思考シグネチャは、モデルの内部的な思考プロセスを暗号化したもので、複数ステップのインタラクションで推論コンテキストを保持するために使用されます。思考モデル(Gemini 3 シリーズや 2.5 シリーズなど)を使用する場合、API はレスポンスのコンテンツ部分内に thoughtSignature フィールドを返すことがあります(例: text または functionCall の一部)。
原則として、モデル レスポンスで思考シグネチャを受け取った場合は、次のターンで会話履歴を送信するときに、受け取ったとおりに渡す必要があります。Gemini 3 モデルを使用する場合は、関数呼び出し中に思考シグネチャを渡す必要があります。そうしないと、検証エラー(4xx ステータス コード)が発生します。これには、Gemini 3 Flash の minimal
思考レベル設定を使用する場合も含まれます。
仕組み
次の図は、Gemini API の関数呼び出しにおける「ターン」と「ステップ」の意味を視覚化したものです。「ターン」とは、ユーザーとモデルの間の会話における 1 回の完全なやり取りです。「ステップ」は、モデルによって実行されるより細かいアクションまたはオペレーションです。多くの場合、ターンを完了するためのより大きなプロセスの一部として実行されます。
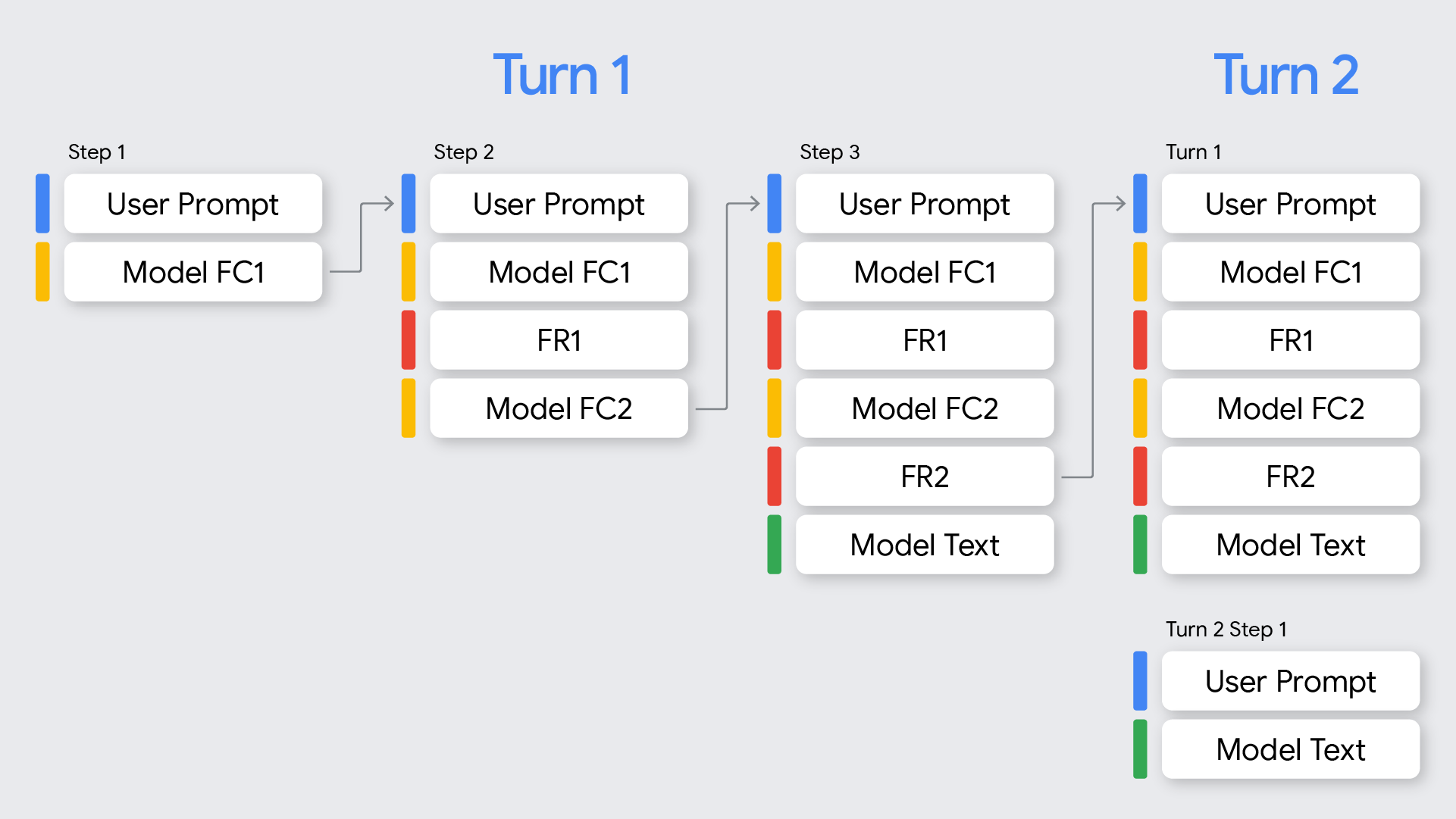
このドキュメントでは、Gemini 3 モデルの関数呼び出しの処理に焦点を当てています。2.5 との相違点については、モデルの動作のセクションをご覧ください。
Gemini 3 は、関数呼び出しを含むすべてのモデル レスポンス(API からのレスポンス)の思考シグネチャを返します。思考シグネチャは、次の場合に表示されます。
- 並列関数呼び出しがある場合、モデル レスポンスから返される最初の関数呼び出し部分には思考シグネチャが含まれます。
- 関数呼び出しが連続している場合(マルチステップ)、各関数呼び出しにシグネチャがあり、すべてのシグネチャを返す必要があります。
- 関数呼び出しのないモデル レスポンスでは、モデルによって返される最後の部分に思考シグネチャを返します。
次の表は、マルチステップ関数呼び出しの可視化を示しています。ターンとステップの定義と、上記のシグネチャの概念を組み合わせています。
Turn |
Step |
ユーザー リクエスト |
モデルのレスポンス |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1 = user_prompt |
FC1 + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request2 = request1 + (FC1 + signature) + FR1 |
FC2 + signature |
FR2 |
1 |
3 |
request3 = request2 + (FC2 + signature) + FR2 |
text_output
|
なし |
関数呼び出しパーツのシグネチャ
Gemini が functionCall を生成するとき、次のターンでツールの出力を正しく処理するために thought_signature に依存します。
- 動作:
- 単一の関数呼び出し:
functionCall部分にthought_signatureが含まれます。 - 並列関数呼び出し: モデルがレスポンスで並列関数呼び出しを生成する場合、
thought_signatureは最初のfunctionCall部分にのみ付加されます。同じレスポンス内の後続のfunctionCall部分には署名が含まれません。
- 単一の関数呼び出し:
- 要件: 会話履歴を返す際は、このシグネチャを受け取った部分に正確に返す必要があります。
- 検証: 現在のターンのすべての関数呼び出しに対して厳密な検証が適用されます。(現在のターンのみが必須です。前のターンは検証しません)
- API は履歴を遡って(新しい順から古い順に)、標準コンテンツ(「
text)を渡します(これは現在のターンの開始位置になります)。これはfunctionResponseにはなりません。be - その特定の使用メッセージの後に発生するすべてのモデル
functionCallターンは、ターンの一部と見なされます。 - 現在のターンの各ステップの最初の
functionCall部分には、そのthought_signatureを含める必要があります。 - 現在のターンのいずれかのステップの最初の
functionCall部分でthought_signatureを省略すると、リクエストは 400 エラーで失敗します。
- API は履歴を遡って(新しい順から古い順に)、標準コンテンツ(「
- 適切なシグネチャが返されない場合のエラー処理
gemini-3-pro-previewとgemini-3-flash-preview: 署名を含めないと、400 エラーが発生します。文言は次の形式になります。<index of contents array>コンテンツ ブロックの関数呼び出し<Function Call>にthought_signatureがありません。たとえば、「1.コンテンツ ブロックの関数呼び出しFC1にthought_signatureがありません。」などです。
順次関数呼び出しの例
このセクションでは、複数のタスクが必要となる複雑な質問をユーザーが行った場合の、複数の関数呼び出しの例を示します。
ユーザーが複数のタスクを必要とする複雑な質問("Check flight status for AA100 and
book a taxi if delayed")をした場合の、マルチターン関数呼び出しの例を見てみましょう。
Turn |
Step |
ユーザー リクエスト |
モデルのレスポンス |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed." |
FC1 ("check_flight") + signature |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request2 = request1 + FC1 ("check_flight") + signature + FR1 |
FC2("book_taxi") + signature |
FR2 |
1 |
3 |
request3 = request2 + FC2 ("book_taxi") + signature + FR2 |
text_output
|
None |
次のコードは、上記の表のシーケンスを示しています。
ターン 1、ステップ 1(ユーザーのリクエスト)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "check_flight",
"description": "Gets the current status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The flight number to check"
}
},
"required": [
"flight"
]
}
},
{
"name": "book_taxi",
"description": "Book a taxi",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "time to book the taxi"
}
},
"required": [
"time"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 1(モデルのレスポンス)
{
"content": {
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>"
}
]
}
}
ターン 1、ステップ 2(ユーザーのレスポンス - ツールの出力を送信)このユーザーのターンには functionResponse のみ(新しいテキストなし)が含まれているため、まだターン 1 です。<Signature_A> を保持する必要があります。
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "check_flight",
"response": {
"status": "delayed",
"departure_time": "12 PM"
}
}
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 2(モデル)モデルは、前のツールの出力に基づいてタクシーを予約することにしました。
{
"content": {
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"args": {
"time": "10 AM"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature B>"
}
]
}
}
ターン 1、ステップ 3(ユーザー - ツールの出力を送信)タクシーの予約確認を送信するには、このループ内のすべての関数呼び出し(<Signature A> + <Signature B>)の署名を含める必要があります。
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "check_flight",
"args": {
"flight": "AA100"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "check_flight",
"response": {
"status": "delayed",
"departure_time": "12 PM"
}
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"args": {
"time": "10 AM"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature B>" //Required and Validated
}
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"response": {
"booking_status": "success"
}
}
}
]
}
}
並列関数呼び出しの例
ユーザーが "Check weather in Paris and London" にモデルが検証を行う場所を尋ねる並列関数呼び出しの例を見てみましょう。
Turn |
Step |
ユーザー リクエスト |
モデルのレスポンス |
FunctionResponse |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
1 |
request1="パリとロンドンの天気を調べて" |
FC1(「パリ」)+ 署名 FC2(「ロンドン」) |
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
リクエスト 2 = リクエスト 1 + FC1(「パリ」)+ 署名 + FC2(「ロンドン」) |
text_output (FC なし) |
なし |
次のコードは、上記の表のシーケンスを示しています。
ターン 1、ステップ 1(ユーザーのリクエスト)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Gets the current temperature for a given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name, e.g. San Francisco"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 1(モデルのレスポンス)
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"location": "Paris"
}
},
"thoughtSignature": "<Signature_A>"// INCLUDED on First FC
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"location": "London"
}// NO signature on subsequent parallel FCs
}
}
]
}
}
ターン 1、ステップ 2(ユーザーのレスポンス - ツールの出力を送信)最初の部分の <Signature_A> は、受け取ったとおりに保持する必要があります。
[
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
},
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"city": "Paris"
}
},
"thought_signature": "<Signature_A>" // MUST BE INCLUDED
},
{
"functionCall": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"args": {
"city": "London"
}
}
} // NO SIGNATURE FIELD
]
},
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"response": {
"temp": "15C"
}
}
},
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"response": {
"temp": "12C"
}
}
}
]
}
]
functionCall 以外のパーツのシグネチャ
Gemini は、関数呼び出し以外の部分のレスポンスの最後の部分で thought_signatures を返すこともあります。
- 動作: モデルから返される最終的なコンテンツ部分(
text, inlineData…)にthought_signatureが含まれることがあります。 - 推奨事項: 特に複雑な指示の実行やエージェント ワークフローのシミュレーションで、モデルが高品質の推論を維持するために、これらのシグネチャを返すことが推奨されます。
- 検証: API は検証を厳密に適用しません。省略してもブロッキング エラーは発生しませんが、パフォーマンスが低下する可能性があります。
テキスト/コンテキスト内推論(検証なし)
ターン 1、ステップ 1(モデルのレスポンス)
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": "I need to calculate the risk. Let me think step-by-step...",
"thought_signature": "<Signature_C>" // OPTIONAL (Recommended)
}
]
}
ターン 2、ステップ 1(ユーザー)
[
{ "role": "user", "parts": [{ "text": "What is the risk?" }] },
{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": "I need to calculate the risk. Let me think step-by-step...",
// If you omit <Signature_C> here, no error will occur.
}
]
},
{ "role": "user", "parts": [{ "text": "Summarize it." }] }
]
OpenAI の互換性のシグネチャ
次の例は、OpenAI 互換性を使用して、チャット補完 API の思考シグネチャを処理する方法を示しています。
順次関数呼び出しの例
これは、ユーザーが複数のタスクを必要とする複雑な質問をした場合の、複数の関数呼び出しの例です。
ユーザーが Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi if delayed を尋ねるマルチターン関数呼び出しの例を見てみましょう。ユーザーが複数のタスクを必要とする複雑な質問をしたときに何が起こるかを確認できます。
Turn |
Step |
ユーザー リクエスト |
モデルのレスポンス |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check the weather in Paris and London" |
FC1 ("Paris") + signature
|
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request 2 = request1 + FC1 ("Paris") + signature + FC2 ("London") |
text_output
|
None |
次のコードは、指定されたシーケンスを処理します。
ターン 1、ステップ 1(ユーザーのリクエスト)
{
"model": "google/gemini-3-pro-preview",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "check_flight",
"description": "Gets the current status of a flight",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"flight": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The flight number to check."
}
},
"required": [
"flight"
]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "book_taxi",
"description": "Book a taxi",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "time to book the taxi"
}
},
"required": [
"time"
]
}
}
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 1(モデルのレスポンス)
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>"
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1",
"type": "function"
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 2(ユーザーのレスポンス - ツールの出力を送信)
このユーザーのターンには functionResponse のみ(新しいテキストなし)が含まれているため、まだターン 1 であり、<Signature_A> を保持する必要があります。
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "check_flight",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-1",
"content": "{\"status\":\"delayed\",\"departure_time\":\"12 PM\"}"
}
]
ターン 1、ステップ 2(モデル)
モデルは、前のツールの出力に基づいてタクシーを予約することにしました。
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature B>"
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"time\":\"10 AM\"}",
"name": "book_taxi"
},
"id": "function-call-2",
"type": "function"
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 3(ユーザー - ツールの出力を送信)
タクシーの予約確認を送信するには、このループ内のすべての関数呼び出し(<Signature A> + <Signature B>)の署名を含める必要があります。
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check flight status for AA100 and book a taxi 2 hours before if delayed."
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"flight\":\"AA100\"}",
"name": "check_flight"
},
"id": "function-call-1d6a1a61-6f4f-4029-80ce-61586bd86da5",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "check_flight",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-1d6a1a61-6f4f-4029-80ce-61586bd86da5",
"content": "{\"status\":\"delayed\",\"departure_time\":\"12 PM\"}"
},
{
"role": "model",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature B>" //Required and Validated
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"time\":\"10 AM\"}",
"name": "book_taxi"
},
"id": "function-call-65b325ba-9b40-4003-9535-8c7137b35634",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"name": "book_taxi",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-65b325ba-9b40-4003-9535-8c7137b35634",
"content": "{\"booking_status\":\"success\"}"
}
]
並列関数呼び出しの例
ユーザーが "Check weather in Paris and London" をリクエストした場合の並列関数呼び出しの例を見てみましょう。モデルが検証を行う場所を確認できます。
Turn |
Step |
ユーザー リクエスト |
モデルのレスポンス |
FunctionResponse |
1 |
1 |
request1="Check the weather in Paris and London" |
FC1 ("Paris") + signature
|
FR1 |
1 |
2 |
request 2 = request1 + FC1 ("Paris") + signature + FC2 ("London") |
text_output
|
None |
指定されたシーケンスをウォークスルーするコードを次に示します。
ターン 1、ステップ 1(ユーザーのリクエスト)
{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Gets the current temperature for a given location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city name, e.g. San Francisco"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 1(モデルのレスポンス)
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Signature returned
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"type": "function"
},
{
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"London\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"type": "function" // No signature on Parallel FC
}
]
}
ターン 1、ステップ 2(ユーザーのレスポンス - ツールの出力を送信)
最初の部分の <Signature_A> は、受け取ったとおりに保持する必要があります。
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Check the weather in Paris and London."
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": [
{
"extra_content": {
"google": {
"thought_signature": "<Signature A>" //Required
}
},
"function": {
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"Paris\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"type": "function"
},
{
"function": { //No Signature
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"London\"}",
"name": "get_current_temperature"
},
"id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"type": "function"
}
]
},
{
"role":"tool",
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-f3b9ecb3-d55f-4076-98c8-b13e9d1c0e01",
"content": "{\"temp\":\"15C\"}"
},
{
"role":"tool",
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"tool_call_id": "function-call-335673ad-913e-42d1-bbf5-387c8ab80f44",
"content": "{\"temp\":\"12C\"}"
}
]
よくある質問
現在のターンとステップの関数呼び出し部分を使用して、別のモデルから Gemini 3 に履歴を転送するにはどうすればよいですか?API で生成されなかったため、関連する思考シグネチャーがない関数呼び出し部分を提供する必要がありますか?
カスタム関数呼び出しブロックをリクエストに挿入することは強く推奨されませんが、避けられない場合(クライアントによって決定論的に実行された関数呼び出しとレスポンスに関する情報をモデルに提供する場合や、思考シグネチャを含まない別のモデルからトレースを転送する場合など)は、思考シグネチャ フィールドに
"context_engineering_is_the_way_to_go"または"skip_thought_signature_validator"の次のダミー シグネチャを設定して、検証をスキップできます。インターリーブされた並列関数呼び出しとレスポンスを送信していますが、API から 400 が返されます。なぜですか?
API が並列関数呼び出し「FC1 + シグネチャ、FC2」を返す場合、ユーザー レスポンスは「FC1 + シグネチャ、FC2、FR1、FR2」になります。「FC1 + 署名、FR1、FC2、FR2」のようにインターリーブされている場合、API は 400 エラーを返します。
ストリーミング時にモデルが関数呼び出しを返さない場合、思考シグネチャが見つからない
ストリーミング リクエストで FC を含まないモデル レスポンスの場合、モデルはテキスト コンテンツ部分が空の部分に思考シグネチャを返すことがあります。モデルから
finish_reasonが返されるまで、リクエスト全体を解析することをおすすめします。
さまざまなモデルの思考シグネチャ
Gemini 3 Pro と Flash、Gemini 3 Pro Image、Gemini 2.5 モデルは、思考シグネチャの動作がそれぞれ異なります。Gemini 3 Pro Image については、画像生成ガイドの思考プロセス セクションをご覧ください。
Gemini 3 モデルと Gemini 2.5 モデルでは、関数呼び出しの思考シグネチャの動作が異なります。
-
レスポンスに関数呼び出しがある場合、
- Gemini 3 では、最初の関数呼び出し部分に常にシグネチャが含まれます。その部品は必ず返送する必要があります。
- Gemini 2.5 では、最初の部分にシグネチャが含まれます(タイプに関係なく)。その部分を返品するかどうかは任意です。
-
レスポンスに関数呼び出しがない場合、
- モデルが思考を生成した場合、Gemini 3 の最後の部分に署名が追加されます。
- Gemini 2.5 には、どの部分にも署名がありません。
Gemini 2.5 モデルの思考シグネチャの動作については、思考のページをご覧ください。
