Google Search के साथ ग्राउंडिंग की सुविधा, Gemini मॉडल को रीयल-टाइम में वेब कॉन्टेंट से कनेक्ट करती है. साथ ही, यह सुविधा सभी उपलब्ध भाषाओं में काम करती है. इससे Gemini को ज़्यादा सटीक जवाब देने में मदद मिलती है. साथ ही, यह पुष्टि किए जा सकने वाले ऐसे सोर्स के बारे में भी बता पाता है जिनके बारे में उसे जानकारी नहीं है.
ग्राउंडिंग की मदद से, ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन बनाए जा सकते हैं जो ये काम कर सकते हैं:
- तथ्यों के सही होने की संभावना बढ़ाना: मॉडल के गलत जानकारी देने की संभावना को कम करना. इसके लिए, जवाबों को असल दुनिया की जानकारी पर आधारित करना.
- रीयल-टाइम में जानकारी ऐक्सेस करना: हाल ही की घटनाओं और विषयों के बारे में सवालों के जवाब पाना.
साइटेशन दें: मॉडल के दावों के सोर्स दिखाकर, उपयोगकर्ताओं का भरोसा जीतें.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
grounding_tool = types.Tool(
google_search=types.GoogleSearch()
)
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[grounding_tool]
)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Who won the euro 2024?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const groundingTool = {
googleSearch: {},
};
const config = {
tools: [groundingTool],
};
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Who won the euro 2024?",
config,
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{"text": "Who won the euro 2024?"}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"google_search": {}
}
]
}'
खोज टूल नोटबुक का इस्तेमाल करके, इस बारे में ज़्यादा जाना जा सकता है.
Google Search से जानकारी लेने की सुविधा कैसे काम करती है
google_search टूल चालू करने पर, मॉडल खोज करने, जानकारी को प्रोसेस करने, और उद्धरण देने जैसे सभी काम अपने-आप करता है.
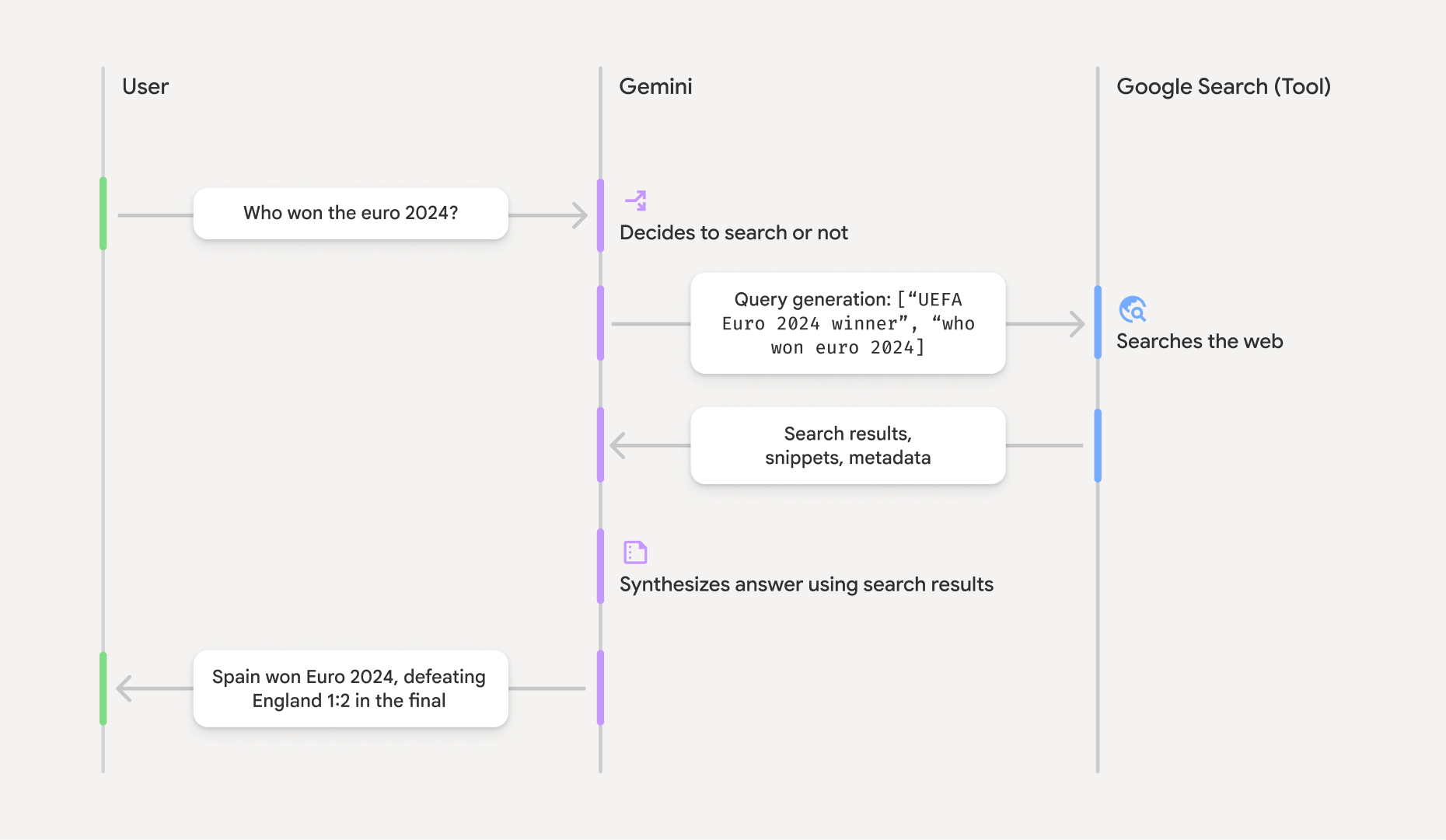
- उपयोगकर्ता का प्रॉम्प्ट: आपका ऐप्लिकेशन, उपयोगकर्ता के प्रॉम्प्ट को Gemini API को भेजता है. इसके लिए,
google_searchटूल चालू होना चाहिए. - प्रॉम्प्ट का विश्लेषण: मॉडल, प्रॉम्प्ट का विश्लेषण करता है और यह तय करता है कि क्या Google Search से जवाब को बेहतर बनाया जा सकता है.
- Google Search: अगर ज़रूरत होती है, तो मॉडल अपने-आप एक या एक से ज़्यादा सर्च क्वेरी जनरेट करता है और उन्हें पूरा करता है.
- खोज के नतीजों को प्रोसेस करना: मॉडल, खोज के नतीजों को प्रोसेस करता है, जानकारी को एक साथ रखता है, और जवाब तैयार करता है.
- भरोसेमंद स्रोतों से मिली जानकारी के आधार पर जवाब देना: एपीआई, खोज के नतीजों के आधार पर उपयोगकर्ता को ऐसा जवाब देता है जो उसके लिए फ़ायदेमंद हो. इस जवाब में, मॉडल का टेक्स्ट वाला जवाब और
groundingMetadataशामिल है. इसमें खोज क्वेरी, वेब नतीजे, और उद्धरण भी शामिल हैं.
भरोसेमंद स्रोतों से मिले जवाब को समझना
जब किसी जवाब में भरोसेमंद सोर्स से जानकारी शामिल की जाती है, तो जवाब में groundingMetadata फ़ील्ड शामिल होता है. दावों की पुष्टि करने और अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में उद्धरणों को ज़्यादा बेहतर तरीके से दिखाने के लिए, यह स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा ज़रूरी है.
{
"candidates": [
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final. This victory marks Spain's record fourth European Championship title."
}
],
"role": "model"
},
"groundingMetadata": {
"webSearchQueries": [
"UEFA Euro 2024 winner",
"who won euro 2024"
],
"searchEntryPoint": {
"renderedContent": "<!-- HTML and CSS for the search widget -->"
},
"groundingChunks": [
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "aljazeera.com"}},
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "uefa.com"}}
],
"groundingSupports": [
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 0, "endIndex": 85, "text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeatin..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0]
},
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 86, "endIndex": 210, "text": "This victory marks Spain's..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0, 1]
}
]
}
}
]
}
Gemini API, groundingMetadata के साथ यह जानकारी दिखाता है:
webSearchQueries: इस्तेमाल की गई खोज क्वेरी का कलेक्शन. यह डीबग करने और मॉडल की तर्क देने की प्रोसेस को समझने के लिए उपयोगी है.searchEntryPoint: इसमें ज़रूरी खोज के सुझावों को रेंडर करने के लिए एचटीएमएल और सीएसएस शामिल होता है. इस्तेमाल से जुड़ी सभी ज़रूरी शर्तों के बारे में, सेवा की शर्तों में बताया गया है.groundingChunks: यह ऑब्जेक्ट का ऐसा कलेक्शन है जिसमें वेब सोर्स (uriऔरtitle) शामिल होते हैं.groundingSupports: यह चंक का ऐसा कलेक्शन है जो मॉडल के जवाबtextकोgroundingChunksमें मौजूद सोर्स से कनेक्ट करता है. हर चंक, टेक्स्टsegmentको एक या उससे ज़्यादाgroundingChunkIndicesसे लिंक करता है. इसेstartIndexऔरendIndexसे तय किया जाता है. यह इनलाइन उद्धरण बनाने का तरीका है.
Google Search से मिली जानकारी का इस्तेमाल, यूआरएल के कॉन्टेक्स्ट वाले टूल के साथ भी किया जा सकता है. इससे, जवाबों में सार्वजनिक वेब डेटा और आपके दिए गए यूआरएल, दोनों से जानकारी शामिल की जा सकती है.
इनलाइन उद्धरणों की मदद से सोर्स एट्रिब्यूट करना
यह एपीआई, स्ट्रक्चर्ड उद्धरण डेटा दिखाता है. इससे आपको यह तय करने का पूरा कंट्रोल मिलता है कि आपको अपने यूज़र इंटरफ़ेस में सोर्स कैसे दिखाने हैं. मॉडल के जवाबों को सीधे उनके सोर्स से लिंक करने के लिए, groundingSupports और groundingChunks फ़ील्ड का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. यहां मेटाडेटा को प्रोसेस करने का सामान्य पैटर्न दिया गया है, ताकि इनलाइन और क्लिक किए जा सकने वाले उद्धरणों के साथ जवाब बनाया जा सके.
Python
def add_citations(response):
text = response.text
supports = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_supports
chunks = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_chunks
# Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
sorted_supports = sorted(supports, key=lambda s: s.segment.end_index, reverse=True)
for support in sorted_supports:
end_index = support.segment.end_index
if support.grounding_chunk_indices:
# Create citation string like [1](link1)[2](link2)
citation_links = []
for i in support.grounding_chunk_indices:
if i < len(chunks):
uri = chunks[i].web.uri
citation_links.append(f"[{i + 1}]({uri})")
citation_string = ", ".join(citation_links)
text = text[:end_index] + citation_string + text[end_index:]
return text
# Assuming response with grounding metadata
text_with_citations = add_citations(response)
print(text_with_citations)
JavaScript
function addCitations(response) {
let text = response.text;
const supports = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingSupports;
const chunks = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingChunks;
// Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
const sortedSupports = [...supports].sort(
(a, b) => (b.segment?.endIndex ?? 0) - (a.segment?.endIndex ?? 0),
);
for (const support of sortedSupports) {
const endIndex = support.segment?.endIndex;
if (endIndex === undefined || !support.groundingChunkIndices?.length) {
continue;
}
const citationLinks = support.groundingChunkIndices
.map(i => {
const uri = chunks[i]?.web?.uri;
if (uri) {
return `[${i + 1}](${uri})`;
}
return null;
})
.filter(Boolean);
if (citationLinks.length > 0) {
const citationString = citationLinks.join(", ");
text = text.slice(0, endIndex) + citationString + text.slice(endIndex);
}
}
return text;
}
const textWithCitations = addCitations(response);
console.log(textWithCitations);
इनलाइन उद्धरणों के साथ नया जवाब ऐसा दिखेगा:
Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final.[1](https:/...), [2](https:/...), [4](https:/...), [5](https:/...) This victory marks Spain's record-breaking fourth European Championship title.[5]((https:/...), [2](https:/...), [3](https:/...), [4](https:/...)
कीमत
Gemini 3 के साथ Google Search की ग्राउंडिंग का इस्तेमाल करने पर, आपके प्रोजेक्ट को हर उस खोज क्वेरी के लिए बिल किया जाता है जिसे मॉडल पूरा करने का फ़ैसला करता है. अगर मॉडल किसी एक प्रॉम्प्ट का जवाब देने के लिए, कई खोज क्वेरी चलाने का फ़ैसला करता है (उदाहरण के लिए, एक ही एपीआई कॉल में "UEFA Euro 2024 winner" और "Spain vs England Euro 2024 final
score" खोजना), तो उस अनुरोध के लिए, इस टूल के दो बार इस्तेमाल करने का शुल्क लिया जाएगा. बिलिंग के लिए, यूनीक क्वेरी की गिनती करते समय, हम वेब पर की गई उन खोज क्वेरी को अनदेखा करते हैं जिनमें कोई कॉन्टेंट नहीं होता. यह बिलिंग मॉडल सिर्फ़ Gemini 3 मॉडल पर लागू होता है. Gemini 2.5 या इससे पुराने मॉडल के साथ खोज के नतीजों से जानकारी लेने की सुविधा इस्तेमाल करने पर, आपके प्रोजेक्ट के लिए हर प्रॉम्प्ट के हिसाब से बिल भेजा जाता है.
शुल्क के बारे में ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Gemini API के शुल्क वाले पेज पर जाएं.
इन मॉडल के साथ काम करता है
इसमें एक्सपेरिमेंट के तौर पर उपलब्ध मॉडल और झलक देखने के लिए उपलब्ध मॉडल शामिल नहीं हैं. इनकी क्षमताओं के बारे में जानने के लिए, मॉडल की खास जानकारी पेज पर जाएं.
| मॉडल | Google Search की मदद से, ज़्यादा जानकारी पाएं |
|---|---|
| Gemini 3.1 Pro की झलक | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Pro की झलक | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash Preview | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ |
इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले टूल कॉम्बिनेशन
ज़्यादा मुश्किल कामों के लिए, Google Search के साथ ग्राउंडिंग की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल अन्य टूल के साथ किया जा सकता है. जैसे, कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन और यूआरएल कॉन्टेक्स्ट.
आगे क्या करना है
- Gemini API की कुकबुक में, Google Search की मदद से जानकारी पाने की सुविधा आज़माएं.
- उपलब्ध अन्य टूल के बारे में जानें. जैसे, फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग.
- यूआरएल कॉन्टेक्स्ट टूल का इस्तेमाल करके, प्रॉम्प्ट में खास यूआरएल जोड़ने का तरीका जानें.
