمادتر، از دمای پایین (مثلاً 0) استفاده کنید.
اعتبارسنجی: اگر فراخوانی یک تابع پیامدهای مهمی دارد (مثلاً ثبت سفارش)، قبل از اجرای آن، فراخوانی را با کاربر اعتبارسنجی کنید.
بررسی دلیل پایان: همیشه
finishReasonدر پاسخ مدل بررسی کنید تا مواردی را که مدل نتوانسته یک فراخوانی تابع معتبر ایجاد کند، مدیریت کنید.مدیریت خطا : مدیریت خطای قوی را در توابع خود پیادهسازی کنید تا ورودیهای غیرمنتظره یا خطاهای API را به طور مناسب مدیریت کنید. پیامهای خطای آموزندهای را برگردانید که مدل میتواند از آنها برای تولید پاسخهای مفید به کاربر استفاده کند.
امنیت: هنگام فراخوانی APIهای خارجی به امنیت توجه داشته باشید. از مکانیزمهای احراز هویت و مجوزدهی مناسب استفاده کنید. از افشای دادههای حساس در فراخوانیهای تابع خودداری کنید.
محدودیتهای توکن: توضیحات تابع و پارامترها در محدودیت توکن ورودی شما محاسبه میشوند. اگر به محدودیت توکن رسیدهاید، محدود کردن تعداد توابع یا طول توضیحات را در نظر بگیرید و وظایف پیچیده را به مجموعه توابع کوچکتر و متمرکزتر تقسیم کنید.
یادداشتها و محدودیتها
- فقط زیرمجموعهای از طرح OpenAPI پشتیبانی میشود.
- برای
ANYحالتی، API ممکن است طرحوارههای بسیار بزرگ یا تودرتو را رد کند. اگر با خطایی مواجه شدید، سعی کنید طرحوارههای پارامتر و پاسخ تابع خود را با کوتاه کردن نام ویژگیها، کاهش تودرتو بودن یا محدود کردن تعداد اعلانهای تابع، ساده کنید. - انواع پارامترهای پشتیبانی شده در پایتون محدود هستند.
- فراخوانی خودکار تابع فقط یک ویژگی SDK پایتون است.

