Gemini can analyze audio input and generate text responses.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file="path/to/sample.mp3")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview", contents=["Describe this audio clip", myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mp3" },
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Describe this audio clip",
]),
});
console.log(response.text);
}
await main();
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
REST
AUDIO_PATH="path/to/sample.mp3"
MIME_TYPE=$(file -b --mime-type "${AUDIO_PATH}")
NUM_BYTES=$(wc -c < "${AUDIO_PATH}")
DISPLAY_NAME=AUDIO
tmp_header_file=upload-header.tmp
# Initial resumable request defining metadata.
# The upload url is in the response headers dump them to a file.
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/upload/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-D upload-header.tmp \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Protocol: resumable" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: start" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Type: ${MIME_TYPE}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{'file': {'display_name': '${DISPLAY_NAME}'}}" 2> /dev/null
upload_url=$(grep -i "x-goog-upload-url: " "${tmp_header_file}" | cut -d" " -f2 | tr -d "\r")
rm "${tmp_header_file}"
# Upload the actual bytes.
curl "${upload_url}" \
-H "Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Offset: 0" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: upload, finalize" \
--data-binary "@${AUDIO_PATH}" 2> /dev/null > file_info.json
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
# Now generate content using that file
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{"text": "Describe this audio clip"},
{"file_data":{"mime_type": "${MIME_TYPE}", "file_uri": '$file_uri'}}]
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
Overview
Gemini can analyze and understand audio input and generate text responses to it, enabling use cases like the following:
- Describe, summarize, or answer questions about audio content.
- Provide a transcription and translation of the audio (speech to text).
- Detect and label different speakers (speaker diarization).
- Detect emotion in speech and music.
- Analyze specific segments of the audio, and provide timestamps.
As of now the Gemini API doesn't support real-time transcription use cases. For real-time voice and video interactions refer to the Live API. For dedicated speech to text models with support for real-time transcription, use the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API.
Transcribe speech to text
This example application shows how to prompt the Gemini API to transcribe, translate, and summarize speech, including timestamps, speaker diarization, and emotion detection using structured outputs.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
YOUTUBE_URL = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM"
def main():
prompt = """
Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.
Requirements:
1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).
2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).
3. Detect the primary language of each segment.
4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.
5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.
6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning.
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[
types.Content(
parts=[
types.Part(
file_data=types.FileData(
file_uri=YOUTUBE_URL
)
),
types.Part(
text=prompt
)
]
)
],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=types.Schema(
type=types.Type.OBJECT,
properties={
"summary": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.STRING,
description="A concise summary of the audio content.",
),
"segments": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.ARRAY,
description="List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
items=types.Schema(
type=types.Type.OBJECT,
properties={
"speaker": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"timestamp": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"content": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"language": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"language_code": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"translation": types.Schema(type=types.Type.STRING),
"emotion": types.Schema(
type=types.Type.STRING,
enum=["happy", "sad", "angry", "neutral"]
),
},
required=["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"],
),
),
},
required=["summary", "segments"],
),
),
)
print(response.text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
Type
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const YOUTUBE_URL = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM";
async function main() {
const prompt = `
Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.
Requirements:
1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).
2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).
3. Detect the primary language of each segment.
4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.
5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.
6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning.
`;
const Emotion = {
Happy: 'happy',
Sad: 'sad',
Angry: 'angry',
Neutral: 'neutral'
};
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: {
parts: [
{
fileData: {
fileUri: YOUTUBE_URL,
},
},
{
text: prompt,
},
],
},
config: {
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseSchema: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
summary: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "A concise summary of the audio content.",
},
segments: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
description: "List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
items: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
speaker: { type: Type.STRING },
timestamp: { type: Type.STRING },
content: { type: Type.STRING },
language: { type: Type.STRING },
language_code: { type: Type.STRING },
translation: { type: Type.STRING },
emotion: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: Object.values(Emotion)
},
},
required: ["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"],
},
},
},
required: ["summary", "segments"],
},
},
});
const json = JSON.parse(response.text);
console.log(json);
}
await main();
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{
"file_data": {
"file_uri": "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ku-N-eS1lgM",
"mime_type": "video/mp4"
}
},
{
"text": "Process the audio file and generate a detailed transcription.\n\nRequirements:\n1. Identify distinct speakers (e.g., Speaker 1, Speaker 2, or names if context allows).\n2. Provide accurate timestamps for each segment (Format: MM:SS).\n3. Detect the primary language of each segment.\n4. If the segment is in a language different than English, also provide the English translation.\n5. Identify the primary emotion of the speaker in this segment. You MUST choose exactly one of the following: Happy, Sad, Angry, Neutral.\n6. Provide a brief summary of the entire audio at the beginning."
}
]
}
],
"generation_config": {
"response_mime_type": "application/json",
"response_schema": {
"type": "OBJECT",
"properties": {
"summary": {
"type": "STRING",
"description": "A concise summary of the audio content."
},
"segments": {
"type": "ARRAY",
"description": "List of transcribed segments with speaker and timestamp.",
"items": {
"type": "OBJECT",
"properties": {
"speaker": { "type": "STRING" },
"timestamp": { "type": "STRING" },
"content": { "type": "STRING" },
"language": { "type": "STRING" },
"language_code": { "type": "STRING" },
"translation": { "type": "STRING" },
"emotion": {
"type": "STRING",
"enum": ["happy", "sad", "angry", "neutral"]
}
},
"required": ["speaker", "timestamp", "content", "language", "language_code", "emotion"]
}
}
},
"required": ["summary", "segments"]
}
}
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
You can prompt AI Studio Build to create an app just like this example transcription app , with the click of a button.
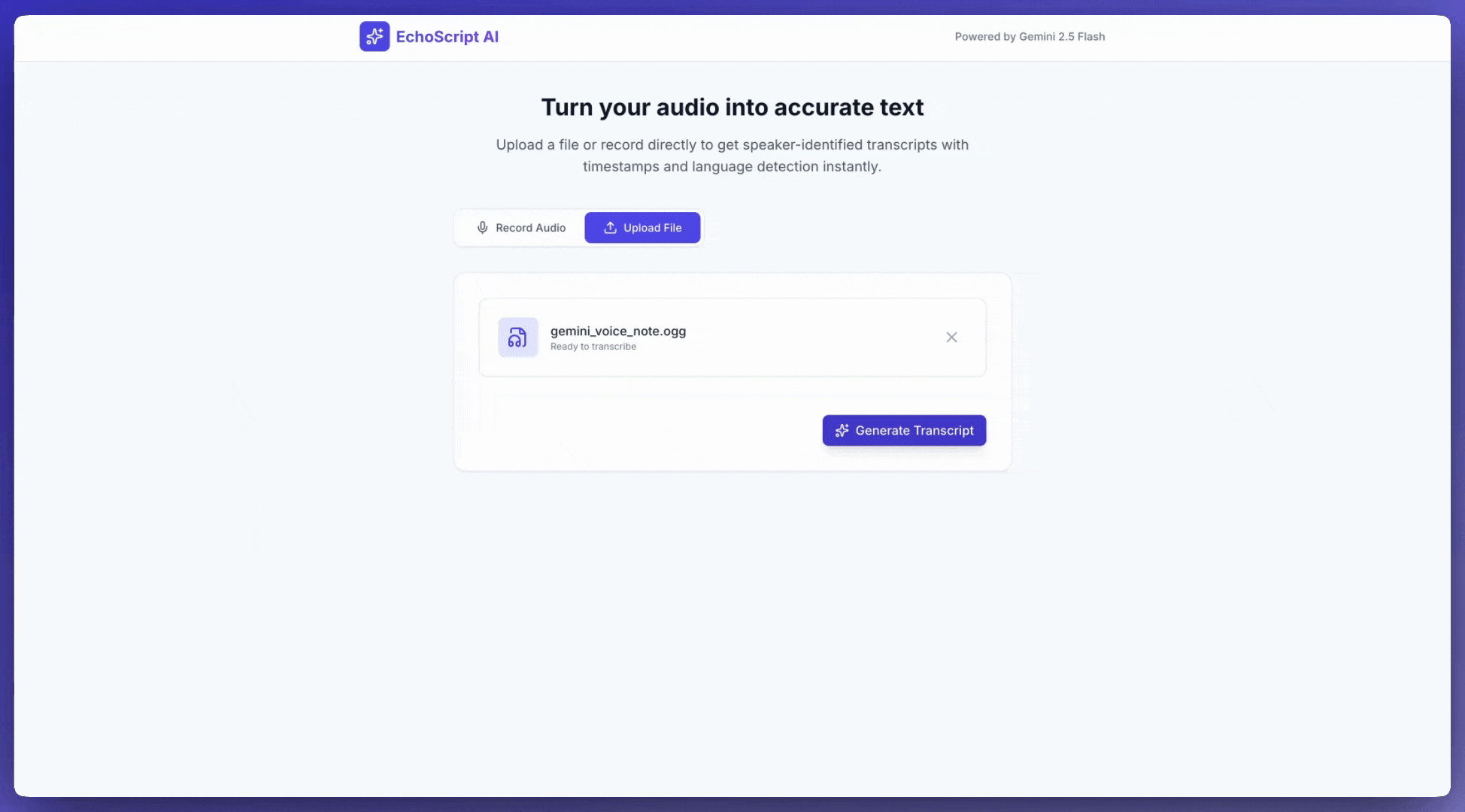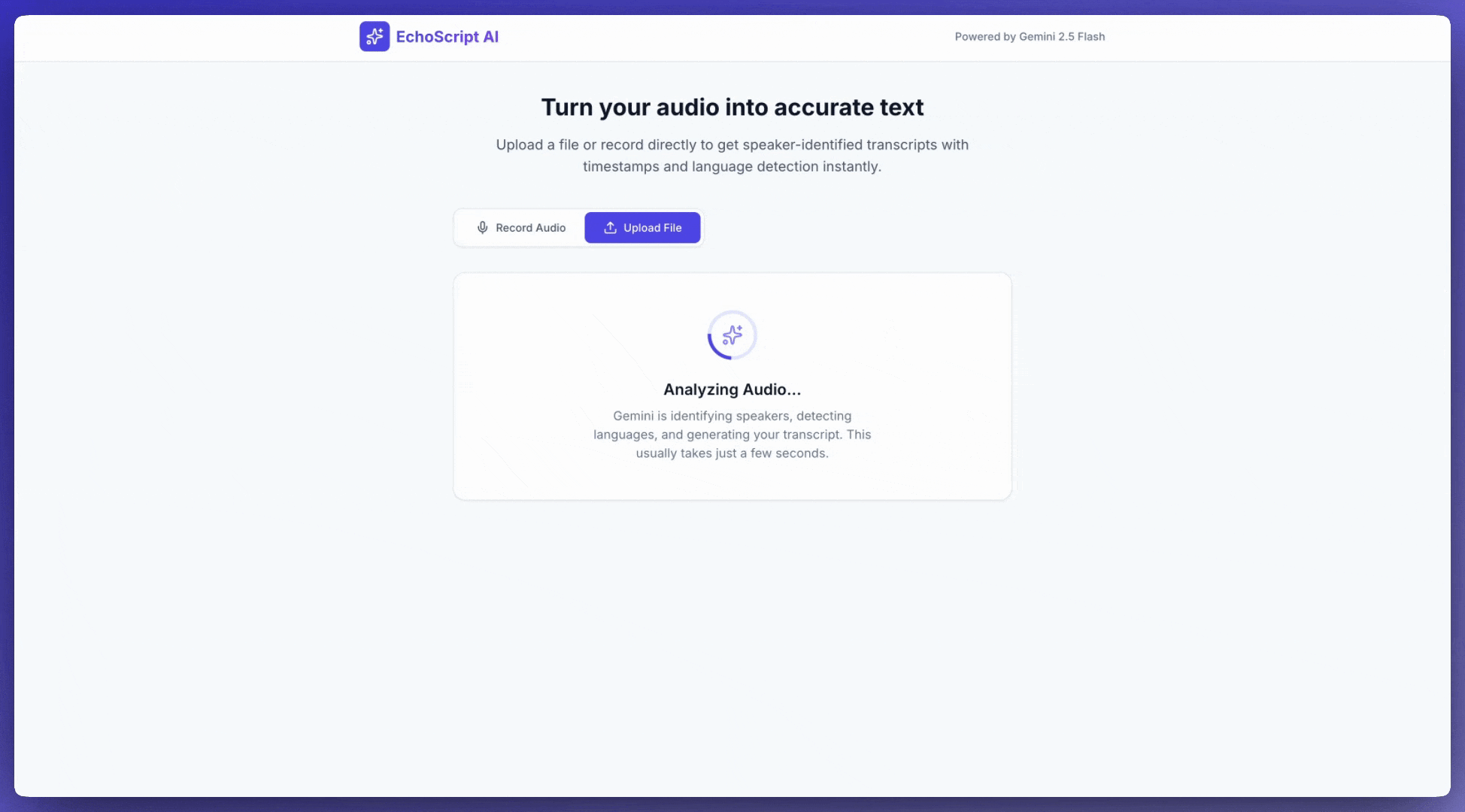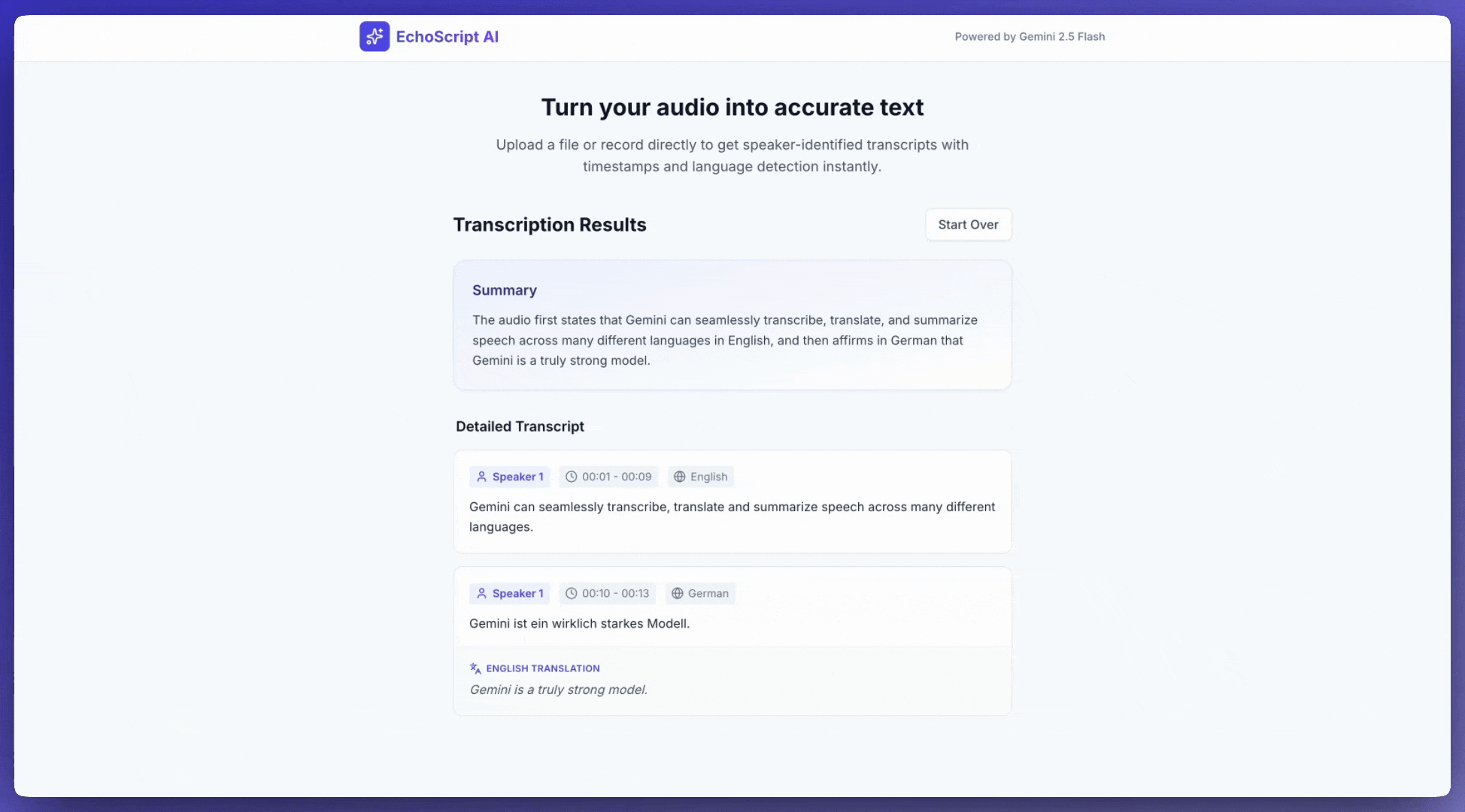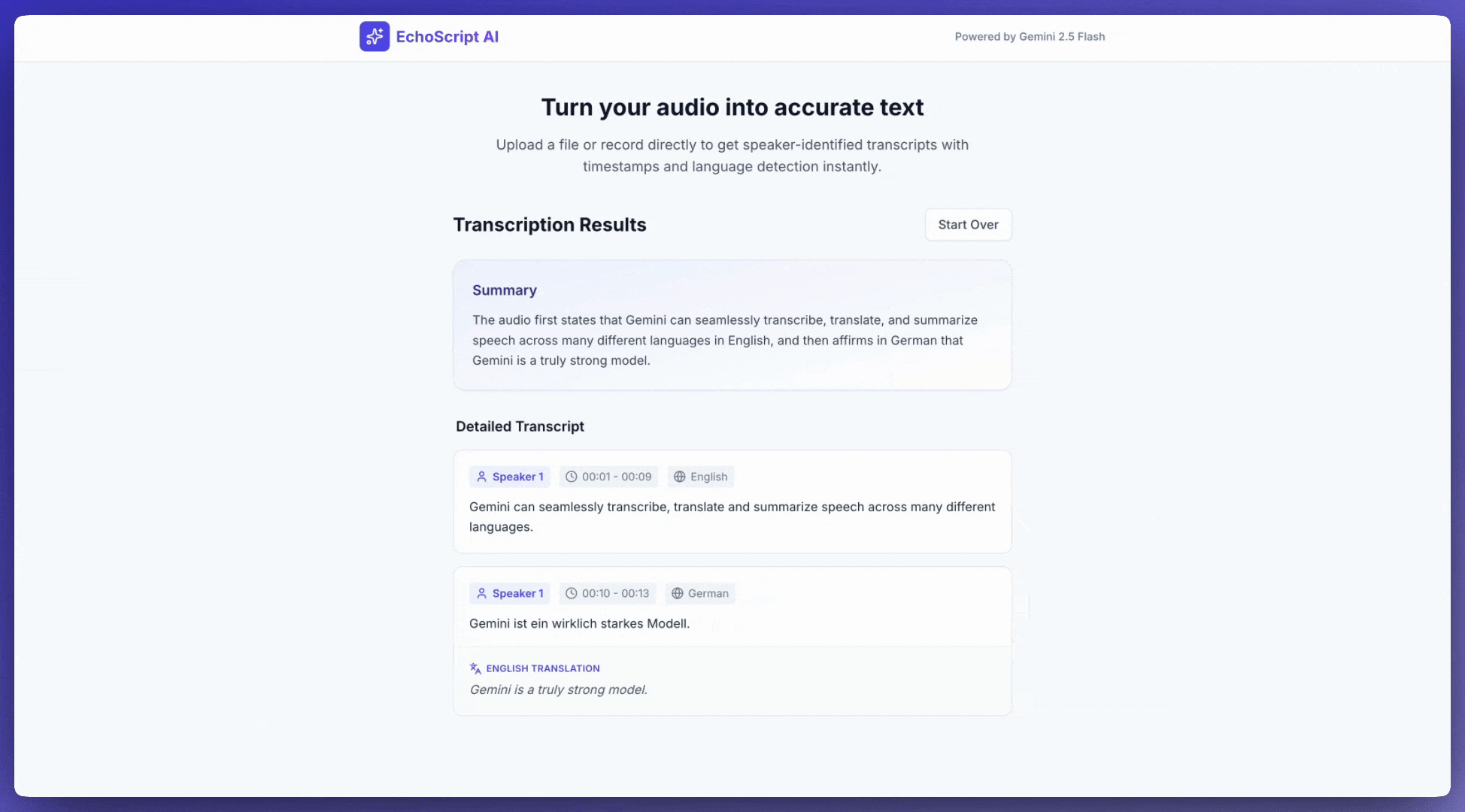
Input audio
You can provide audio data to Gemini in the following ways:
- Upload an audio file before making a request to
generateContent. - Pass inline audio data with the request to
generateContent.
To learn about other file input methods, see the File input methods guide.
Upload an audio file
You can use the Files API to upload an audio file. Always use the Files API when the total request size (including the files, text prompt, system instructions, etc.) is larger than 20 MB.
The following code uploads an audio file and then uses the file in a call to
generateContent.
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file="path/to/sample.mp3")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview", contents=["Describe this audio clip", myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function main() {
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mp3" },
});
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Describe this audio clip",
]),
});
console.log(response.text);
}
await main();
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
REST
AUDIO_PATH="path/to/sample.mp3"
MIME_TYPE=$(file -b --mime-type "${AUDIO_PATH}")
NUM_BYTES=$(wc -c < "${AUDIO_PATH}")
DISPLAY_NAME=AUDIO
tmp_header_file=upload-header.tmp
# Initial resumable request defining metadata.
# The upload url is in the response headers dump them to a file.
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/upload/v1beta/files" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-D upload-header.tmp \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Protocol: resumable" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: start" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Header-Content-Type: ${MIME_TYPE}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{'file': {'display_name': '${DISPLAY_NAME}'}}" 2> /dev/null
upload_url=$(grep -i "x-goog-upload-url: " "${tmp_header_file}" | cut -d" " -f2 | tr -d "\r")
rm "${tmp_header_file}"
# Upload the actual bytes.
curl "${upload_url}" \
-H "Content-Length: ${NUM_BYTES}" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Offset: 0" \
-H "X-Goog-Upload-Command: upload, finalize" \
--data-binary "@${AUDIO_PATH}" 2> /dev/null > file_info.json
file_uri=$(jq ".file.uri" file_info.json)
echo file_uri=$file_uri
# Now generate content using that file
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{"text": "Describe this audio clip"},
{"file_data":{"mime_type": "${MIME_TYPE}", "file_uri": '$file_uri'}}]
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
echo
jq ".candidates[].content.parts[].text" response.json
To learn more about working with media files, see Files API.
Pass audio data inline
Instead of uploading an audio file, you can pass inline audio data in the
request to generateContent:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
with open('path/to/small-sample.mp3', 'rb') as f:
audio_bytes = f.read()
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[
'Describe this audio clip',
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=audio_bytes,
mime_type='audio/mp3',
)
]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
import * as fs from "node:fs";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const base64AudioFile = fs.readFileSync("path/to/small-sample.mp3", {
encoding: "base64",
});
const contents = [
{ text: "Please summarize the audio." },
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: "audio/mp3",
data: base64AudioFile,
},
},
];
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: contents,
});
console.log(response.text);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
audioBytes, _ := os.ReadFile("/path/to/small-sample.mp3")
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Describe this audio clip"),
&genai.Part{
InlineData: &genai.Blob{
MIMEType: "audio/mp3",
Data: audioBytes,
},
},
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
A few things to keep in mind about inline audio data:
- The maximum request size is 20 MB, which includes text prompts, system instructions, and files provided inline. If your file's size will make the total request size exceed 20 MB, then use the Files API to upload an audio file for use in the request.
- If you're using an audio sample multiple times, it's more efficient to upload an audio file.
Get a transcript
To get a transcript of audio data, just ask for it in the prompt:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
myfile = client.files.upload(file='path/to/sample.mp3')
prompt = 'Generate a transcript of the speech.'
response = client.models.generate_content(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[prompt, myfile]
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
"Generate a transcript of the speech.",
]),
});
console.log("result.text=", result.text);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Generate a transcript of the speech."),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
Refer to timestamps
You can refer to specific sections of an audio file using timestamps of the form
MM:SS. For example, the following prompt requests a transcript that
- Starts at 2 minutes 30 seconds from the beginning of the file.
Ends at 3 minutes 29 seconds from the beginning of the file.
Python
# Create a prompt containing timestamps.
prompt = "Provide a transcript of the speech from 02:30 to 03:29."
JavaScript
// Create a prompt containing timestamps.
const prompt = "Provide a transcript of the speech from 02:30 to 03:29."
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromText("Provide a transcript of the speech " +
"between the timestamps 02:30 and 03:29."),
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
}
Count tokens
Call the countTokens method to get a count of the number of tokens in an
audio file. For example:
Python
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.count_tokens(
model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents=[myfile]
)
print(response)
JavaScript
import {
GoogleGenAI,
createUserContent,
createPartFromUri,
} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const myfile = await ai.files.upload({
file: "path/to/sample.mp3",
config: { mimeType: "audio/mpeg" },
});
const countTokensResponse = await ai.models.countTokens({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: createUserContent([
createPartFromUri(myfile.uri, myfile.mimeType),
]),
});
console.log(countTokensResponse.totalTokens);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
localAudioPath := "/path/to/sample.mp3"
uploadedFile, _ := client.Files.UploadFromPath(
ctx,
localAudioPath,
nil,
)
parts := []*genai.Part{
genai.NewPartFromURI(uploadedFile.URI, uploadedFile.MIMEType),
}
contents := []*genai.Content{
genai.NewContentFromParts(parts, genai.RoleUser),
}
tokens, _ := client.Models.CountTokens(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
nil,
)
fmt.Printf("File %s is %d tokens\n", localAudioPath, tokens.TotalTokens)
}
Supported audio formats
Gemini supports the following audio format MIME types:
- WAV -
audio/wav - MP3 -
audio/mp3 - AIFF -
audio/aiff - AAC -
audio/aac - OGG Vorbis -
audio/ogg - FLAC -
audio/flac
Technical details about audio
- Gemini represents each second of audio as 32 tokens; for example, one minute of audio is represented as 1,920 tokens.
- Gemini can "understand" non-speech components, such as birdsong or sirens.
- The maximum supported length of audio data in a single prompt is 9.5 hours. Gemini doesn't limit the number of audio files in a single prompt; however, the total combined length of all audio files in a single prompt can't exceed 9.5 hours.
- Gemini downsamples audio files to a 16 Kbps data resolution.
- If the audio source contains multiple channels, Gemini combines those channels into a single channel.
What's next
This guide shows how to generate text in response to audio data. To learn more, see the following resources:
- File prompting strategies: The Gemini API supports prompting with text, image, audio, and video data, also known as multimodal prompting.
- System instructions: System instructions let you steer the behavior of the model based on your specific needs and use cases.
- Safety guidance: Sometimes generative AI models produce unexpected outputs, such as outputs that are inaccurate, biased, or offensive. Post-processing and human evaluation are essential to limit the risk of harm from such outputs.
