Gemini, ऑडियो इनपुट का विश्लेषण करके टेक्स्ट में जवाब जनरेट कर सकता है.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file="path/to/sample.mp3")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview", contents=["Describe this audio clip", myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mp3" },
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Describe this audio clip",
]),
});
console.log(response.text);
}
await main();
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
REST
AUDIO_PATH="path/to/sample.mp3"
MIME_TYPE=$(file -b --mime-type "${AUDIO_PATH}")
NUM_BYTES=$(wc -c < "${AUDIO_PATH}")
DISPLAY_NAME=AUDIO
tmp_header_file=upload-header.tmp
# Initial resumable request defining metadata.
# The upload url is in the response headers dump them to a file.
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/upload/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-D upload-header.tmp \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Protocol: resumable" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: start" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Type: ${MIME_TYPE}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{'file': {'display_name': '${DISPLAY_NAME}'}}" 2> /dev/null
upload_url=$(grep -i "x-goog-upload-url: " "${tmp_header_file}" | cut -d" " -f2 | tr -d "\r")
rm "${tmp_header_file}"
# Upload the actual bytes.
curl "${upload_url}" \
-H "Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Offset: 0" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: upload, finalize" \
--data-binary "@${AUDIO_PATH}" 2> /dev/null > file_info.json
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
# Now generate content using that file
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{"text": "Describe this audio clip"},
{"file_data":{"mime_type": "${MIME_TYPE}", "file_uri": '$file_uri'}}]
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
खास जानकारी
Gemini, ऑडियो इनपुट का विश्लेषण करके उसे समझ सकता है और उसके जवाब में टेक्स्ट जनरेट कर सकता है. इससे, यहां दिए गए उदाहरणों की तरह कई काम किए जा सकते हैं:
- ऑडियो कॉन्टेंट के बारे में जानकारी देना, खास जानकारी देना या सवालों के जवाब देना.
- ऑडियो (बोले गए शब्दों को टेक्स्ट में बदलने की सुविधा) की ट्रांसक्रिप्शन और अनुवाद की सुविधा उपलब्ध कराता है.
- अलग-अलग लोगों की आवाज़ का पता लगाना और उन्हें लेबल करना (स्पीकर डायराइज़ेशन).
- इससे, बोली और संगीत में मौजूद भावना का पता लगाया जा सकता है.
- ऑडियो के खास सेगमेंट का विश्लेषण करना और टाइमस्टैंप देना.
फ़िलहाल, Gemini API का इस्तेमाल करके, रीयल-टाइम में ट्रांसक्रिप्शन नहीं किया जा सकता. रीयल-टाइम में आवाज़ और वीडियो से इंटरैक्ट करने के लिए, Live API देखें. रीयल-टाइम ट्रांसक्रिप्शन की सुविधा के साथ, बोली को लिखाई में बदलने वाले मॉडल का इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API का इस्तेमाल करें.
बोले जा रहे शब्दों को टेक्स्ट में बदलना
इस उदाहरण ऐप्लिकेशन में दिखाया गया है कि Gemini API को, ऑडियो को ट्रांसक्राइब करने, उसका अनुवाद करने, और उसकी खास जानकारी देने के लिए कैसे प्रॉम्प्ट किया जाए. इसमें टाइमस्टैंप, स्पीकर की पहचान, और स्ट्रक्चर्ड आउटपुट का इस्तेमाल करके, भावना का पता लगाने जैसी सुविधाएं शामिल हैं.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
YOUTUBE_URL = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM"
def main():
prompt = """
Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.
Requirements:
1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).
2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).
3. Detect the primary language of each segment.
4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.
5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.
6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning.
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[
types.Content(
parts=[
types.Part(
file_data=types.FileData(
file_uri=YOUTUBE_URL
)
),
types.Part(
text=prompt
)
]
)
],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=types.Schema(
type=types.Type.OBJECT,
properties={
"summary": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.STRING,
description="A concise summary of the audio content.",
),
"segments": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.ARRAY,
description="List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
items=types.Schema(
type=types.Type.OBJECT,
properties={
"speaker": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"timestamp": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"content": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"language": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"language_code": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"translation": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"emotion": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.STRING,
enum=["happy", "sad", "angry", "neutral"]
),
},
required=["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"],
),
),
},
required=["summary", "segments"],
),
),
)
print(response.text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
Type
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const YOUTUBE_URL = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM";
async function main() {
const prompt = `
Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.
Requirements:
1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).
2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).
3. Detect the primary language of each segment.
4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.
5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.
6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning.
`;
const Emotion = {
Happy: 'happy',
Sad: 'sad',
Angry: 'angry',
Neutral: 'neutral'
};
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: {
parts: [
{
fileData: {
fileUri: YOUTUBE_URL,
},
},
{
text: prompt,
},
],
},
config: {
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseSchema: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
summary: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "A concise summary of the audio content.",
},
segments: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
description: "List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
items: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
speaker: { type: Type.STRING },
timestamp: { type: Type.STRING },
content: { type: Type.STRING },
language: { type: Type.STRING },
language_code: { type: Type.STRING },
translation: { type: Type.STRING },
emotion: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: Object.values(Emotion)
},
},
required: ["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"],
},
},
},
required: ["summary", "segments"],
},
},
});
const json = JSON.parse(response.text);
console.log(json);
}
await main();
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{
"file_data": {
"file_uri": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM",
"mime_type": "video/mp4"
}
},
{
"text": "Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.\n\nRequirements:\n1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).\n2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).\n3. Detect the primary language of each segment.\n4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.\n5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.\n6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning."
}
]
}
],
"generation_config": {
"response_mime_type": "application/json",
"response_schema": {
"type": "OBJECT",
"properties": {
"summary": {
"type": "STRING",
"description": "A concise summary of the audio content."
},
"segments": {
"type": "ARRAY",
"description": "List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
"items": {
"type": "OBJECT",
"properties": {
"speaker": { "type": "STRING" },
"timestamp": { "type": "STRING" },
"content": { "type": "STRING" },
"language": { "type": "STRING" },
"language_code": { "type": "STRING" },
"translation": { "type": "STRING" },
"emotion": {
"type": "STRING",
"enum": ["happy", "sad", "angry", "neutral"]
}
},
"required": ["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"]
}
}
},
"required": ["summary", "segments"]
}
}
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
AI Studio Build को प्रॉम्प्ट देकर, इस उदाहरण में दिए गए ट्रांसक्रिप्शन ऐप्लिकेशन की तरह कोई ऐप्लिकेशन बनाया जा सकता है. इसके लिए, आपको सिर्फ़ एक बटन पर क्लिक करना होगा.
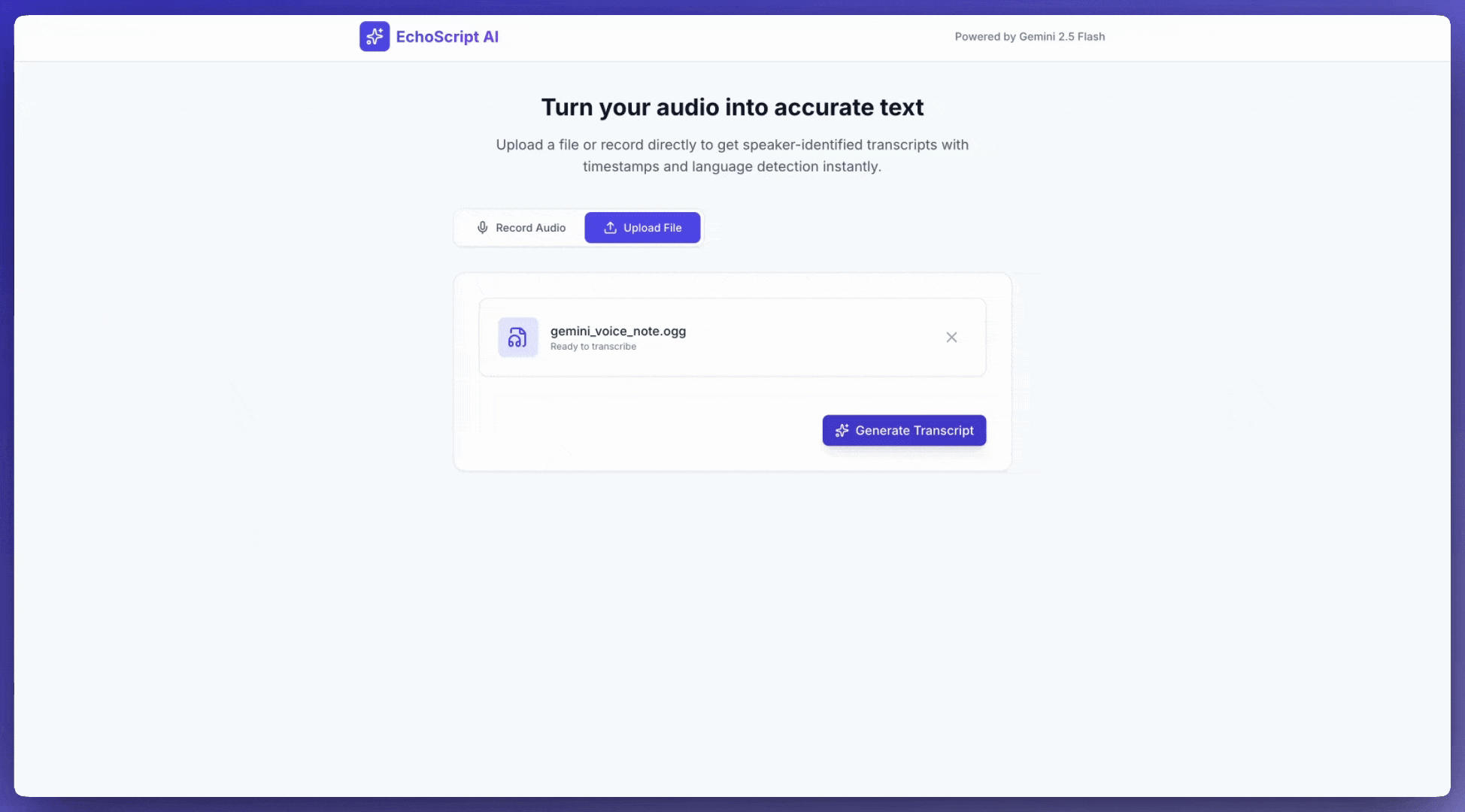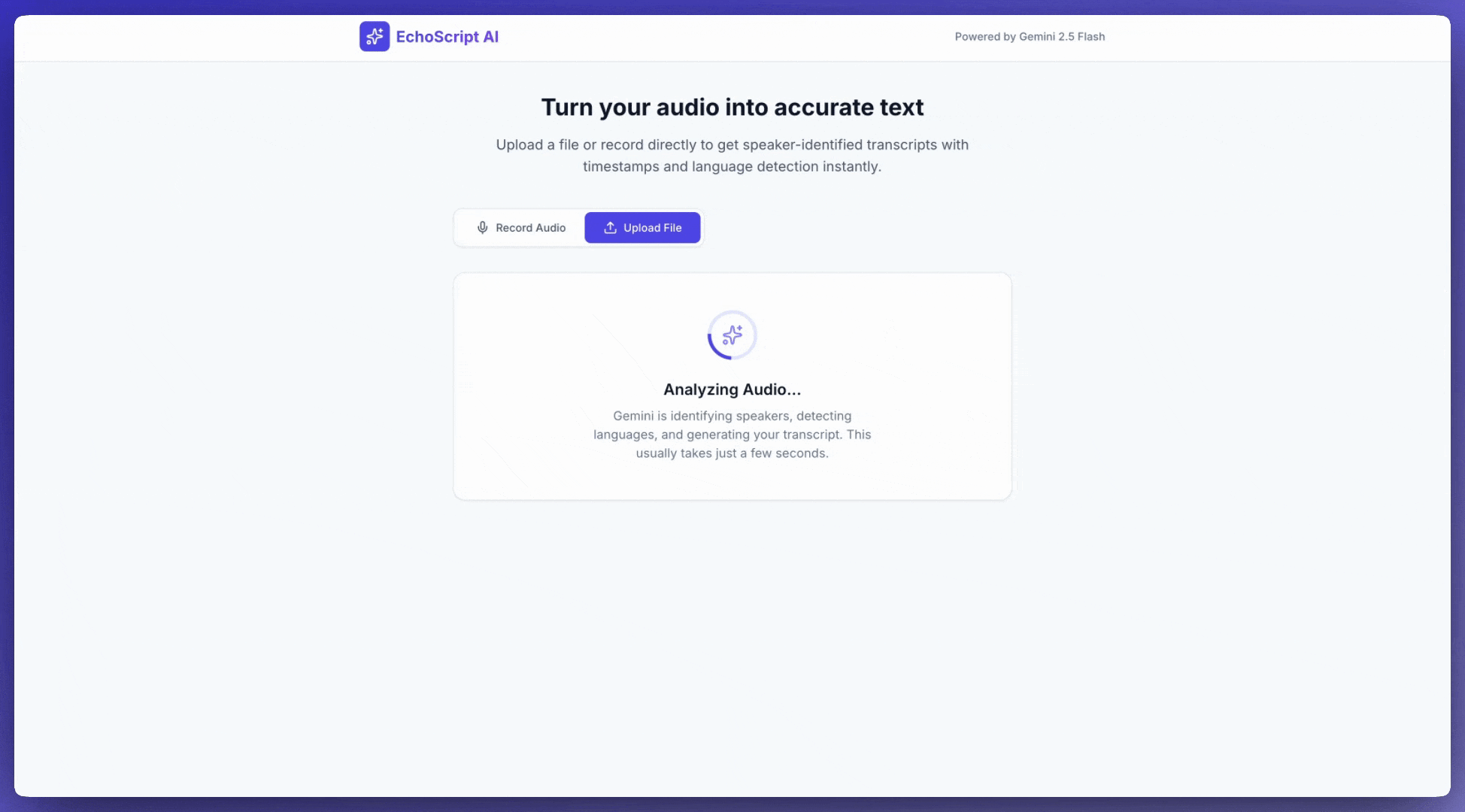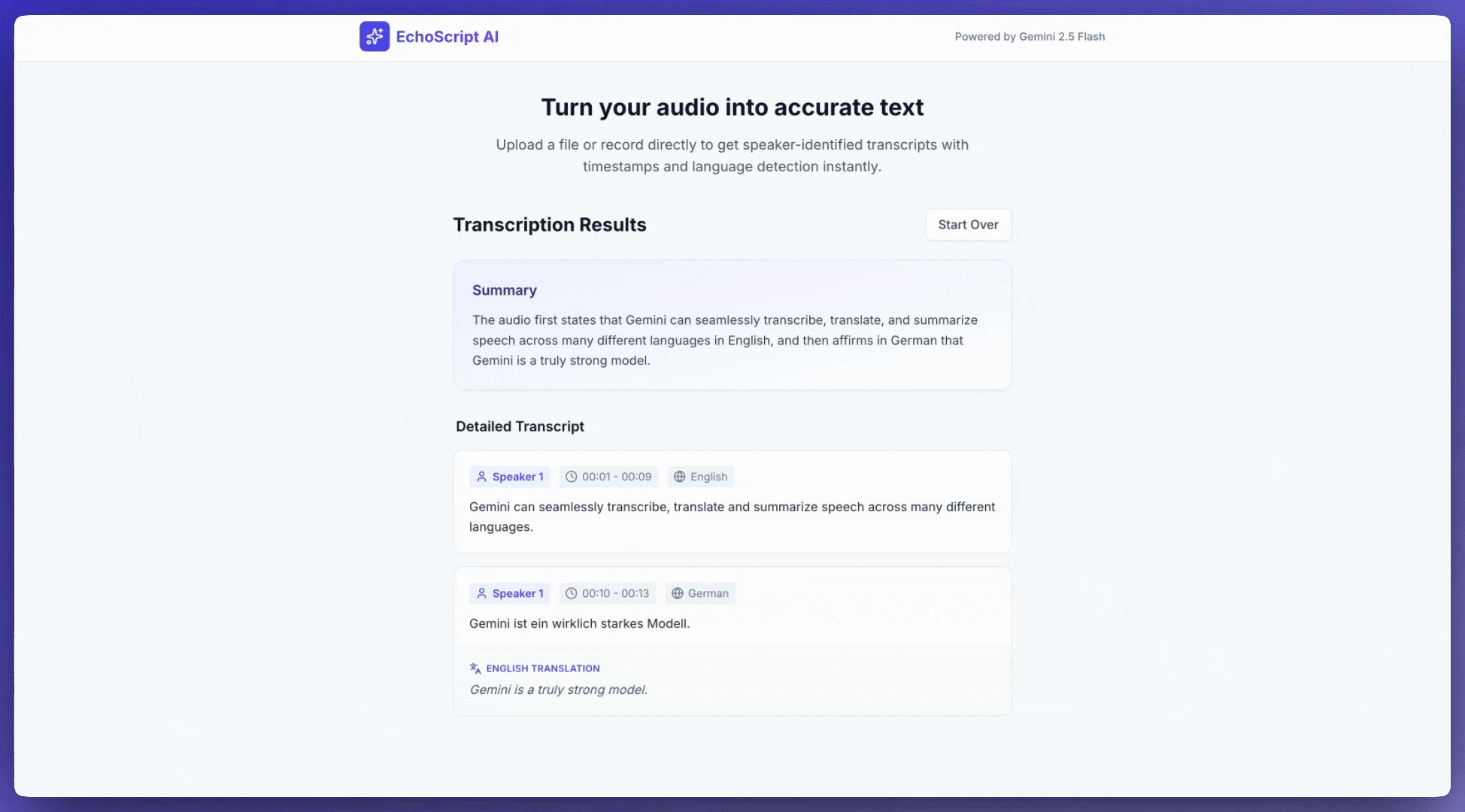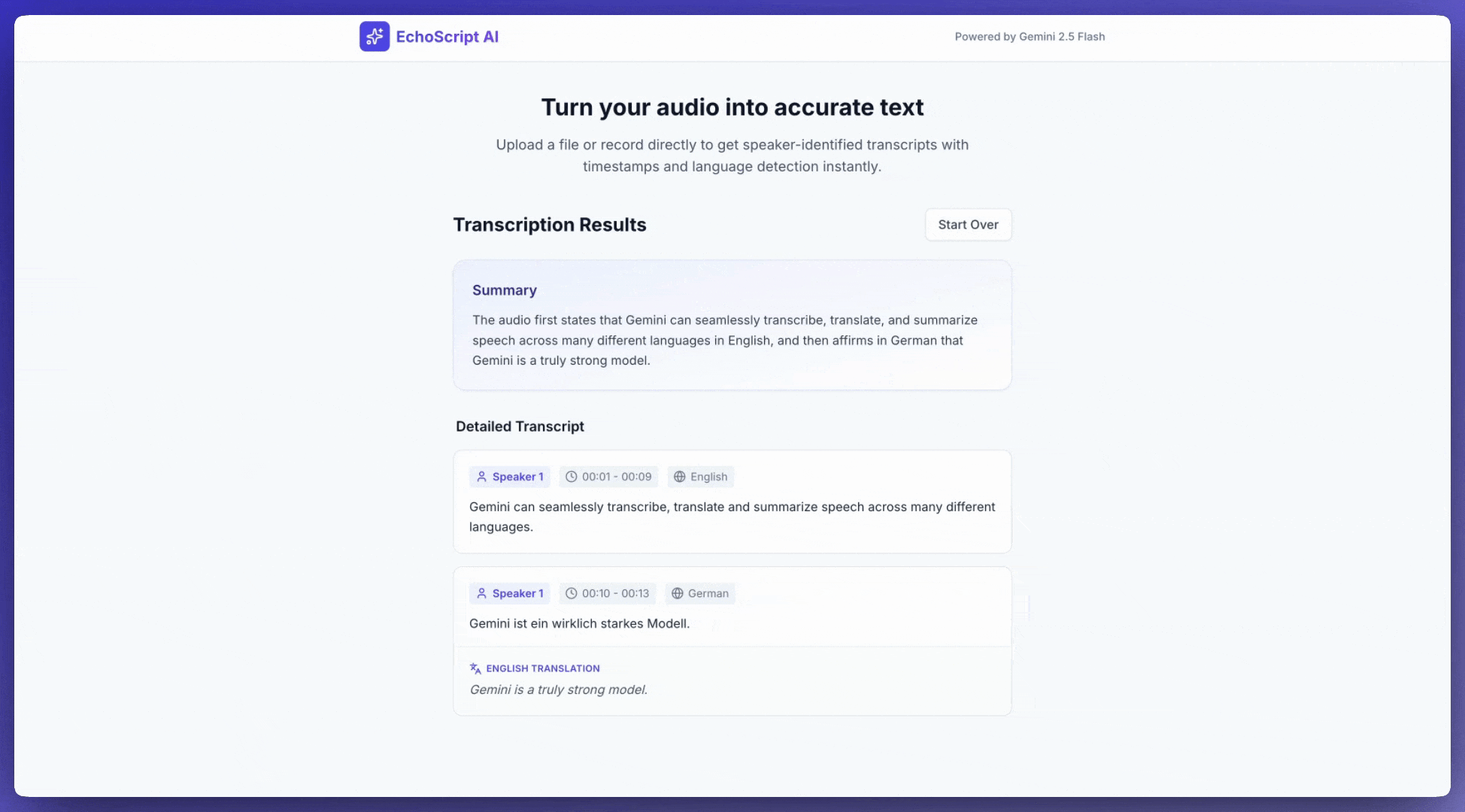
ऑडियो इनपुट करना
Gemini को ऑडियो डेटा इन तरीकों से दिया जा सकता है:
generateContentसे अनुरोध करने से पहले, ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करें.generateContentको किए गए अनुरोध के साथ, इनलाइन ऑडियो डेटा पास करें.
फ़ाइल इनपुट करने के अन्य तरीकों के बारे में जानने के लिए, फ़ाइल इनपुट करने के तरीके गाइड देखें.
ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करना
ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करने के लिए, Files API का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. जब अनुरोध का कुल साइज़ (इसमें फ़ाइलें, टेक्स्ट प्रॉम्प्ट, सिस्टम के निर्देश वगैरह शामिल हैं) 20 एमबी से ज़्यादा हो, तब हमेशा Files API का इस्तेमाल करें.
नीचे दिए गए कोड से, एक ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड की जाती है. इसके बाद, इस फ़ाइल का इस्तेमाल generateContent को कॉल करने के लिए किया जाता है.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file="path/to/sample.mp3")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview", contents=["Describe this audio clip", myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mp3" },
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Describe this audio clip",
]),
});
console.log(response.text);
}
await main();
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
REST
AUDIO_PATH="path/to/sample.mp3"
MIME_TYPE=$(file -b --mime-type "${AUDIO_PATH}")
NUM_BYTES=$(wc -c < "${AUDIO_PATH}")
DISPLAY_NAME=AUDIO
tmp_header_file=upload-header.tmp
# Initial resumable request defining metadata.
# The upload url is in the response headers dump them to a file.
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/upload/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-D upload-header.tmp \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Protocol: resumable" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: start" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Type: ${MIME_TYPE}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{'file': {'display_name': '${DISPLAY_NAME}'}}" 2> /dev/null
upload_url=$(grep -i "x-goog-upload-url: " "${tmp_header_file}" | cut -d" " -f2 | tr -d "\r")
rm "${tmp_header_file}"
# Upload the actual bytes.
curl "${upload_url}" \
-H "Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Offset: 0" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: upload, finalize" \
--data-binary "@${AUDIO_PATH}" 2> /dev/null > file_info.json
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
# Now generate content using that file
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{"text": "Describe this audio clip"},
{"file_data":{"mime_type": "${MIME_TYPE}", "file_uri": '$file_uri'}}]
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
मीडिया फ़ाइलों के साथ काम करने के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, Files API देखें.
ऑडियो डेटा को इनलाइन पास करना
ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करने के बजाय, generateContent को किए गए अनुरोध में ऑडियो डेटा को इनलाइन किया जा सकता है:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
with open('path/to/small-sample.mp3', 'rb') as f:
audio_bytes = f.read()
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[
'Describe this audio clip',
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=audio_bytes,
mime_type='audio/mp3',
)
]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
import * as fs from "node:fs";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const base64AudioFile = fs.readFileSync("path/to/small-sample.mp3", {
encoding: "base64",
});
const contents = [
{ text: "Please summarize the audio." },
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: "audio/mp3",
data: base64AudioFile,
},
},
];
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: contents,
});
console.log(response.text);
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
audioBytes, _ := os.ReadFile("/path/to/small-sample.mp3")
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
&genai.Part{
InlineData: &genai.Blob{
MIMEType: "audio/mp3",
Data: audioBytes,
},
},
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
इनलाइन ऑडियो डेटा के बारे में कुछ बातों का ध्यान रखें:
- अनुरोध का साइज़ ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 20 एमबी हो सकता है. इसमें टेक्स्ट प्रॉम्प्ट, सिस्टम के निर्देश, और इनलाइन फ़ाइलें शामिल हैं. अगर आपकी फ़ाइल का साइज़, अनुरोध के कुल साइज़ को 20 एमबी से ज़्यादा कर देता है, तो Files API का इस्तेमाल करके, अनुरोध में इस्तेमाल करने के लिए कोई ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करें.
- अगर आपको किसी ऑडियो सैंपल का इस्तेमाल कई बार करना है, तो ऑडियो फ़ाइल अपलोड करना ज़्यादा बेहतर है.
ट्रांसक्रिप्ट पाना
ऑडियो डेटा की ट्रांसक्रिप्ट पाने के लिए, प्रॉम्प्ट में बस इतना पूछें:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file='path/to/sample.mp3')
prompt = 'Generate a transcript of the speech.'
response = client.models.generate_content(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[prompt, myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Generate a transcript of the speech.",
]),
});
console.log("result.text=", result.text);
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Generate a transcript of the speech."),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
टाइमस्टैंप देखें
MM:SS फ़ॉर्मैट वाले टाइमस्टैंप का इस्तेमाल करके, ऑडियो फ़ाइल के किसी खास सेक्शन का रेफ़रंस दिया जा सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, यहां दिए गए प्रॉम्प्ट में ऐसी ट्रांसक्रिप्ट का अनुरोध किया गया है
- फ़ाइल की शुरुआत से 2 मिनट 30 सेकंड पर शुरू होता है.
यह फ़ाइल की शुरुआत से 3 मिनट 29 सेकंड पर खत्म होती है.
Python
# Create a prompt containing timestamps.
prompt = "Provide a transcript of the speech from 02:30 to 03:29."
JavaScript
// Create a prompt containing timestamps.
const prompt = "Provide a transcript of the speech from 02:30 to 03:29."
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Provide a transcript of the speech " +
"between the timestamps 02:30 and 03:29."),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
टोकन गिनें
किसी ऑडियो फ़ाइल में मौजूद टोकन की संख्या जानने के लिए, countTokens तरीके को कॉल करें. उदाहरण के लिए:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.count_tokens(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[myfile]
)
print(response)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const countTokensResponse = await ai.models.countTokens({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
]),
});
console.log(countTokensResponse.totalTokens);
ऐप पर जाएं
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
tokens, _ := client.Models.CountTokens(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Printf("File %s is %d tokens\n", localAudioPath, tokens.TotalTokens)
}
इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले ऑडियो फ़ॉर्मैट
Gemini, ऑडियो फ़ॉर्मैट के इन MIME टाइप के साथ काम करता है:
- WAV -
audio/wav - MP3 -
audio/mp3 - AIFF -
audio/aiff - AAC -
audio/aac - OGG Vorbis -
audio/ogg - FLAC -
audio/flac
ऑडियो के बारे में तकनीकी जानकारी
- Gemini, ऑडियो के हर सेकंड को 32 टोकन के तौर पर दिखाता है. उदाहरण के लिए, एक मिनट के ऑडियो को 1,920 टोकन के तौर पर दिखाया जाता है.
- Gemini, बिना बोले गए कॉम्पोनेंट को "समझ" सकता है. जैसे, पक्षियों का चहचहाना या सायरन.
- एक प्रॉम्प्ट में, ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 9.5 घंटे का ऑडियो डेटा इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. Gemini, एक प्रॉम्प्ट में ऑडियो फ़ाइलों की संख्या को सीमित नहीं करता. हालांकि, एक प्रॉम्प्ट में मौजूद सभी ऑडियो फ़ाइलों की कुल अवधि 9.5 घंटे से ज़्यादा नहीं होनी चाहिए.
- Gemini, ऑडियो फ़ाइलों को 16 केबीपीएस के डेटा रिज़ॉल्यूशन में डाउनसैंपल करता है.
- अगर ऑडियो सोर्स में एक से ज़्यादा चैनल हैं, तो Gemini उन चैनलों को एक ही चैनल में जोड़ देता है.
आगे क्या करना है
इस गाइड में, ऑडियो डेटा के जवाब में टेक्स्ट जनरेट करने का तरीका बताया गया है. ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, ये संसाधन देखें:
- फ़ाइल प्रॉम्प्ट करने की रणनीतियां: Gemini API, टेक्स्ट, इमेज, ऑडियो, और वीडियो डेटा के साथ प्रॉम्प्ट करने की सुविधा देता है. इसे मल्टीमॉडल प्रॉम्प्टिंग भी कहा जाता है.
- सिस्टम के लिए निर्देश: सिस्टम के लिए निर्देश देने की सुविधा की मदद से, अपनी खास ज़रूरतों और इस्तेमाल के उदाहरणों के आधार पर, मॉडल के व्यवहार को कंट्रोल किया जा सकता है.
- सुरक्षा से जुड़ी गाइडलाइन: कभी-कभी जनरेटिव एआई मॉडल ऐसे आउटपुट जनरेट करते हैं जिनकी उम्मीद नहीं होती. जैसे, गलत, पक्षपात वाले या आपत्तिजनक आउटपुट. इस तरह के आउटपुट से होने वाले नुकसान के जोखिम को कम करने के लिए, प्रोसेस होने के बाद और मैन्युअल तरीके से समीक्षा करना ज़रूरी है.
