Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 adalah model bahasa-penglihatan (VLM) yang menghadirkan kemampuan agentik Gemini ke robotik. Gemini 1.5 Pro dirancang untuk penalaran tingkat lanjut di dunia fisik, sehingga memungkinkan robot menafsirkan data visual yang kompleks, melakukan penalaran spasial, dan merencanakan tindakan dari perintah bahasa alami.
Fitur dan manfaat utama:
- Peningkatan otonomi: Robot dapat bernalar, beradaptasi, dan merespons perubahan di lingkungan terbuka.
- Interaksi bahasa alami: Memudahkan penggunaan robot dengan memungkinkan penugasan tugas yang kompleks menggunakan bahasa alami.
- Pengaturan tugas: Menguraikan perintah bahasa alami menjadi subtugas dan berintegrasi dengan pengontrol dan perilaku robot yang ada untuk menyelesaikan tugas jangka panjang.
- Kemampuan serbaguna: Menemukan dan mengidentifikasi objek, memahami hubungan antarobjek, merencanakan genggaman dan lintasan, serta menafsirkan adegan dinamis.
Dokumen ini menjelaskan fungsi model dan memandu Anda melalui beberapa contoh yang menyoroti kemampuan agen model.
Jika ingin langsung mencobanya, Anda dapat mencoba model ini di Google AI Studio.
Keamanan
Meskipun Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 dibuat dengan mempertimbangkan keamanan, Anda bertanggung jawab untuk menjaga lingkungan yang aman di sekitar robot. Model AI generatif dapat membuat kesalahan, dan robot fisik dapat menyebabkan kerusakan. Keamanan adalah prioritas, dan membuat model AI generatif aman saat digunakan dengan robotika dunia nyata adalah area penelitian kami yang aktif dan penting. Untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut, buka halaman keamanan robotik Google DeepMind.
Mulai: Menemukan objek dalam adegan
Contoh berikut menunjukkan kasus penggunaan robotik umum. Contoh ini menunjukkan cara
meneruskan gambar dan perintah teks ke model menggunakan
metode generateContent
untuk mendapatkan daftar objek yang diidentifikasi dengan titik 2D yang sesuai.
Model menampilkan titik untuk item yang diidentifikasi dalam gambar, menampilkan
koordinat dan label 2D yang dinormalisasi.
Anda dapat menggunakan output ini dengan API robotik atau memanggil model vision-language-action (VLA) atau fungsi yang ditentukan pengguna pihak ketiga lainnya untuk menghasilkan tindakan yang akan dilakukan robot.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
PROMPT = """
Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned
should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format
normalized to 0-1000.
"""
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image
with open("my-image.png", 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/png',
),
PROMPT
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
REST
# First, ensure you have the image file locally.
# Encode the image to base64
IMAGE_BASE64=$(base64 -w 0 my-image.png)
curl -X POST \
"https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview:generateContent \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"mimeType": "image/png",
"data": "'"${IMAGE_BASE64}"'"
}
},
{
"text": "Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected. The answer should follow the json format: [{\"point\": [y, x], \"label\": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."
}
]
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"temperature": 0.5,
"thinkingConfig": {
"thinkingBudget": 0
}
}
}'
Outputnya akan berupa array JSON yang berisi objek, yang masing-masing memiliki point
(koordinat [y, x] yang dinormalisasi) dan label yang mengidentifikasi objek.
JSON
[
{"point": [376, 508], "label": "small banana"},
{"point": [287, 609], "label": "larger banana"},
{"point": [223, 303], "label": "pink starfruit"},
{"point": [435, 172], "label": "paper bag"},
{"point": [270, 786], "label": "green plastic bowl"},
{"point": [488, 775], "label": "metal measuring cup"},
{"point": [673, 580], "label": "dark blue bowl"},
{"point": [471, 353], "label": "light blue bowl"},
{"point": [492, 497], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [525, 429], "label": "lime"}
]
Gambar berikut adalah contoh cara titik-titik ini dapat ditampilkan:
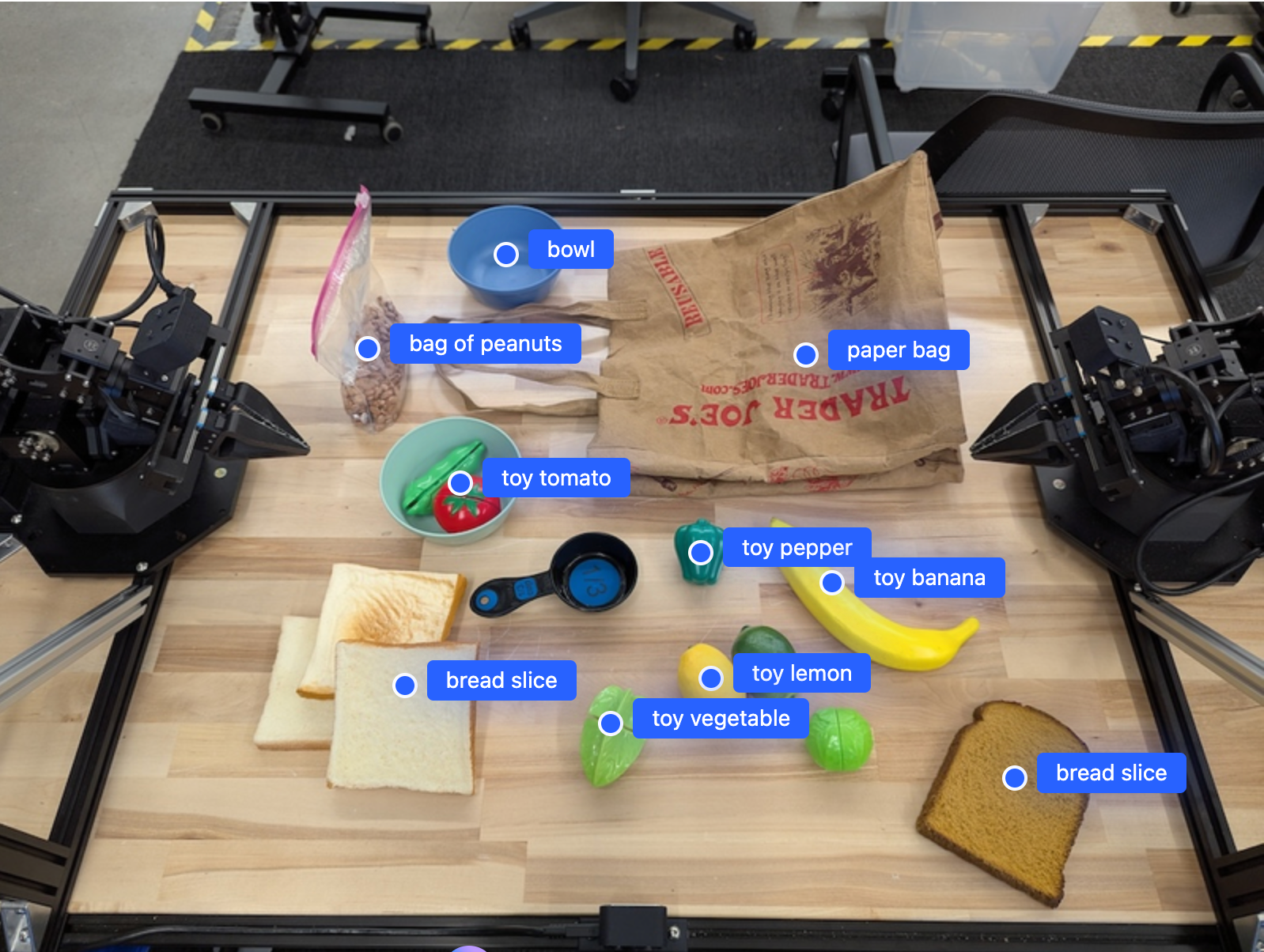

Cara kerjanya
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 memungkinkan robot Anda memahami konteks dan bekerja di dunia fisik menggunakan pemahaman spasial. Model ini menerima input gambar/video/audio dan perintah bahasa alami untuk:
- Memahami objek dan konteks adegan: Mengidentifikasi objek, dan alasan tentang hubungannya dengan adegan, termasuk kemampuan yang ditawarkannya.
- Memahami petunjuk tugas: Menafsirkan tugas yang diberikan dalam bahasa alami, seperti "temukan pisang".
- Menalar secara spasial dan temporal: Memahami urutan tindakan dan cara objek berinteraksi dengan adegan dari waktu ke waktu.
- Menyediakan output terstruktur: Menampilkan koordinat (titik atau kotak pembatas) yang mewakili lokasi objek.
Hal ini memungkinkan robot "melihat" dan "memahami" lingkungannya secara terprogram.
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 juga bersifat agentik, yang berarti ia dapat memecah tugas yang kompleks (seperti "taruh apel di mangkuk") menjadi sub-tugas untuk mengatur tugas dengan cakupan waktu yang panjang:
- Mengurutkan sub-tugas: Menguraikan perintah menjadi urutan langkah-langkah yang logis.
- Panggilan fungsi/Eksekusi kode: Mengeksekusi langkah-langkah dengan memanggil fungsi/alat robot yang ada atau mengeksekusi kode yang dihasilkan.
Baca selengkapnya tentang cara kerja panggilan fungsi dengan Gemini di halaman Panggilan Fungsi.
Menggunakan anggaran pemikiran dengan Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 memiliki anggaran pemikiran yang fleksibel yang memberi Anda kontrol atas latensi versus akurasi. Untuk tugas pemahaman spasial seperti deteksi objek, model dapat mencapai performa tinggi dengan anggaran pemikiran yang kecil. Tugas penalaran yang lebih kompleks seperti penghitungan dan estimasi berat akan lebih baik jika menggunakan anggaran pemikiran yang lebih besar. Dengan demikian, Anda dapat menyeimbangkan kebutuhan respons latensi rendah dengan hasil akurasi tinggi untuk tugas yang lebih sulit.
Untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut anggaran pemikiran, lihat halaman kemampuan inti Pemikiran.
Kemampuan agentic untuk robotika
Bagian ini membahas berbagai kemampuan Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5, yang menunjukkan cara menggunakan model untuk aplikasi persepsi, penalaran, dan perencanaan robotik.
Contoh dalam bagian ini menunjukkan kemampuan mulai dari menunjuk dan menemukan objek dalam gambar hingga merencanakan lintasan dan mengatur tugas horizon panjang. Agar lebih sederhana, cuplikan kode telah dikurangi untuk menampilkan perintah
dan panggilan ke API generate_content. Kode yang dapat dijalankan sepenuhnya serta contoh tambahan dapat ditemukan di Robotics cookbook.
Menunjuk objek
Menunjuk dan menemukan objek dalam gambar atau frame video adalah kasus penggunaan umum untuk model vision-and-language (VLM) dalam robotika. Contoh berikut meminta model untuk menemukan objek tertentu dalam gambar dan menampilkan koordinatnya dalam gambar.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
queries = [
"bread",
"starfruit",
"banana",
]
prompt = f"""
Get all points matching the following objects: {', '.join(queries)}. The
label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Outputnya akan mirip dengan contoh memulai, yaitu JSON yang berisi koordinat objek yang ditemukan dan labelnya.
[
{"point": [671, 317], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [738, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [702, 237], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [629, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [833, 800], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [609, 663], "label": "banana"},
{"point": [770, 483], "label": "starfruit"}
]
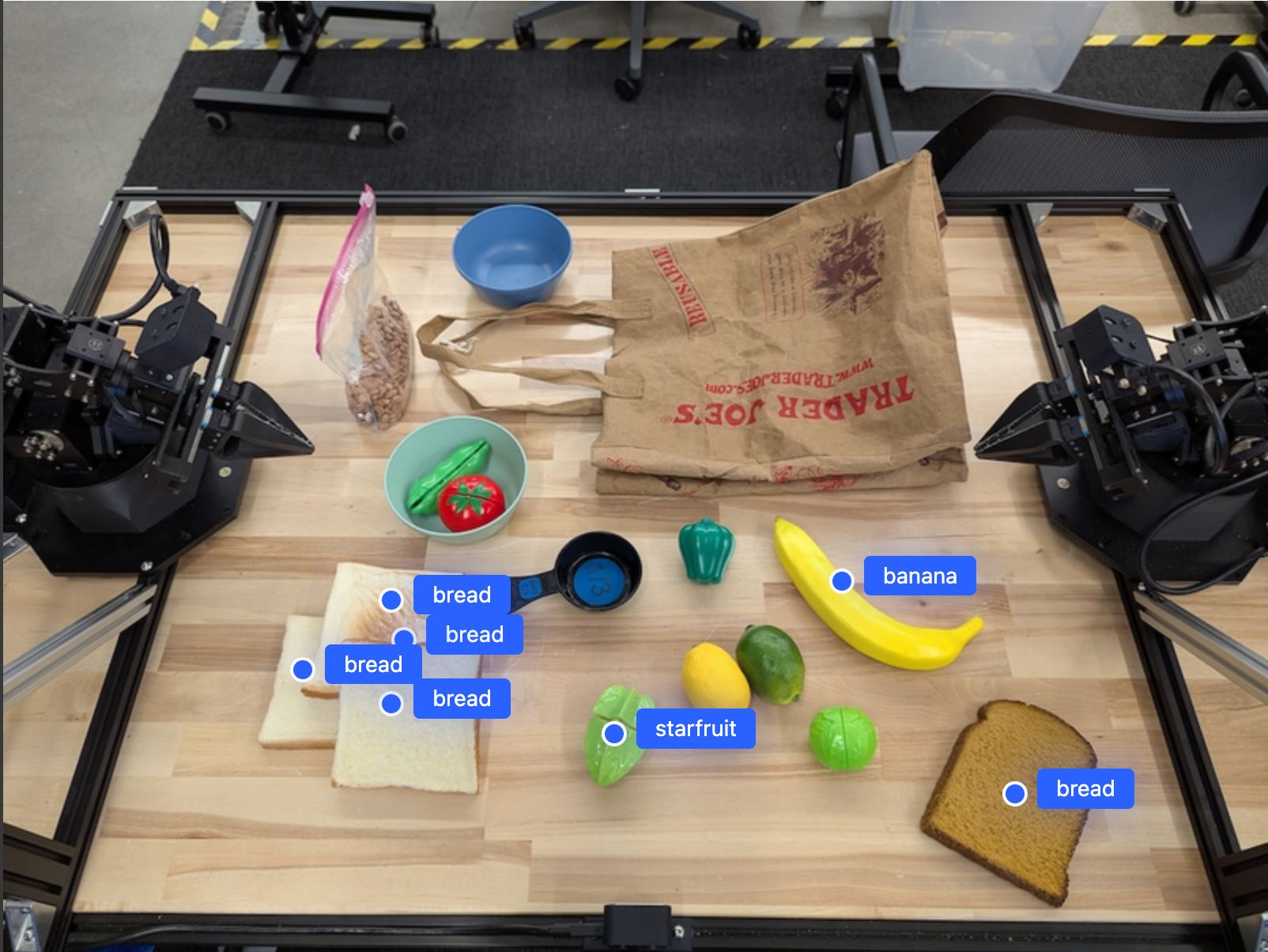

Gunakan perintah berikut untuk meminta model menafsirkan kategori abstrak seperti "buah" dan bukan objek tertentu, serta menemukan semua instance dalam gambar.
Python
prompt = f"""
Get all points for fruit. The label returned should be an identifying
name for the object detected.
""" + """The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."""
Buka halaman pemahaman gambar untuk teknik pemrosesan gambar lainnya.
Melacak objek dalam video
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 juga dapat menganalisis frame video untuk melacak objek dari waktu ke waktu. Lihat Input video untuk mengetahui daftar format video yang didukung.
Berikut adalah perintah dasar yang digunakan untuk menemukan objek tertentu di setiap frame yang dianalisis model:
Python
# Define the objects to find
queries = [
"pen (on desk)",
"pen (in robot hand)",
"laptop (opened)",
"laptop (closed)",
]
base_prompt = f"""
Point to the following objects in the provided image: {', '.join(queries)}.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
If no objects are found, return an empty JSON list [].
"""
Output menunjukkan pena dan laptop yang dilacak di seluruh frame video.
![]()
Untuk kode yang dapat dijalankan sepenuhnya, lihat Robotics cookbook.
Deteksi objek dan kotak pembatas
Selain titik tunggal, model juga dapat menampilkan kotak pembatas 2D, yang menyediakan area persegi panjang yang mengelilingi objek.
Contoh ini meminta kotak pembatas 2D untuk objek yang dapat diidentifikasi pada tabel. Model diinstruksikan untuk membatasi output hingga 25 objek dan memberi nama beberapa instance secara unik.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Return bounding boxes as a JSON array with labels. Never return masks
or code fencing. Limit to 25 objects. Include as many objects as you
can identify on the table.
If an object is present multiple times, name them according to their
unique characteristic (colors, size, position, unique characteristics, etc..).
The format should be as follows: [{"box_2d": [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax],
"label": <label for the object>}] normalized to 0-1000. The values in
box_2d must only be integers
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Berikut ini menampilkan kotak yang ditampilkan dari model.
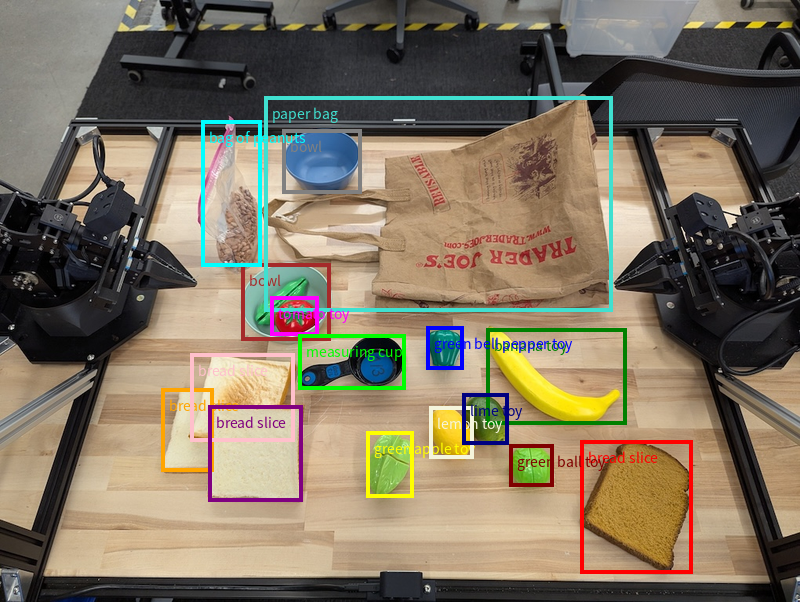
Untuk kode yang dapat dijalankan sepenuhnya, lihat Robotics cookbook. Halaman Pemahaman gambar juga memiliki contoh tambahan tugas visual seperti segmentasi dan deteksi objek.
Contoh kotak pembatas tambahan dapat ditemukan di halaman Pemahaman gambar.
Lintasan
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 dapat membuat urutan titik yang menentukan trajektori, yang berguna untuk memandu pergerakan robot.
Contoh ini meminta lintasan untuk memindahkan pena merah ke pengatur, termasuk titik awal dan serangkaian titik perantara.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
points_data = []
prompt = """
Place a point on the red pen, then 15 points for the trajectory of
moving the red pen to the top of the organizer on the left.
The points should be labeled by order of the trajectory, from '0'
(start point at left hand) to <n> (final point)
The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Responsnya adalah sekumpulan koordinat yang menjelaskan lintasan jalur yang harus diikuti pena merah untuk menyelesaikan tugas memindahkannya ke atas pengelola:
[
{"point": [550, 610], "label": "0"},
{"point": [500, 600], "label": "1"},
{"point": [450, 590], "label": "2"},
{"point": [400, 580], "label": "3"},
{"point": [350, 550], "label": "4"},
{"point": [300, 520], "label": "5"},
{"point": [250, 490], "label": "6"},
{"point": [200, 460], "label": "7"},
{"point": [180, 430], "label": "8"},
{"point": [160, 400], "label": "9"},
{"point": [140, 370], "label": "10"},
{"point": [120, 340], "label": "11"},
{"point": [110, 320], "label": "12"},
{"point": [105, 310], "label": "13"},
{"point": [100, 305], "label": "14"},
{"point": [100, 300], "label": "15"}
]
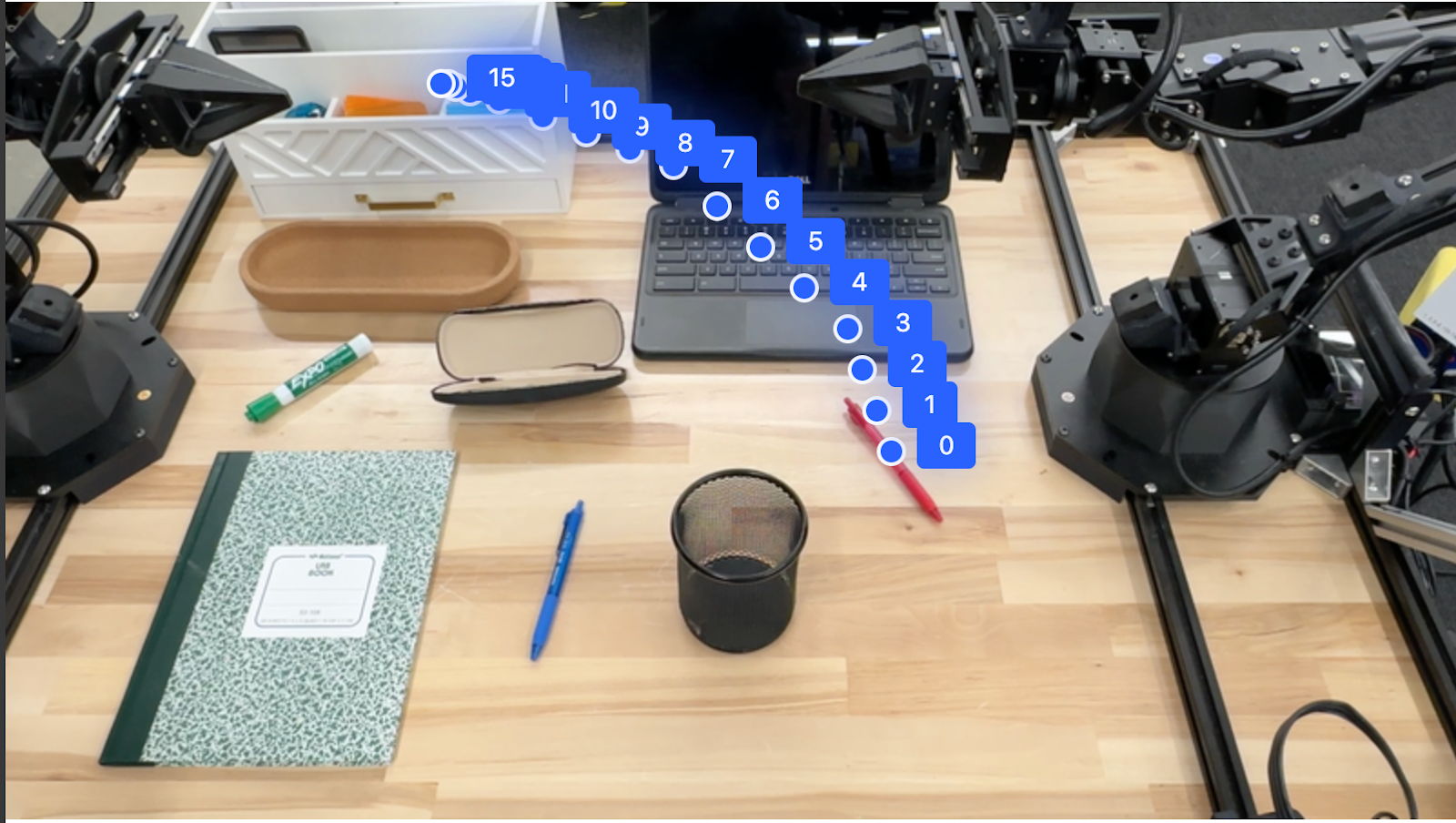

Orkestrasi
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 dapat melakukan penalaran spasial tingkat yang lebih tinggi, menyimpulkan tindakan atau mengidentifikasi lokasi optimal berdasarkan pemahaman kontekstual.
Menyediakan ruang untuk laptop
Contoh ini menunjukkan cara Gemini Robotics-ER dapat memahami ruang. Perintah meminta model untuk mengidentifikasi objek mana yang perlu dipindahkan untuk membuat ruang bagi item lain.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Point to the object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Respons berisi koordinat 2D objek yang menjawab pertanyaan pengguna, dalam hal ini, objek yang harus dipindahkan untuk memberi ruang bagi laptop.
[
{"point": [672, 301], "label": "The object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop"}
]
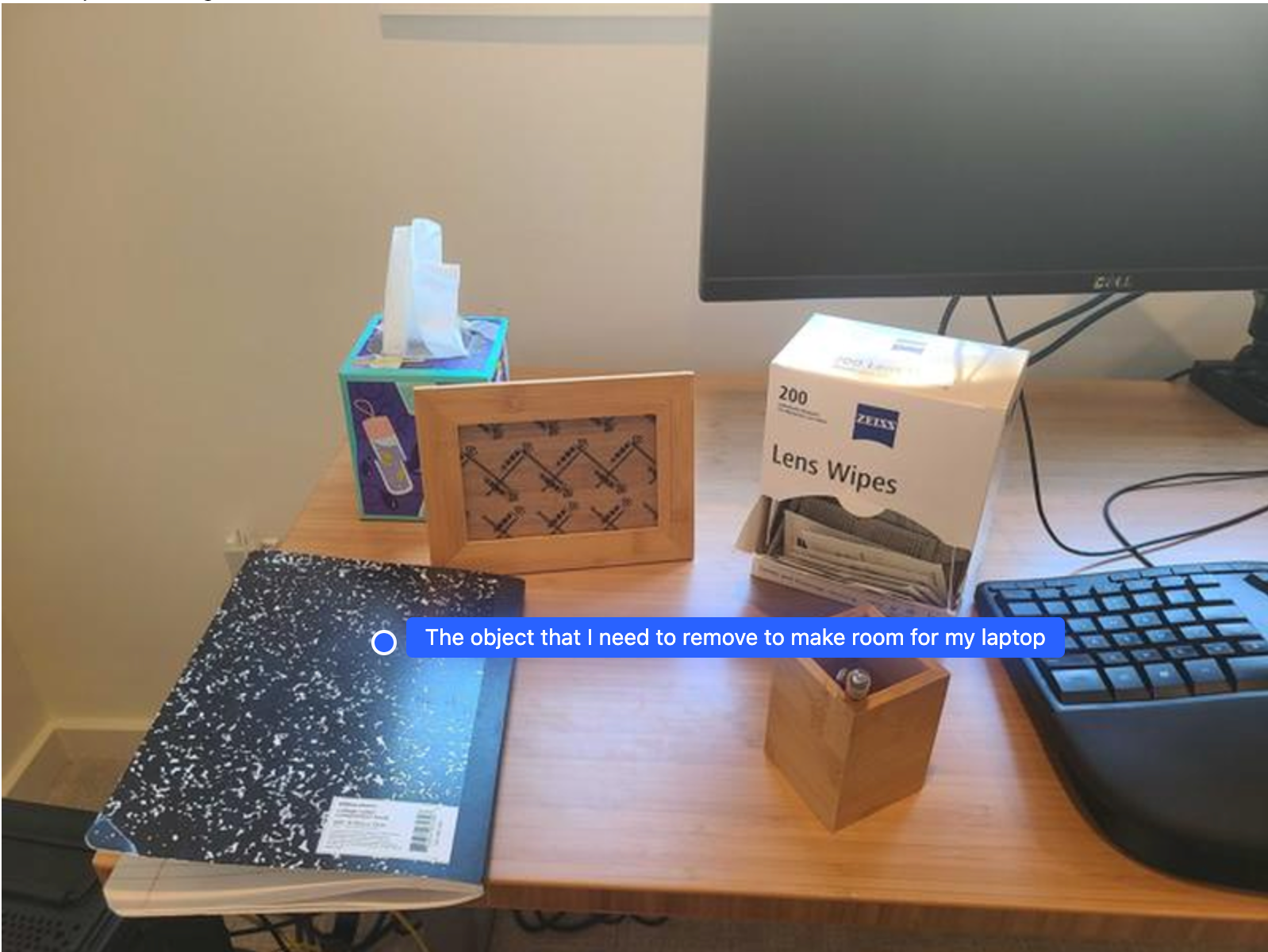

Mengepak Bekal Makan Siang
Model ini juga dapat memberikan petunjuk untuk tugas multi-langkah dan menunjukkan objek yang relevan untuk setiap langkah. Contoh ini menunjukkan cara model merencanakan serangkaian langkah untuk mengemas tas bekal.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-lunch.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Explain how to pack the lunch box and lunch bag. Point to each
object that you refer to. Each point should be in the format:
[{"point": [y, x], "label": }], where the coordinates are
normalized between 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
Respons terhadap perintah ini adalah serangkaian petunjuk langkah demi langkah tentang cara mengemas tas makan siang dari input gambar.
Gambar input
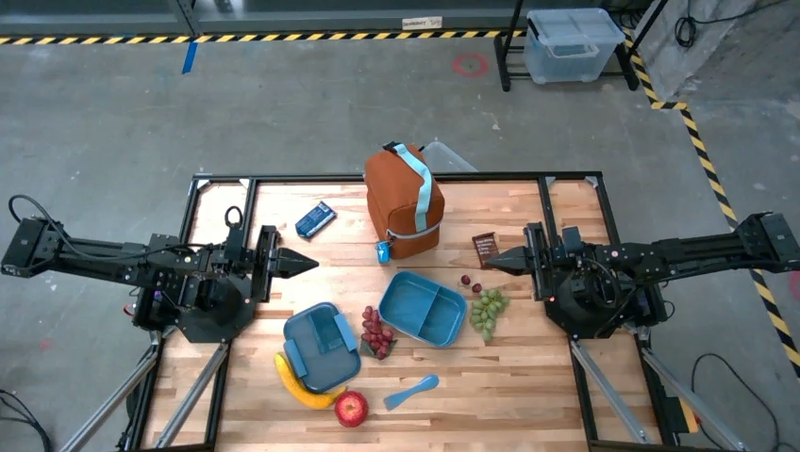
Output model
Based on the image, here is a plan to pack the lunch box and lunch bag:
1. **Pack the fruit into the lunch box.** Place the [apple](apple), [banana](banana), [red grapes](red grapes), and [green grapes](green grapes) into the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
2. **Add the spoon to the lunch box.** Put the [blue spoon](blue spoon) inside the lunch box as well.
3. **Close the lunch box.** Secure the lid on the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
4. **Place the lunch box inside the lunch bag.** Put the closed [blue lunch box](blue lunch box) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
5. **Pack the remaining items into the lunch bag.** Place the [blue snack bar](blue snack bar) and the [brown snack bar](brown snack bar) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
Here is the list of objects and their locations:
* [{"point": [899, 440], "label": "apple"}]
* [{"point": [814, 363], "label": "banana"}]
* [{"point": [727, 470], "label": "red grapes"}]
* [{"point": [675, 608], "label": "green grapes"}]
* [{"point": [706, 529], "label": "blue lunch box"}]
* [{"point": [864, 517], "label": "blue spoon"}]
* [{"point": [499, 401], "label": "blue snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [614, 705], "label": "brown snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [448, 501], "label": "brown lunch bag"}]
Memanggil API robot kustom
Contoh ini menunjukkan orkestrasi tugas dengan API robot kustom. API ini memperkenalkan API tiruan yang dirancang untuk operasi ambil dan letakkan. Tugasnya adalah mengambil balok biru dan meletakkannya di mangkuk oranye:
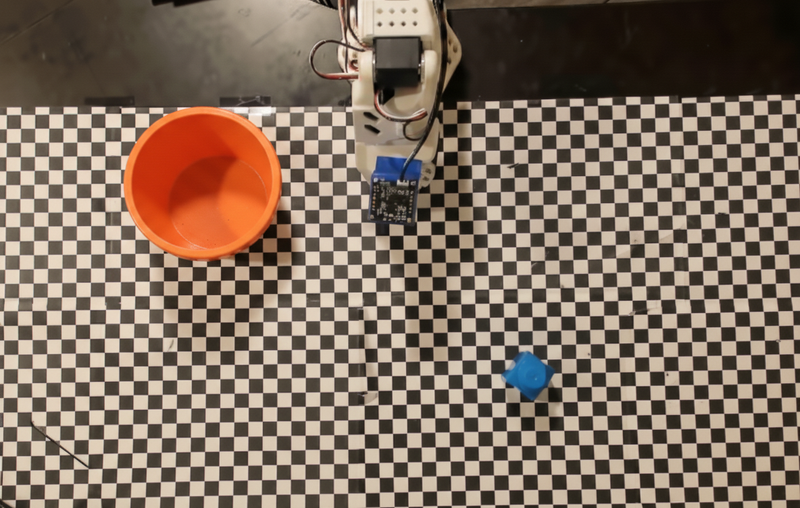
Mirip dengan contoh lain di halaman ini, kode yang dapat dijalankan sepenuhnya tersedia di Robotics cookbook.
Langkah pertama adalah menemukan kedua item dengan perintah berikut:
Python
prompt = """
Locate and point to the blue block and the orange bowl. The label
returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
Respons model mencakup koordinat blok dan mangkuk yang dinormalisasi:
[
{"point": [389, 252], "label": "orange bowl"},
{"point": [727, 659], "label": "blue block"}
]
Contoh ini menggunakan mock robot API berikut:
Python
def move(x, y, high):
print(f"moving to coordinates: {x}, {y}, {15 if high else 5}")
def setGripperState(opened):
print("Opening gripper" if opened else "Closing gripper")
def returnToOrigin():
print("Returning to origin pose")
Langkah berikutnya adalah memanggil urutan fungsi API dengan logika yang diperlukan untuk mengeksekusi tindakan. Perintah berikut menyertakan deskripsi robot API yang harus digunakan model saat mengatur tugas ini.
Python
prompt = f"""
You are a robotic arm with six degrees-of-freedom. You have the
following functions available to you:
def move(x, y, high):
# moves the arm to the given coordinates. The boolean value 'high' set
to True means the robot arm should be lifted above the scene for
avoiding obstacles during motion. 'high' set to False means the robot
arm should have the gripper placed on the surface for interacting with
objects.
def setGripperState(opened):
# Opens the gripper if opened set to true, otherwise closes the gripper
def returnToOrigin():
# Returns the robot to an initial state. Should be called as a cleanup
operation.
The origin point for calculating the moves is at normalized point
y={robot_origin_y}, x={robot_origin_x}. Use this as the new (0,0) for
calculating moves, allowing x and y to be negative.
Perform a pick and place operation where you pick up the blue block at
normalized coordinates ({block_x}, {block_y}) (relative coordinates:
{block_relative_x}, {block_relative_y}) and place it into the orange
bowl at normalized coordinates ({bowl_x}, {bowl_y})
(relative coordinates: {bowl_relative_x}, {bowl_relative_y}).
Provide the sequence of function calls as a JSON list of objects, where
each object has a "function" key (the function name) and an "args" key
(a list of arguments for the function).
Also, include your reasoning before the JSON output.
For example:
Reasoning: To pick up the block, I will first move the arm to a high
position above the block, open the gripper, move down to the block,
close the gripper, lift the arm, move to a high position above the bowl,
move down to the bowl, open the gripper, and then lift the arm back to
a high position.
"""
Berikut adalah kemungkinan output model berdasarkan perintah dan API robot tiruan. Output mencakup proses pemikiran model dan tugas yang direncanakannya sebagai hasilnya. Bagian ini juga menampilkan output panggilan fungsi robot yang diurutkan oleh model.
Reasoning: To perform the pick and place operation, I will first move the
robotic arm to a high position above the blue block to ensure clearance. Then, I
will open the gripper in preparation for grasping. Next, I will lower the arm to
the surface level to position the gripper around the block and close the gripper
to secure it. After picking up the block, I will lift the arm to clear the
surface and move towards the orange bowl, maintaining a high position to avoid
collisions. Once positioned above the bowl, I will lower the arm to place the
block inside. I will then open the gripper to release the block. Finally, I will
lift the arm out of the bowl and call `returnToOrigin` to reset the robot's
state.
[
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
false
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "returnToOrigin",
"args": []
}
]
Executing Function Calls:
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 5
Closing gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 5
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
Returning to origin pose
Eksekusi kode
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 dapat menyarankan dan mengeksekusi kode Python untuk melakukan tugas yang memerlukan tindakan dinamis, seperti memperbesar area gambar untuk mendapatkan detail yang lebih baik.
Contoh ini menunjukkan cara model dapat menyarankan penggunaan alat eksekusi kode untuk "memperbesar" area tertentu pada gambar, yang kemudian dilakukan untuk menjawab pertanyaan pengguna.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-object.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
What is the air quality reading? Using the code execution feature,
zoom in on the image to take a closer look.
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
)
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
Berikut adalah kemungkinan respons model untuk tugas ini. Output menunjukkan model yang menghasilkan kode untuk memperbesar gambar agar layar lebih mudah dibaca. Bagian ini juga menunjukkan proses pemikiran di balik penyesuaian yang dilakukan pada pemangkasan. Untuk output sampel lengkap, lihat Robotics cookbook.
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
# Based on visual inspection, the display is roughly centered around [430, 430] to [500, 500] in a 1000x1000 scale.
# Let's try to zoom in on the display area.
# Bounding box for display: [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax] in pixels.
# From visual inspection of the original image (size 90489 bytes, resolution
unknown but let's assume a standard aspect ratio and roughly 1000x1000 for
relative positioning),
# the display is located at approximately y=380-480, x=410-540.
# Let's define a larger area around it for context.
# Let's say we want to crop from y=350 to y=550 and x=350 to x=650.
...
thought
The crop was too tight and only captured part of the display. Let's adjust the bounding box.
The previous crop was `img.crop((400, 350, 600, 500))`. This means xmin=400, ymin=350, xmax=600, ymax=500.
The display is centered around x=480, y=430.
The previous crop captured the left side of the display.
Let's expand the x range to the right and y range to cover the whole circle.
New bounding box estimate: ymin=370, xmin=400, ymax=500, xmax=600.
Let's try again with a wider crop.
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
…
The reading of 14 falls into the "Moderate" category.
The prompt asks for the "air quality reading", which can be interpreted as
either the numerical value or the categorical description. Given the numerical
value is explicitly displayed, it's the primary reading.
Let's provide the numerical value as the reading.
The reading is 014.
Based on the display on the air purifier, the air quality reading is **014**.
Praktik terbaik
Untuk mengoptimalkan performa dan akurasi aplikasi robotik Anda, Anda harus memahami cara berinteraksi dengan model Gemini secara efektif. Bagian ini menguraikan praktik terbaik dan strategi utama untuk membuat perintah, menangani data visual, dan menyusun tugas untuk mendapatkan hasil yang paling andal.
Gunakan bahasa yang jelas dan sederhana.
Gunakan bahasa alami: Model Gemini dirancang untuk memahami bahasa percakapan yang alami. Susun perintah Anda dengan cara yang jelas secara semantik dan mencerminkan cara seseorang memberikan petunjuk secara alami.
Gunakan terminologi sehari-hari: Pilih bahasa umum sehari-hari daripada jargon teknis atau khusus. Jika model tidak merespons seperti yang diharapkan untuk istilah tertentu, coba parafrasakan dengan sinonim yang lebih umum.
Mengoptimalkan input visual.
Perbesar untuk melihat detail: Saat berurusan dengan objek yang kecil atau sulit dibedakan dalam bidikan yang lebih luas, gunakan fungsi kotak pembatas untuk mengisolasi objek yang diinginkan. Kemudian, Anda dapat memangkas gambar sesuai pilihan ini dan mengirim gambar baru yang lebih fokus ke model untuk analisis yang lebih mendetail.
Bereksperimen dengan pencahayaan dan warna: Persepsi model dapat terpengaruh oleh kondisi pencahayaan yang sulit dan kontras warna yang buruk.
Uraikan masalah kompleks menjadi langkah-langkah yang lebih kecil. Dengan menangani setiap langkah yang lebih kecil satu per satu, Anda dapat memandu model untuk mencapai hasil yang lebih presisi dan berhasil.
Meningkatkan akurasi melalui konsensus. Untuk tugas yang memerlukan tingkat presisi yang tinggi, Anda dapat membuat kueri model beberapa kali dengan perintah yang sama. Dengan merata-ratakan hasil yang ditampilkan, Anda dapat mencapai "konsensus" yang sering kali lebih akurat dan andal.
Batasan
Pertimbangkan batasan berikut saat mengembangkan dengan Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5:
- Status pratinjau: Model saat ini dalam Pratinjau. API dan kemampuan dapat berubah, dan mungkin tidak cocok untuk aplikasi penting produksi tanpa pengujian menyeluruh.
- Latensi: Kueri yang kompleks, input resolusi tinggi, atau
thinking_budgetyang ekstensif dapat menyebabkan waktu pemrosesan yang lebih lama. - Halusinasi: Seperti semua model bahasa besar, Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 terkadang dapat "berhalusinasi" atau memberikan informasi yang salah, terutama untuk perintah yang ambigu atau input di luar distribusi.
- Ketergantungan pada kualitas perintah: Kualitas output model sangat bergantung pada kejelasan dan kekhususan perintah input. Perintah yang tidak jelas atau disusun dengan buruk dapat menghasilkan hasil yang kurang optimal.
- Biaya komputasi: Menjalankan model, terutama dengan input video atau
thinking_budgettinggi, menggunakan resource komputasi dan menimbulkan biaya. Lihat halaman Pemikiran untuk mengetahui detail selengkapnya. - Jenis input: Lihat topik berikut untuk mengetahui detail batasan untuk setiap mode.
Pemberitahuan Privasi
Anda memahami bahwa model yang dirujuk dalam dokumen ini ("Model Robotik") memanfaatkan data video dan audio untuk mengoperasikan dan menggerakkan hardware Anda sesuai dengan petunjuk Anda. Oleh karena itu, Anda dapat mengoperasikan Model Robotik sehingga data dari orang yang dapat diidentifikasi, seperti data suara, gambar, dan kemiripan ("Data Pribadi"), akan dikumpulkan oleh Model Robotik. Jika Anda memilih untuk mengoperasikan Model Robotik dengan cara yang mengumpulkan Data Pribadi, Anda setuju bahwa Anda tidak akan mengizinkan orang yang dapat diidentifikasi untuk berinteraksi dengan, atau berada di area sekitar, Model Robotik, kecuali dan hingga orang yang dapat diidentifikasi tersebut telah diberi tahu dan menyetujui secara memadai bahwa Data Pribadi mereka dapat diberikan kepada dan digunakan oleh Google sebagaimana diuraikan dalam Persyaratan Layanan Tambahan Gemini API yang dapat ditemukan di https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/terms (selanjutnya disebut "Persyaratan"), termasuk sesuai dengan bagian yang berjudul "Cara Google Menggunakan Data Anda". Anda akan memastikan bahwa pemberitahuan tersebut mengizinkan pengumpulan dan penggunaan Data Pribadi sebagaimana diuraikan dalam Persyaratan, dan Anda akan menggunakan upaya yang wajar secara komersial untuk meminimalkan pengumpulan dan distribusi Data Pribadi dengan menggunakan teknik seperti mengaburkan wajah dan mengoperasikan Model Robotik di area yang tidak berisi orang yang dapat diidentifikasi sejauh yang dapat dilakukan.
Harga
Untuk mengetahui informasi mendetail tentang harga dan wilayah yang tersedia, lihat halaman harga.
Versi model
| Properti | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Kode model | gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview |
| Jenis data yang didukung |
Input Teks, gambar, video, audio Output Teks |
| Batas token[*] |
Batas token input 1.048.576 Batas token output 65,536 |
| Kemampuan |
Pembuatan audio Tidak didukung Batch API Tidak didukung Menyimpan ke cache Tidak didukung Eksekusi kode Didukung Panggilan fungsi Didukung Melakukan grounding dengan Google Maps Tidak didukung Pembuatan gambar Tidak didukung Live API Tidak didukung Grounding penelusuran Didukung Output terstruktur Didukung Berpikir Didukung Konteks URL Didukung |
| Versi |
|
| Pembaruan terbaru | September 2025 |
| Batas informasi | Januari 2025 |
Langkah berikutnya
- Jelajahi kemampuan lainnya dan terus bereksperimen dengan berbagai perintah dan input untuk menemukan lebih banyak aplikasi Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5. Lihat Robotics cookbook untuk contoh lainnya.
- Untuk mempelajari cara model Gemini Robotics dibuat dengan mempertimbangkan keamanan, buka halaman keamanan robotik Google DeepMind.
- Baca info terbaru tentang model Gemini Robotics di halaman landing Gemini Robotics.
