Thought signatures are encrypted representations of the model's internal thought
process and are used to preserve reasoning context across multi-step
interactions.
When using thinking models (such as the Gemini 3 and 2.5 series), the API may
return a thoughtSignature field within the content parts
of the response (e.g., text or functionCall parts).
As a general rule, if you receive a thought signature in a model response,
you should pass it back exactly as received when sending the conversation
history in the next turn.
When using Gemini 3 models, you must pass back thought signatures during
function calling, otherwise you will get a validation error (4xx status code).
This includes when using the minimal
thinking level setting for Gemini 3
Flash.
How it works
The graphic below visualizes the meaning of "turn" and "step" as they pertain to function calling in the Gemini API. A "turn" is a single, complete exchange in a conversation between a user and a model. A "step" is a finer-grained action or operation performed by the model, often as part of a larger process to complete a turn.
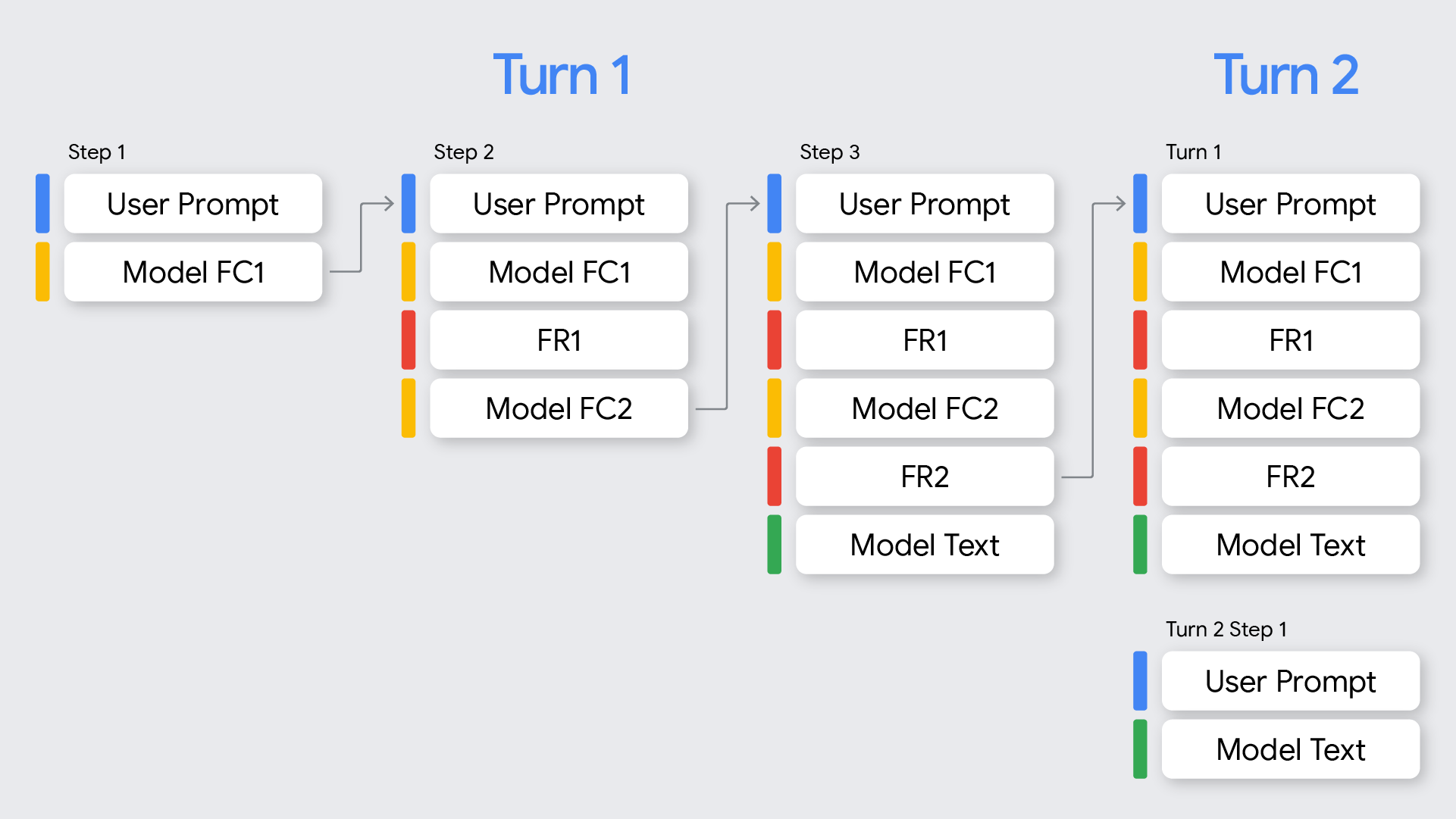
This document focuses on handling function calling for Gemini 3 models. Refer to the model behavior section for discrepancies with 2.5.
Gemini 3 returns thought signatures for all model responses (responses from the API) with a function call. Thought signatures show up in the following cases:
- When there are parallel function calls, the first function call part returned by the model response will have a thought signature.
- When there are sequential function calls (multi-step), each function call will have a signature and you must pass all signatures back.
- Model responses without a function call will return a thought signature inside the last part returned by the model.
The following table provides a visualization for multi-step function calls, combining the definitions of turns and steps with the concept of signatures introduced above:
Turn |
Step |
User Request |
Model Response |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1 = user_prompt |
FC1 + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request2 = request1 + (FC1 + signature) + FR1 |
FC2 + signature |
FR2 |
1 |
3 |
request3 = request2 + (FC2 + signature) + FR2 |
text_output |
None |
Signatures in function calling parts
When Gemini generates a functionCall, it relies on the thought_signature
to process the tool's output correctly in the next turn.
- Behavior:
- Single Function Call: The
functionCallpart will contain athought_signature. - Parallel Function Calls: If the model generates parallel function calls
in a response, the
thought_signatureis attached only to the firstfunctionCallpart. SubsequentfunctionCallparts in the same response will not contain a signature.
- Single Function Call: The
- Requirement: You must return this signature in the exact part where it was received when sending the conversation history back.
- Validation: Strict validation is enforced for all function calls within
the current turn . (Only current turn is required; we don't validate on
previous turns)
- The API goes back in the history (newest to oldest) to find the most recent
User message that contains standard content (e.g.,
text) ( which would be the start of the current turn). This will not be afunctionResponse. - All model
functionCallturns occurring after that specific use message are considered part of the turn. - The first
functionCallpart in each step of the current turn must include itsthought_signature. - If you omit a
thought_signaturefor the firstfunctionCallpart in any step of the current turn, the request will fail with a 400 error.
- The API goes back in the history (newest to oldest) to find the most recent
User message that contains standard content (e.g.,
- If proper signatures are not returned, here is how you will error out
gemini-3-pro-previewandgemini-3-flash-preview: Failure to include signatures will result in a 400 error. The verbiage will be of the form:- Function call
<Function Call>in the<index of contents array>content block is missing athought_signature. For example, Function callFC1in the1.content block is missing athought_signature.
- Function call
Sequential function calling example
This section shows an example of multiple function calls where the user asks a complex question requiring multiple tasks.
Let's walk through a multiple-turn function calling example where the user asks
a complex question requiring multiple tasks: "Check flight status for AA100 and
book a taxi if delayed".
Turn |
Step |
User Request |
Model Response |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed." |
FC1 ("check_flight") + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request2 = request1 + FC1 ("check_flight") + signature + FR1 |
FC2("book_taxi") + signature |
FR2 |
1 |
3 |
request3 = request2 + FC2 ("book_taxi") + signature + FR2 |
text_output |
None |
The following code illustrates the sequence in the above table.
Turn 1, Step 1 (User request)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "check_flight",
"description": "Gets the current status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The flight number to check"
}
},
"required": [
"flight"
]
}
},
{
"name": "book_taxi",
"description": "Book a taxi",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "time to book the taxi"
}
},
"required": [
"time"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 1 (Model response)
{
"content": {
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>"
}
]
}
}
Turn 1, Step 2 (User response - Sending tool outputs) Since this user turn
only contains a functionResponse (no fresh text), we are still in Turn 1. We
must preserve <Signature_A>.
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "check_flight",
"response": {
"status": "delayed",
"departure_time": "12 PM"
}
}
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 2 (Model) The model now decides to book a taxi based on the previous tool output.
{
"content": {
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"args": {
"time": "10 AM"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature B>"
}
]
}
}
Turn 1, Step 3 (User - Sending tool output) To send the taxi booking
confirmation, we must include signatures for ALL function calls in this loop
(<Signature A> + <Signature B>).
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "check_flight",
"response": {
"status": "delayed",
"departure_time": "12 PM"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"args": {
"time": "10 AM"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature B>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"response": {
"booking_status": "success"
}
}
}
]
}
}
Parallel function calling example
Let's walk through a parallel function calling example where the users asks
"Check weather in Paris and London" to see where the model does validation.
Turn |
Step |
User Request |
Model Response |
FunctionResponse |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
1 |
request1="Check the weather in Paris and London" |
FC1 ("Paris") + signature FC2 ("London") |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request 2 = request1 + FC1 ("Paris") + signature + FC2 ("London") |
text_output (no FCs) |
None |
The following code illustrates the sequence in the above table.
Turn 1, Step 1 (User request)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Gets the current temperature for a given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name, e.g. San Francisco"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 1 (Model response)
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"location": "Paris"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature_A>"// INCLUDED on First FC
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"location": "London"
}// NO signature on subsequent parallel FCs
}
}
]
}
}
Turn 1, Step 2 (User response - Sending tool outputs) We must preserve
<Signature_A> on the first part exactly as received.
[
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"city": "Paris"
}
},
"thought_signature": "<Signature_A>" // MUST BE INCLUDED
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"city": "London"
}
}
} // NO SIGNATURE FIELD
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"response": {
"temp": "15C"
}
}
},
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"response": {
"temp": "12C"
}
}
}
]
}
]
Signatures in non functionCall parts
Gemini may also return thought_signatures in the final part of the response
in non-function-call parts.
- Behavior: The final content part (
text, inlineData…) returned by the model may contain athought_signature. - Recommendation: Returning these signatures is recommended to ensure the model maintains high-quality reasoning, especially for complex instruction following or simulated agentic workflows.
- Validation: The API does not strictly enforce validation. You won't receive a blocking error if you omit them, though performance may degrade.
Text/In-context reasoning (No validation)
Turn 1, Step 1 (Model response)
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": "I need to calculate the risk. Let me think step-by-step...",
"thought_signature": "<Signature_C>" // OPTIONAL (Recommended)
}
]
}
Turn 2, Step 1 (User)
[
{ "role": "user", "parts": [{ "text": "What is the risk?" }] },
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": "I need to calculate the risk. Let me think step-by-step...",
// If you omit <Signature_C> here, no error will occur.
}
]
},
{ "role": "user", "parts": [{ "text": "Summarize it." }] }
]
Signatures for OpenAI compatibility
The following examples shows how to handle thought signatures for a chat completion API using OpenAI compatibility.
Sequential function calling example
This is an example of multiple function calling where the user asks a complex question requiring multiple tasks.
Let's walk through a multiple-turn function calling example where the user asks
Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi if delayed and you can see what
happens when the user asks a complex question requiring multiple tasks.
Turn |
Step |
User Request |
Model Response |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check the weather in Paris and London" |
FC1 ("Paris") + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request 2 = request1 + FC1 ("Paris") + signature + FC2 ("London") |
text_output |
None |
The following code walks through the given sequence.
Turn 1, Step 1 (User Request)
{
"model": "google/gemini-3-pro-preview",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "check_flight",
"description": "Gets the current status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The flight number to check."
}
},
"required": [
"flight"
]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"description": "Book a taxi",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "time to book the taxi"
}
},
"required": [
"time"
]
}
}
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 1 (Model Response)
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>"
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1",
"type": "function"
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 2 (User Response - Sending Tool Outputs)
Since this user turn only contains a functionResponse (no fresh text), we are
still in Turn 1 and must preserve <Signature_A>.
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "check_flight",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-1",
"content": "{\"status\":\"delayed\",\"departure_time\":\"12 PM\"}"
}
]
Turn 1, Step 2 (Model)
The model now decides to book a taxi based on the previous tool output.
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature B>"
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"time\":\"10 AM\"}",
"name": "book_taxi"
},
"id": "function-call-2",
"type": "function"
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 3 (User - Sending Tool Output)
To send the taxi booking confirmation, we must include signatures for ALL
function calls in this loop (<Signature A> + <Signature B>).
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1d6a1a61-6f4f-4029-80ce-61586bd86da5",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "check_flight",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-1d6a1a61-6f4f-4029-80ce-61586bd86da5",
"content": "{\"status\":\"delayed\",\"departure_time\":\"12 PM\"}"
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature B>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"time\":\"10 AM\"}",
"name": "book_taxi"
},
"id": "function-call-65b325ba-9b40-4003-9535-8c7137b35634",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "book_taxi",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-65b325ba-9b40-4003-9535-8c7137b35634",
"content": "{\"booking_status\":\"success\"}"
}
]
Parallel function calling example
Let's walk through a parallel function calling example where the users asks
"Check weather in Paris and London" and you can see where the model does
validation.
Turn |
Step |
User Request |
Model Response |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check the weather in Paris and London" |
FC1 ("Paris") + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request 2 = request1 + FC1 ("Paris") + signature + FC2 ("London") |
text_output |
None |
Here's the code to walk through the given sequence.
Turn 1, Step 1 (User Request)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Gets the current temperature for a given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name, e.g. San Francisco"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 1 (Model Response)
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Signature returned
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"type": "function"
},
{
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"London\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"type": "function" // No signature on Parallel FC
}
]
}
Turn 1, Step 2 (User Response - Sending Tool Outputs)
You must preserve <Signature_A> on the first part exactly as received.
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"type": "function"
},
{
"function": { //No Signature
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"London\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role":"tool",
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"content": "{\"temp\":\"15C\"}"
},
{
"role":"tool",
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"content": "{\"temp\":\"12C\"}"
}
]
FAQs
How do I transfer history from a different model to Gemini 3 with a function call part in the current turn and step? I need to provide function call parts that were not generated by the API and therefore don't have an associated thought signature?
While injecting custom function call blocks into the request is strongly discouraged, in cases where it can't be avoided, e.g. providing information to the model on function calls and responses that were executed deterministically by the client, or transferring a trace from a different model that does not include thought signatures, you can set the following dummy signatures of either
"context_engineering_is_the_way_to_go"or"skip_thought_signature_validator"in the thought signature field to skip validation.I am sending back interleaved parallel function calls and responses and the API is returning a 400. Why?
When the API returns parallel function calls "FC1 + signature, FC2", the user response expected is "FC1+ signature, FC2, FR1, FR2". If you have them interleaved as "FC1 + signature, FR1, FC2, FR2" the API will return a 400 error.
When streaming and the model is not returning a function call I can't find the thought signature
During a model response not containing a FC with a streaming request, the model may return the thought signature in a part with an empty text content part. It is advisable to parse the entire request until the
finish_reasonis returned by the model.
Thought signatures for different models
Gemini 3 Pro and Flash, Gemini 3 Pro Image and Gemini 2.5 models each behave differently with thought signatures. For Gemini 3 Pro Image see the thinking process section of the image generation guide.
Gemini 3 models and Gemini 2.5 models behave differently with thought signatures in function calls:
- If there are function calls in a response,
- Gemini 3 will always have the signature on the first function call part. It is mandatory to return that part.
- Gemini 2.5 will have the signature in the first part (regardless of type). It is optional to return that part.
- If there are no function calls in a response,
- Gemini 3 will have the signature on the last part if the model generates a thought.
- Gemini 2.5 won't have a signature in any part.
For Gemini 2.5 models thought signature behavior, refer to the Thinking page.
