Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 是視覺語言模型 (VLM),可將 Gemini 的代理功能帶入機器人領域。這項技術專為實體世界的高階推理而設計,可讓機器人解讀複雜的視覺資料、執行空間推理,並根據自然語言指令規劃動作。
主要功能和優點:
- 自主性提升:機器人可以推理、適應開放式環境的變化並做出回應。
- 自然語言互動:讓使用者能以自然語言指派複雜工作,輕鬆操作機器人。
- 工作協調:將自然語言指令分解為子工作,並與現有的機器人控制器和行為整合,以完成長期任務。
- 多功能:定位及辨識物體、瞭解物體關係、規劃抓取和軌跡,以及解讀動態場景。
如要立即開始使用,可以在 Google AI Studio 中試用模型。
安全性
雖然 Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 的設計以安全為考量,但您仍有責任維護機器人周圍環境的安全。生成式 AI 模型可能會出錯,實體機器人則可能造成損壞。安全是我們的首要考量,因此我們積極投入研究,確保生成式 AI 模型用於實際機器人時安全無虞,這也是我們研究的重點領域。如要瞭解詳情,請前往 Google DeepMind 機器人安全頁面。
開始使用:尋找場景中的物件
以下範例說明常見的機器人應用實例。這個範例說明如何使用 generateContent 方法,將圖片和文字提示傳遞至模型,以取得已識別物件的清單,以及對應的 2D 點。模型會傳回圖片中識別項目的點,並傳回這些項目的標準化 2D 座標和標籤。
您可以將這項輸出內容搭配機器人 API 使用,或呼叫視覺語言動作 (VLA) 模型或任何其他第三方使用者定義函式,為機器人生成要執行的動作。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
PROMPT = """
Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned
should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format
normalized to 0-1000.
"""
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image
with open("my-image.png", 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/png',
),
PROMPT
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
REST
# First, ensure you have the image file locally.
# Encode the image to base64
IMAGE_BASE64=$(base64 -w 0 my-image.png)
curl -X POST \
"https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview:generateContent \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"mimeType": "image/png",
"data": "'"${IMAGE_BASE64}"'"
}
},
{
"text": "Point to no more than 10 items in the image. The label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected. The answer should follow the json format: [{\"point\": [y, x], \"label\": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."
}
]
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"temperature": 0.5,
"thinkingConfig": {
"thinkingBudget": 0
}
}
}'
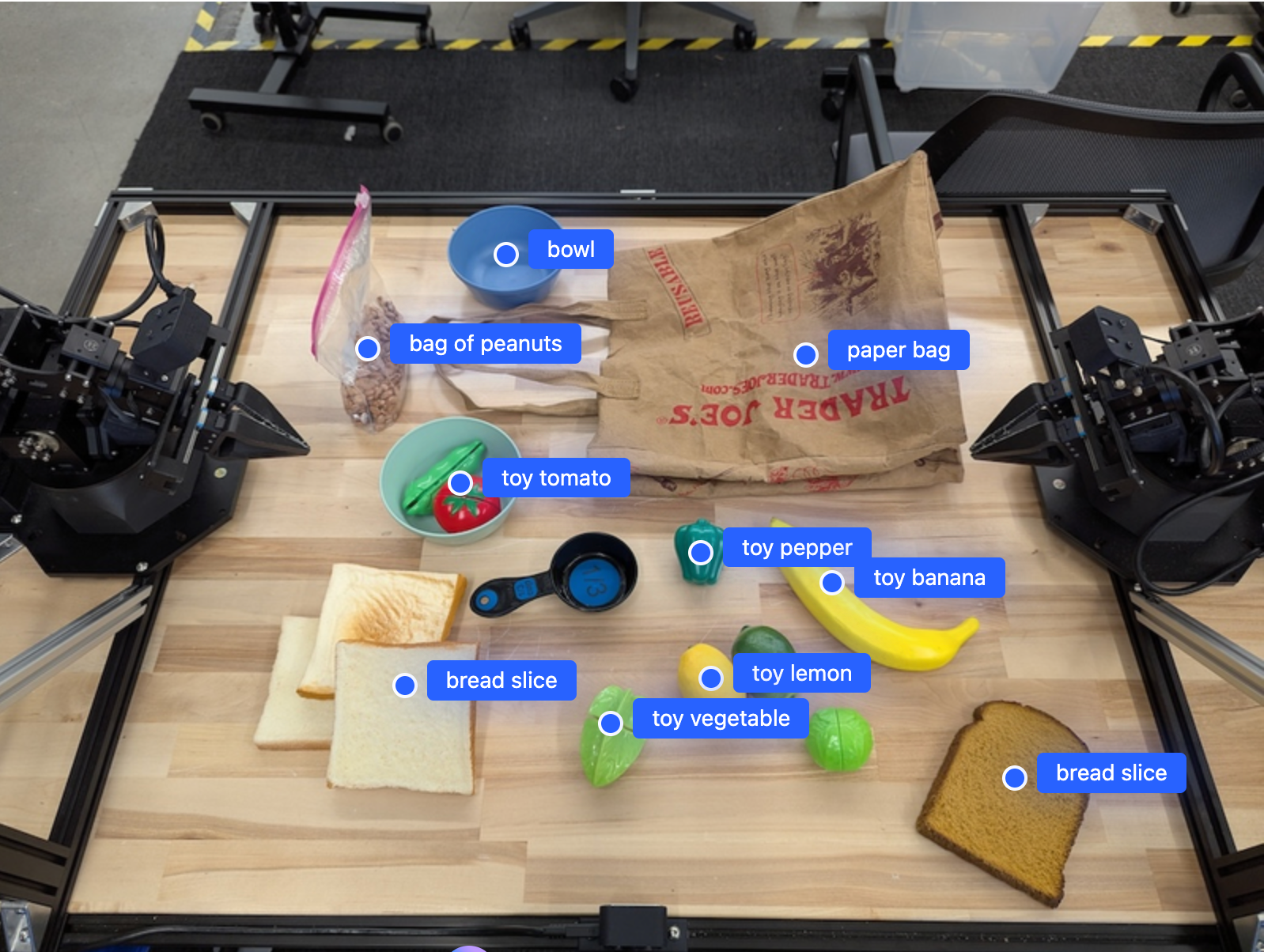
輸出內容會是包含物件的 JSON 陣列,每個物件都有 point (標準化 [y, x] 座標) 和用於識別物件的 label。
JSON
[
{"point": [376, 508], "label": "small banana"},
{"point": [287, 609], "label": "larger banana"},
{"point": [223, 303], "label": "pink starfruit"},
{"point": [435, 172], "label": "paper bag"},
{"point": [270, 786], "label": "green plastic bowl"},
{"point": [488, 775], "label": "metal measuring cup"},
{"point": [673, 580], "label": "dark blue bowl"},
{"point": [471, 353], "label": "light blue bowl"},
{"point": [492, 497], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [525, 429], "label": "lime"}
]
下圖顯示這些點的範例:

運作方式
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 可讓機器人運用空間解讀功能,瞭解實體世界並在其中運作。這項功能會接收圖片/影片/音訊輸入內容和自然語言提示,然後:
- 瞭解物件和場景脈絡:識別物件,以及物件與場景的關係 (包括可供性)。
- 瞭解工作指令:解讀以自然語言下達的工作,例如「找出香蕉」。
- 空間和時間推理:瞭解動作序列,以及物體如何隨時間與場景互動。
- 提供結構化輸出:傳回代表物件位置的座標 (點或定界框)。
這項技術可讓機器人透過程式輔助「看見」及「瞭解」周遭環境。
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 也具備代理功能,可將複雜工作 (例如「把蘋果放進碗裡」) 分解為子工作,以協調長期工作:
- 子工作排序:將指令分解為符合邏輯的步驟序列。
- 函式呼叫/程式碼執行:呼叫現有的機器人函式/工具或執行生成的程式碼,藉此執行步驟。
如要進一步瞭解 Gemini 函式呼叫的運作方式,請參閱函式呼叫頁面。
使用 Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 的思考預算
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 具有彈性的思考預算,可讓您控管延遲與準確度之間的取捨。對於物件偵測等空間理解工作,模型可以運用少量思考預算,達到高成效。對於計數和重量估算等較複雜的推理工作,較大的思考預算有助於提升準確度。這樣一來,您就能在需要低延遲回應的同時,兼顧較困難任務的高準確度結果。
如要進一步瞭解思考預算,請參閱「思考」 核心功能頁面。
機器人代理能力
本節將逐步說明 Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 的各種功能,示範如何將模型用於機器人感知、推理和規劃應用程式。
本節範例將展示各項功能,包括在圖片中指出及尋找物體、規劃路徑,以及協調長期任務。為簡化起見,程式碼片段已縮減,只顯示提示和對 generate_content API 的呼叫。如需完整的可執行程式碼和更多範例,請參閱「機器人食譜」。
指向物件
在圖片或影片影格中指出並尋找物件,是機器人領域中視覺與語言模型 (VLM) 的常見用途。在下列範例中,我們要求模型找出圖片中的特定物件,並傳回圖片中的座標。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
queries = [
"bread",
"starfruit",
"banana",
]
prompt = f"""
Get all points matching the following objects: {', '.join(queries)}. The
label returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
輸出內容會與入門範例類似,也就是包含找到的物件座標和標籤的 JSON。
[
{"point": [671, 317], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [738, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [702, 237], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [629, 307], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [833, 800], "label": "bread"},
{"point": [609, 663], "label": "banana"},
{"point": [770, 483], "label": "starfruit"}
]
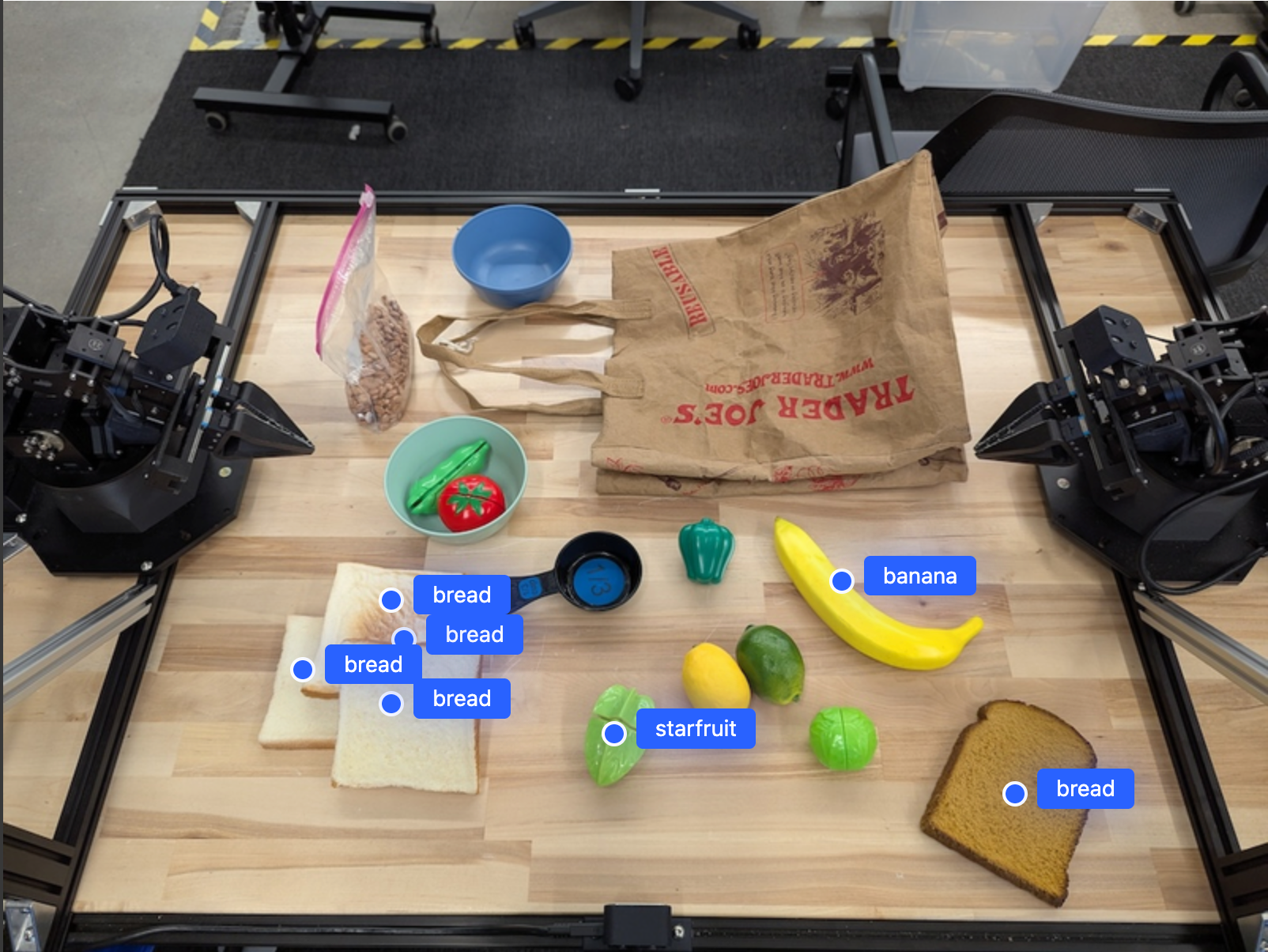

使用下列提示要求模型解讀抽象類別 (例如「水果」),而非特定物件,並找出圖片中的所有例項。
Python
prompt = f"""
Get all points for fruit. The label returned should be an identifying
name for the object detected.
""" + """The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in
[y, x] format normalized to 0-1000."""
如需其他圖像處理技術,請參閱圖像理解頁面。
追蹤影片中的物件
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 也能分析影片影格,追蹤物件隨時間的變化。如需支援的影片格式清單,請參閱「影片輸入」。
以下是基礎提示,用於在模型分析的每個影格中尋找特定物件:
Python
# Define the objects to find
queries = [
"pen (on desk)",
"pen (in robot hand)",
"laptop (opened)",
"laptop (closed)",
]
base_prompt = f"""
Point to the following objects in the provided image: {', '.join(queries)}.
The answer should follow the json format:
[{{"point": , "label": }}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
If no objects are found, return an empty JSON list [].
"""
輸出結果會顯示在影片影格中追蹤的筆和筆電。
![]()
如需完整的可執行程式碼,請參閱機器人食譜。
物件偵測和定界框
除了單一點之外,模型也會傳回 2D 邊界框,提供封閉物件的矩形區域。
這個範例會要求取得桌上可辨識物件的 2D 邊界框。模型會收到指令,將輸出內容限制為 25 個物件,並為多個執行個體命名專屬名稱。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Return bounding boxes as a JSON array with labels. Never return masks
or code fencing. Limit to 25 objects. Include as many objects as you
can identify on the table.
If an object is present multiple times, name them according to their
unique characteristic (colors, size, position, unique characteristics, etc..).
The format should be as follows: [{"box_2d": [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax],
"label": <label for the object>}] normalized to 0-1000. The values in
box_2d must only be integers
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
以下顯示模型傳回的方塊。
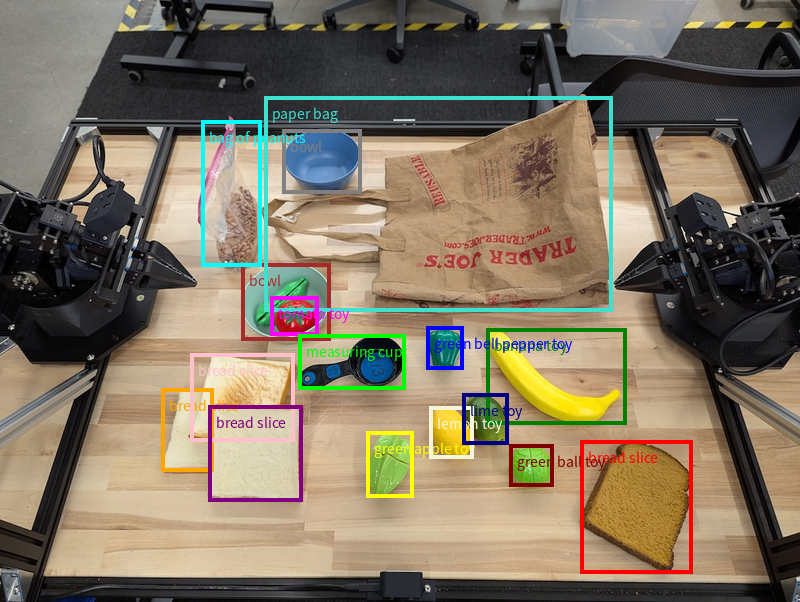
如需完整的可執行程式碼,請參閱 Robotics cookbook。「圖像理解」頁面也提供其他視覺工作範例,例如分割和物件偵測。
如需其他邊界方塊範例,請參閱「圖片理解」頁面。
軌跡
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 可生成定義軌跡的點序列,有助於引導機器人移動。
這個範例要求將紅筆移動到收納盒的軌跡,包括起點和一系列中間點。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
points_data = []
prompt = """
Place a point on the red pen, then 15 points for the trajectory of
moving the red pen to the top of the organizer on the left.
The points should be labeled by order of the trajectory, from '0'
(start point at left hand) to <n> (final point)
The answer should follow the json format:
[{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
)
)
print(image_response.text)
回應是一組座標,說明紅筆應遵循的路徑軌跡,才能完成將紅筆移到收納盒頂端的任務:
[
{"point": [550, 610], "label": "0"},
{"point": [500, 600], "label": "1"},
{"point": [450, 590], "label": "2"},
{"point": [400, 580], "label": "3"},
{"point": [350, 550], "label": "4"},
{"point": [300, 520], "label": "5"},
{"point": [250, 490], "label": "6"},
{"point": [200, 460], "label": "7"},
{"point": [180, 430], "label": "8"},
{"point": [160, 400], "label": "9"},
{"point": [140, 370], "label": "10"},
{"point": [120, 340], "label": "11"},
{"point": [110, 320], "label": "12"},
{"point": [105, 310], "label": "13"},
{"point": [100, 305], "label": "14"},
{"point": [100, 300], "label": "15"}
]
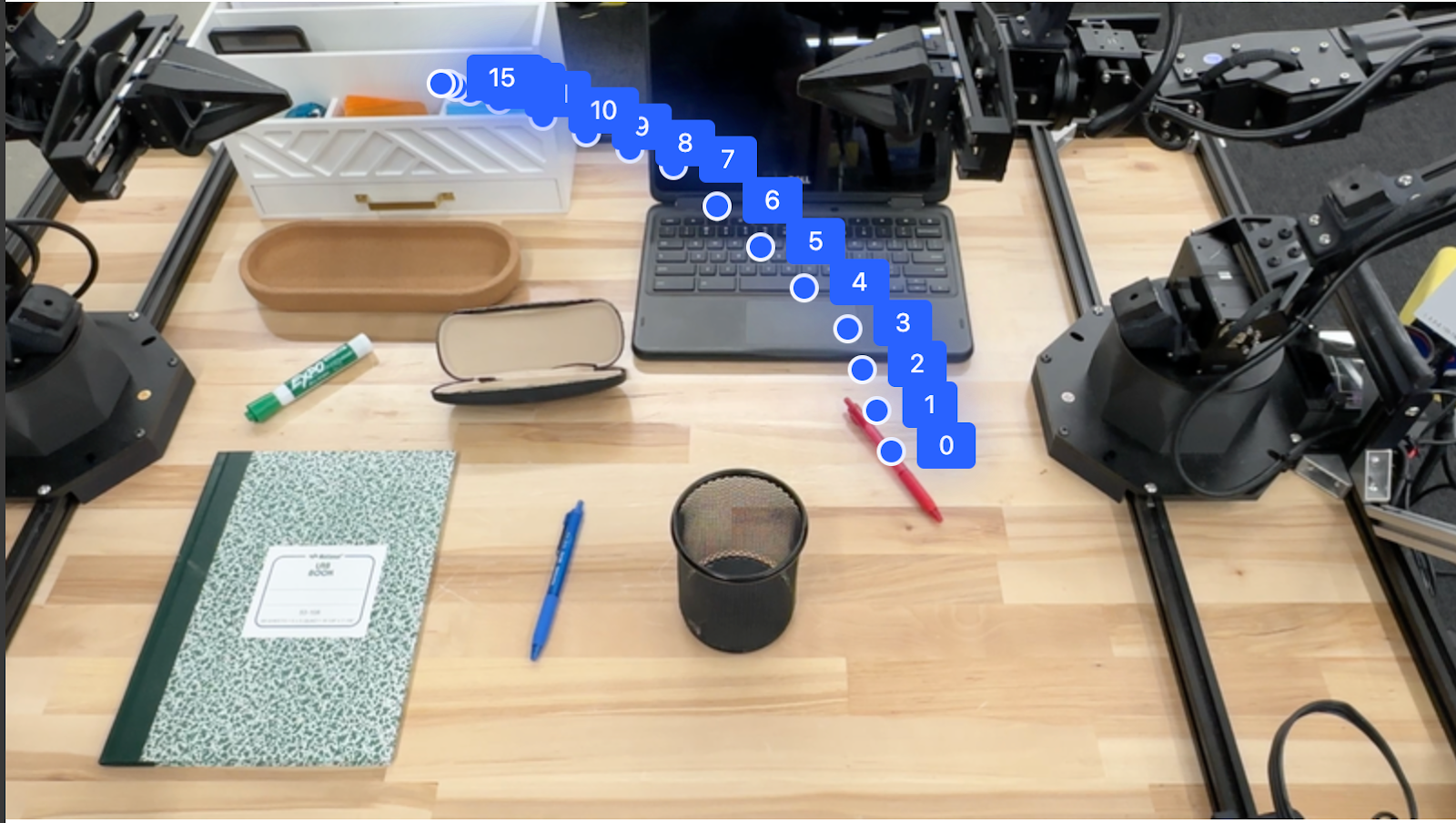

自動化調度管理
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 可執行更高階的空間推理,根據脈絡理解推斷動作或找出最佳位置。
為筆電預留空間
這個範例說明 Gemini Robotics-ER 如何推論空間。提示會要求模型找出需要移動的物件,以便為其他項目騰出空間。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-with-objects.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Point to the object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>,
"label": <label1>}, ...]. The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
回覆內容包含可回答使用者問題的物體 2D 座標,在本例中,該物體應移動,為筆電騰出空間。
[
{"point": [672, 301], "label": "The object that I need to remove to make room for my laptop"}
]
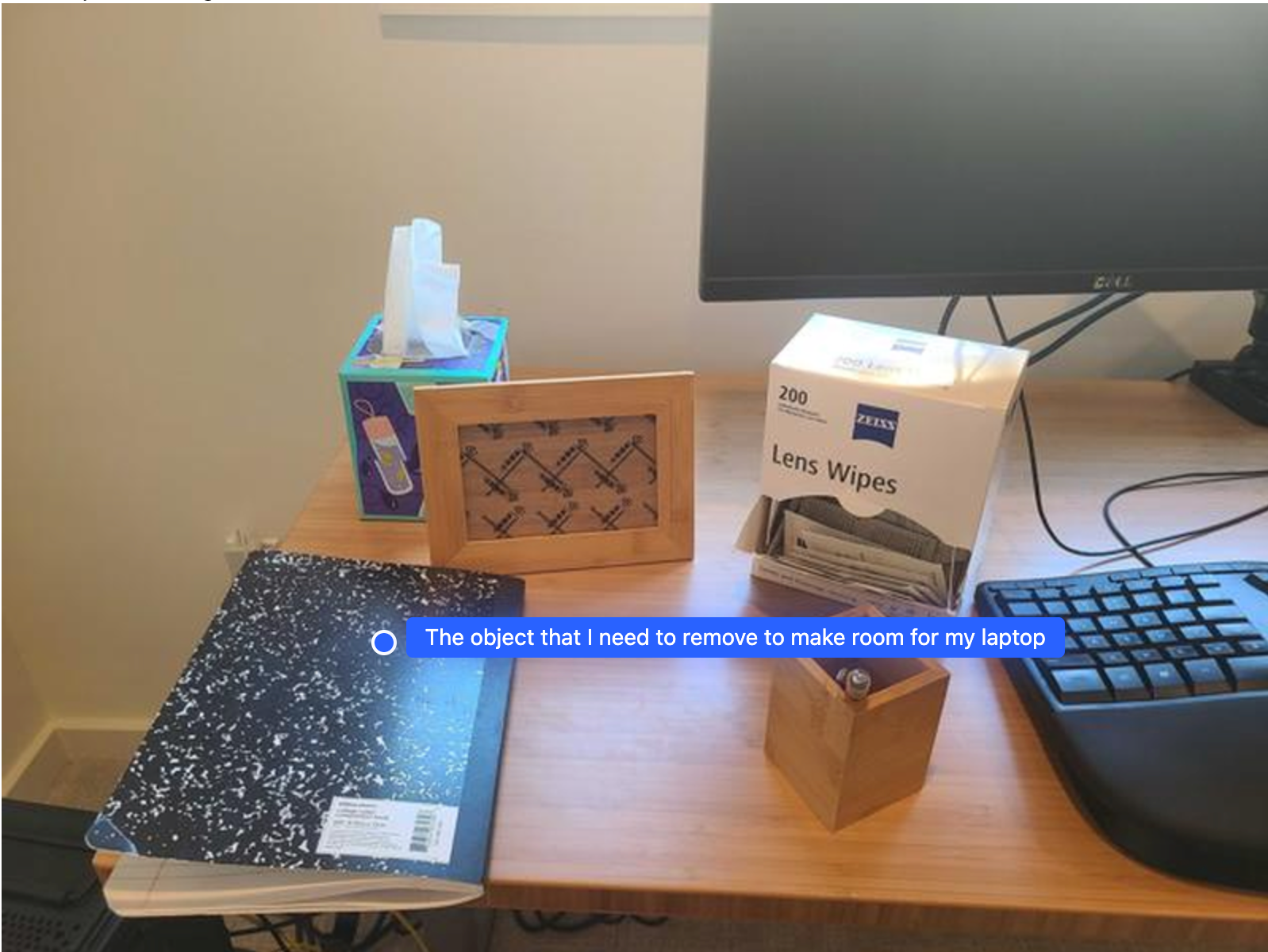

準備午餐
模型也能提供多步驟工作的操作說明,並指出每個步驟的相關物件。這個範例顯示模型如何規劃一系列步驟來打包午餐袋。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-lunch.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
Explain how to pack the lunch box and lunch bag. Point to each
object that you refer to. Each point should be in the format:
[{"point": [y, x], "label": }], where the coordinates are
normalized between 0-1000.
"""
image_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(thinking_budget=0)
)
)
print(image_response.text)
這項提示的回覆是一組逐步操作說明,內容為如何根據輸入的圖片打包午餐袋。
輸入圖片
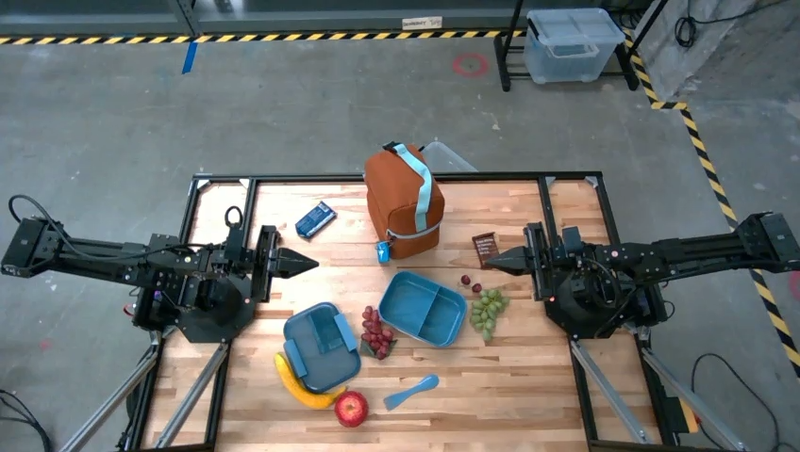
模型輸出
Based on the image, here is a plan to pack the lunch box and lunch bag:
1. **Pack the fruit into the lunch box.** Place the [apple](apple), [banana](banana), [red grapes](red grapes), and [green grapes](green grapes) into the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
2. **Add the spoon to the lunch box.** Put the [blue spoon](blue spoon) inside the lunch box as well.
3. **Close the lunch box.** Secure the lid on the [blue lunch box](blue lunch box).
4. **Place the lunch box inside the lunch bag.** Put the closed [blue lunch box](blue lunch box) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
5. **Pack the remaining items into the lunch bag.** Place the [blue snack bar](blue snack bar) and the [brown snack bar](brown snack bar) into the [brown lunch bag](brown lunch bag).
Here is the list of objects and their locations:
* [{"point": [899, 440], "label": "apple"}]
* [{"point": [814, 363], "label": "banana"}]
* [{"point": [727, 470], "label": "red grapes"}]
* [{"point": [675, 608], "label": "green grapes"}]
* [{"point": [706, 529], "label": "blue lunch box"}]
* [{"point": [864, 517], "label": "blue spoon"}]
* [{"point": [499, 401], "label": "blue snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [614, 705], "label": "brown snack bar"}]
* [{"point": [448, 501], "label": "brown lunch bag"}]
呼叫自訂機器人 API
這個範例說明如何使用自訂機器人 API 編排工作。這個 API 專為取放作業設計,這項工作的目標是拿起藍色積木,然後放入橘色碗中:
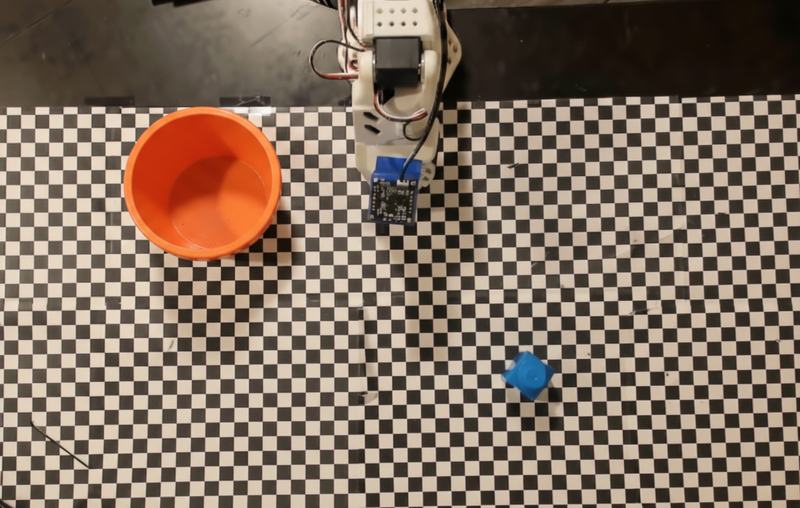
與本頁的其他範例類似,完整的可執行程式碼位於 Robotics 食譜。
第一步是使用下列提示找出這兩項物品:
Python
prompt = """
Locate and point to the blue block and the orange bowl. The label
returned should be an identifying name for the object detected.
The answer should follow the json format: [{"point": <point>, "label": <label1>}, ...].
The points are in [y, x] format normalized to 0-1000.
"""
模型回應會包含積木和碗的標準化座標:
[
{"point": [389, 252], "label": "orange bowl"},
{"point": [727, 659], "label": "blue block"}
]
本範例使用下列模擬機器人 API:
Python
def move(x, y, high):
print(f"moving to coordinates: {x}, {y}, {15 if high else 5}")
def setGripperState(opened):
print("Opening gripper" if opened else "Closing gripper")
def returnToOrigin():
print("Returning to origin pose")
下一步是呼叫一系列 API 函式,並使用必要邏輯執行動作。下列提示包含機器人 API 的說明,模型應在協調這項工作時使用。
Python
prompt = f"""
You are a robotic arm with six degrees-of-freedom. You have the
following functions available to you:
def move(x, y, high):
# moves the arm to the given coordinates. The boolean value 'high' set
to True means the robot arm should be lifted above the scene for
avoiding obstacles during motion. 'high' set to False means the robot
arm should have the gripper placed on the surface for interacting with
objects.
def setGripperState(opened):
# Opens the gripper if opened set to true, otherwise closes the gripper
def returnToOrigin():
# Returns the robot to an initial state. Should be called as a cleanup
operation.
The origin point for calculating the moves is at normalized point
y={robot_origin_y}, x={robot_origin_x}. Use this as the new (0,0) for
calculating moves, allowing x and y to be negative.
Perform a pick and place operation where you pick up the blue block at
normalized coordinates ({block_x}, {block_y}) (relative coordinates:
{block_relative_x}, {block_relative_y}) and place it into the orange
bowl at normalized coordinates ({bowl_x}, {bowl_y})
(relative coordinates: {bowl_relative_x}, {bowl_relative_y}).
Provide the sequence of function calls as a JSON list of objects, where
each object has a "function" key (the function name) and an "args" key
(a list of arguments for the function).
Also, include your reasoning before the JSON output.
For example:
Reasoning: To pick up the block, I will first move the arm to a high
position above the block, open the gripper, move down to the block,
close the gripper, lift the arm, move to a high position above the bowl,
move down to the bowl, open the gripper, and then lift the arm back to
a high position.
"""
以下是模型根據提示和模擬機器人 API 可能產生的輸出內容。輸出內容包括模型的思考過程,以及因此規劃的任務。此外,也會顯示模型依序執行的機器人函式呼叫輸出內容。
Reasoning: To perform the pick and place operation, I will first move the
robotic arm to a high position above the blue block to ensure clearance. Then, I
will open the gripper in preparation for grasping. Next, I will lower the arm to
the surface level to position the gripper around the block and close the gripper
to secure it. After picking up the block, I will lift the arm to clear the
surface and move towards the orange bowl, maintaining a high position to avoid
collisions. Once positioned above the bowl, I will lower the arm to place the
block inside. I will then open the gripper to release the block. Finally, I will
lift the arm out of the bowl and call `returnToOrigin` to reset the robot's
state.
[
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
false
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
163,
427,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
false
]
},
{
"function": "setGripperState",
"args": [
true
]
},
{
"function": "move",
"args": [
-247,
90,
true
]
},
{
"function": "returnToOrigin",
"args": []
}
]
Executing Function Calls:
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 5
Closing gripper
moving to coordinates: 163, 427, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 5
Opening gripper
moving to coordinates: -247, 90, 15
Returning to origin pose
程式碼執行
Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 可以建議及執行 Python 程式碼,以執行需要動態動作的工作,例如放大圖片區域以查看更多細節。
這個範例說明模型如何建議使用「程式碼執行」工具「放大」圖片的特定區域,然後執行這項操作來回答使用者的問題。
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
# Load your image and set up your prompt
with open('path/to/image-of-object.jpg', 'rb') as f:
image_bytes = f.read()
prompt = """
What is the air quality reading? Using the code execution feature,
zoom in on the image to take a closer look.
"""
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview",
contents=[
types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes,
mime_type='image/jpeg',
),
prompt
],
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0.5,
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
)
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
以下是這項工作的可能模型回覆。輸出內容會顯示模型生成的程式碼,用於放大圖片,以便更清楚地閱讀畫面內容。 此外,這項功能也會顯示系統調整裁剪方式的思考過程。如需完整的範例輸出內容,請參閱「Robotics cookbook」。
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
# Based on visual inspection, the display is roughly centered around [430, 430] to [500, 500] in a 1000x1000 scale.
# Let's try to zoom in on the display area.
# Bounding box for display: [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax] in pixels.
# From visual inspection of the original image (size 90489 bytes, resolution
unknown but let's assume a standard aspect ratio and roughly 1000x1000 for
relative positioning),
# the display is located at approximately y=380-480, x=410-540.
# Let's define a larger area around it for context.
# Let's say we want to crop from y=350 to y=550 and x=350 to x=650.
...
thought
The crop was too tight and only captured part of the display. Let's adjust the bounding box.
The previous crop was `img.crop((400, 350, 600, 500))`. This means xmin=400, ymin=350, xmax=600, ymax=500.
The display is centered around x=480, y=430.
The previous crop captured the left side of the display.
Let's expand the x range to the right and y range to cover the whole circle.
New bounding box estimate: ymin=370, xmin=400, ymax=500, xmax=600.
Let's try again with a wider crop.
# Detect relevant objects and output in json format
# [{"box_2d": [379, 407, 481, 553], "label": "display"}]
from PIL import Image
# Open the image
img = Image.open("input_file_0.jpeg")
# Define the coordinates for cropping (normalized to 0-1000)
…
The reading of 14 falls into the "Moderate" category.
The prompt asks for the "air quality reading", which can be interpreted as
either the numerical value or the categorical description. Given the numerical
value is explicitly displayed, it's the primary reading.
Let's provide the numerical value as the reading.
The reading is 014.
Based on the display on the air purifier, the air quality reading is **014**.
最佳做法
如要提升機器人應用程式的效能和準確度,請務必瞭解如何有效與 Gemini 模型互動。本節將說明撰寫提示、處理視覺資料和建構工作時的最佳做法和重要策略,協助您獲得最可靠的結果。
使用簡單明瞭的語言。
使用自然語言:Gemini 模型可理解自然對話語言。請以語意清楚的方式建構提示,並模擬人類自然給予指令的方式。
使用日常用語:請使用常見的日常用語,避免使用技術或專業術語。如果模型對特定字詞的回應不如預期,請嘗試使用更常見的同義字重新措辭。
最佳化視覺輸入內容。
放大檢視詳細資訊:處理小型或難以辨識的物件時,請使用定界框函式,將感興趣的物件獨立出來。接著,您可以將圖片裁剪成所選範圍,然後將新圖片傳送給模型,進行更詳細的分析。
嘗試調整光線和色彩:光線不佳和色彩對比度不足,可能會影響模型的感知能力。
將複雜問題細分為較小的步驟。逐一處理每個較小的步驟,引導模型得出更精確的結果。
透過共識提高準確度。對於需要高度精確的任務,您可以多次使用相同提示查詢模型。只要將傳回的結果平均,即可得出「共識」,這通常會更準確且可靠。
限制
使用 Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 開發時,請注意下列限制:
- 預覽狀態:模型目前處於預覽階段。API 和功能可能會變更,且未經過徹底測試,因此可能不適合用於生產環境關鍵應用程式。
- 延遲:複雜的查詢、高解析度輸入內容或大量資料可能會導致處理時間增加。
thinking_budget - 幻覺:與所有大型語言模型一樣,Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 有時可能會「產生幻覺」或提供不正確的資訊,尤其是針對模稜兩兩可的提示或超出分布範圍的輸入內容。
- 取決於提示品質:模型輸出內容的品質高度取決於輸入提示的清晰度和具體程度。如果提示含糊不清或結構不佳,可能會導致結果不盡理想。
- 運算成本:執行模型 (尤其是使用影片輸入內容或高
thinking_budget時) 會消耗運算資源並產生費用。詳情請參閱「思考」頁面。 - 輸入類型:如要瞭解各模式的限制,請參閱下列主題。
隱私權聲明
您瞭解本文件提及的機器人模型 (以下簡稱「機器人模型」) 會運用影片和音訊資料,根據您的指示操作及移動硬體。因此,您可能會操作機器人模型,讓模型收集可識別身分者的資料,例如語音、圖像和肖像資料 (以下簡稱「個人資料」)。如果您選擇以會蒐集個人資料的方式操作機器人模型,您同意不會允許任何可識別身分者與機器人模型互動或出現在機器人模型周圍區域,除非且直到這類可識別身分者已充分瞭解並同意,他們的個人資料可能會提供給 Google 並由 Google 使用,如《Gemini API 額外服務條款》(請參閱 https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/terms,以下簡稱「條款」) 所述,包括根據「Google 如何使用您的資料」一節的規定。您應確保這類通知允許收集及使用《條款》所述的個人資料,並盡可能運用商業上合理的努力,透過臉部模糊處理等技術,以及在不含可識別身分者的區域操作機器人模型,盡量減少個人資料的收集和散布。
定價
如需價格和適用區域的詳細資訊,請參閱價格頁面。
模型版本
| 屬性 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| 模型代碼 | gemini-robotics-er-1.5-preview |
| 支援的資料類型 |
輸入裝置 文字、圖片、影片、音訊 輸出內容 文字 |
| 代幣限制[*] |
輸入權杖限制 1,048,576 輸出詞元限制 65,536 |
| 功能 |
語音生成 不支援 批次 API 不支援 快取 不支援 程式碼執行 支援 函式呼叫 支援 運用 Google 地圖建立基準 不支援 圖像生成 不支援 Live API 不支援 以 Google 搜尋為參考依據 支援 結構化輸出內容 支援 思考 支援 網址內容 支援 |
| 個版本 |
|
| 最新更新 | 2025 年 9 月 |
| 知識截點 | 2025 年 1 月 |
後續步驟
- 探索其他功能,並繼續嘗試不同的提示詞和輸入內容,發掘 Gemini Robotics-ER 1.5 的更多應用。 如需更多範例,請參閱「機器人食譜」。
- 如要瞭解 Gemini Robotics 模型如何以安全為優先考量而建構,請前往 Google DeepMind 機器人安全頁面。
- 如要瞭解 Gemini Robotics 模型最新消息,請前往 Gemini Robotics 登陸頁面。
