그래픽 처리 장치 (GPU)를 사용하여 머신러닝 (ML) 모델 실행 모델의 성능과 사용자 경험을 크게 향상할 수 있습니다. ML 지원 애플리케이션을 관리할 수 있습니다 iOS 기기에서는 TensorFlow를 사용하여 모델의 GPU 가속 실행 위임). 대리인은 LiteRT - GPU 프로세서에서 모델의 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다.
이 페이지에서는 다음에서 LiteRT 모델에 GPU 가속을 사용 설정하는 방법을 설명합니다. iOS 앱 LiteRT용 GPU 대리자를 사용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 자세한 내용은 GPU 위임 페이지를 참조하세요.
Interpreter API와 함께 GPU 사용
LiteRT 인터프리터 API는 일반적인 머신러닝 애플리케이션 빌드를 위한 API를 살펴보았습니다 다음 안내에서는 iOS 앱에 GPU 지원을 추가하는 방법을 안내합니다. 이 가이드 ML 모델을 성공적으로 실행할 수 있는 iOS 앱이 이미 있다고 가정합니다. .
GPU 지원을 포함하도록 Podfile 수정
LiteRT 2.3.0 출시부터 GPU 대리자가 제외됩니다.
바이너리 크기를 줄일 수 있습니다 다음과 같은 방법으로 포함할 수 있습니다.
TensorFlowLiteSwift 포드의 하위 사양입니다.
pod 'TensorFlowLiteSwift/Metal', '~> 0.0.1-nightly',
또는
pod 'TensorFlowLiteSwift', '~> 0.0.1-nightly', :subspecs => ['Metal']
사용하려면 TensorFlowLiteObjC 또는 TensorFlowLiteC를 사용할 수도 있습니다.
Objective-C(버전 2.4.0 이상에서 사용 가능) 또는 C API
GPU 대리자 초기화 및 사용
LiteRT 인터프리터와 함께 GPU 대리자를 사용할 수 있습니다. API를 사용하여 있습니다. Swift 및 Objective-C를 사용하는 것이 좋지만 C++ 및 있습니다. 이전 버전의 LiteRT를 사용 중인 경우 C를 사용해야 합니다. 더 높습니다. 다음 코드 예에서는 각 있습니다.
Swift
import TensorFlowLite // Load model ... // Initialize LiteRT interpreter with the GPU delegate. let delegate = MetalDelegate() if let interpreter = try Interpreter(modelPath: modelPath, delegates: [delegate]) { // Run inference ... }
Objective-C
// Import module when using CocoaPods with module support @import TFLTensorFlowLite; // Or import following headers manually #import "tensorflow/lite/objc/apis/TFLMetalDelegate.h" #import "tensorflow/lite/objc/apis/TFLTensorFlowLite.h" // Initialize GPU delegate TFLMetalDelegate* metalDelegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] init]; // Initialize interpreter with model path and GPU delegate TFLInterpreterOptions* options = [[TFLInterpreterOptions alloc] init]; NSError* error = nil; TFLInterpreter* interpreter = [[TFLInterpreter alloc] initWithModelPath:modelPath options:options delegates:@[ metalDelegate ] error:&error]; if (error != nil) { /* Error handling... */ } if (![interpreter allocateTensorsWithError:&error]) { /* Error handling... */ } if (error != nil) { /* Error handling... */ } // Run inference ...
C++
// Set up interpreter. auto model = FlatBufferModel::BuildFromFile(model_path); if (!model) return false; tflite::ops::builtin::BuiltinOpResolver op_resolver; std::unique_ptr<Interpreter> interpreter; InterpreterBuilder(*model, op_resolver)(&interpreter); // Prepare GPU delegate. auto* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(/*default options=*/nullptr); if (interpreter->ModifyGraphWithDelegate(delegate) != kTfLiteOk) return false; // Run inference. WriteToInputTensor(interpreter->typed_input_tensor<float>(0)); if (interpreter->Invoke() != kTfLiteOk) return false; ReadFromOutputTensor(interpreter->typed_output_tensor<float>(0)); // Clean up. TFLGpuDelegateDelete(delegate);
C (2.4.0 이전)
#include "tensorflow/lite/c/c_api.h" #include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate.h" // Initialize model TfLiteModel* model = TfLiteModelCreateFromFile(model_path); // Initialize interpreter with GPU delegate TfLiteInterpreterOptions* options = TfLiteInterpreterOptionsCreate(); TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGPUDelegateCreate(nil); // default config TfLiteInterpreterOptionsAddDelegate(options, metal_delegate); TfLiteInterpreter* interpreter = TfLiteInterpreterCreate(model, options); TfLiteInterpreterOptionsDelete(options); TfLiteInterpreterAllocateTensors(interpreter); NSMutableData *input_data = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:input_size * sizeof(float)]; NSMutableData *output_data = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:output_size * sizeof(float)]; TfLiteTensor* input = TfLiteInterpreterGetInputTensor(interpreter, 0); const TfLiteTensor* output = TfLiteInterpreterGetOutputTensor(interpreter, 0); // Run inference TfLiteTensorCopyFromBuffer(input, inputData.bytes, inputData.length); TfLiteInterpreterInvoke(interpreter); TfLiteTensorCopyToBuffer(output, outputData.mutableBytes, outputData.length); // Clean up TfLiteInterpreterDelete(interpreter); TFLGpuDelegateDelete(metal_delegate); TfLiteModelDelete(model);
GPU API 언어 사용 참고사항
- 2.4.0 이전의 LiteRT 버전은 Objective-C
- C++ API는 bazel을 사용하거나 TensorFlow를 빌드할 때만 사용할 수 있습니다. 나만의 세상. C++ API는 CocoaPods와 함께 사용할 수 없습니다.
- C++로 GPU 대리자와 함께 LiteRT를 사용하는 경우 GPU 가져오기
TFLGpuDelegateCreate()함수를 통해 위임한 다음Interpreter::ModifyGraphWithDelegate(), 호출하지 않음Interpreter::AllocateTensors()입니다.
출시 모드로 빌드 및 테스트
적절한 Metal API 가속기 설정이 있는 출시 빌드로 변경합니다. 성능을 향상하고 최종 테스트를 수행할 수 있습니다. 이 섹션에서는 출시 빌드를 사용 설정하고 Metal 가속 설정을 구성하세요.
출시 빌드로 변경하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- Product(제품) > 스키마 > 스키마 수정... 실행을 선택합니다.
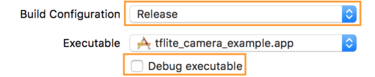
- Info 탭에서 Build Configuration을 Release로 변경하고
실행 파일 디버그를 선택 해제합니다. <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
 </ph>
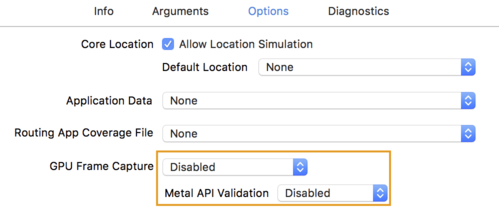
</ph> - Options(옵션) 탭을 클릭하고 GPU Frame Capture(GPU 프레임 캡처)를 Disabled(사용 중지됨)로 변경합니다.
금속 API 유효성 검사를 사용 안함으로 변경합니다.
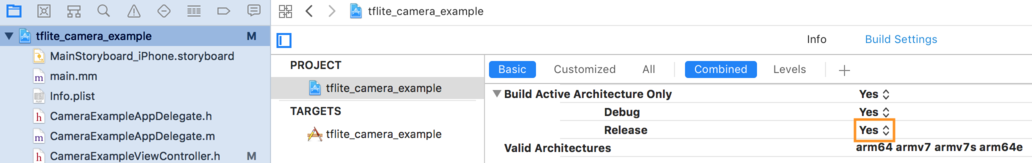
- 64비트 아키텍처에서 출시 전용 빌드를 선택해야 합니다. 미달
프로젝트 탐색기 > tflite_camera_example> 프로젝트 > 프로젝트 이름 >
Build Settings(빌드 설정)에서 Build Active Architecture Only(활성 아키텍처만 빌드) > 릴리스 대상
예. <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
 </ph>
</ph>
고급 GPU 지원
이 섹션에서는 다음을 포함한 iOS용 GPU 대리자의 고급 사용에 대해 다룹니다. 위임 옵션, 입력 및 출력 버퍼, 양자화 모델의 사용에 관한 한 가지 주요 개념입니다.
iOS용 위임 옵션
GPU 위임을 위한 생성자는 Swift의 struct 옵션을 허용합니다.
API를 사용하여
Objective-C
API를 참고하세요
및 C
API를 참고하세요.
nullptr (C API) 또는 아무것도 (Objective-C 및 Swift API)를
이니셜라이저는
참조).
Swift
// THIS: var options = MetalDelegate.Options() options.isPrecisionLossAllowed = false options.waitType = .passive options.isQuantizationEnabled = true let delegate = MetalDelegate(options: options) // IS THE SAME AS THIS: let delegate = MetalDelegate()
Objective-C
// THIS: TFLMetalDelegateOptions* options = [[TFLMetalDelegateOptions alloc] init]; options.precisionLossAllowed = false; options.waitType = TFLMetalDelegateThreadWaitTypePassive; options.quantizationEnabled = true; TFLMetalDelegate* delegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] initWithOptions:options]; // IS THE SAME AS THIS: TFLMetalDelegate* delegate = [[TFLMetalDelegate alloc] init];
C
// THIS: const TFLGpuDelegateOptions options = { .allow_precision_loss = false, .wait_type = TFLGpuDelegateWaitType::TFLGpuDelegateWaitTypePassive, .enable_quantization = true, }; TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(options); // IS THE SAME AS THIS: TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(nullptr);
C++ API를 사용하는 입력/출력 버퍼
GPU에서 계산하려면 GPU에서 데이터를 사용할 수 있어야 합니다. 이 요구사항은 종종 메모리 복사를 수행해야 한다는 것을 의미합니다. 피해야 할 사항: 이 작업은 CPU/GPU 메모리 경계를 넘습니다. 이는 CPU/GPU 메모리 경계를 넘어서 오래 걸리지 않습니다. 보통은 이러한 교차를 피할 수 없지만, 어떤 경우에는 특수한 경우 둘 중 하나를 생략할 수 있습니다.
네트워크의 입력이 GPU 메모리에 이미 로드된 이미지인 경우( 예: 카메라 피드를 포함하는 GPU 텍스처)는 GPU 메모리에 남아 있을 수 있습니다. 데이터를 얻을 수 있습니다. 마찬가지로 네트워크의 출력이 이미지 스타일과 같이 렌더링 가능한 이미지 형식 전송 사용하면 결과를 화면에 직접 표시할 수 있습니다.
최상의 성능을 달성하기 위해 LiteRT는 사용자가 TensorFlow 하드웨어 버퍼에서 직접 읽고 쓰고 이를 우회합니다. 메모리 사본을 만들 수 있습니다
이미지 입력이 GPU 메모리에 있다고 가정하면 먼저 이미지 입력을 위한
Metal용 MTLBuffer 객체입니다. TfLiteTensor를
사용자가 TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor()(으)로 MTLBuffer를 준비함
함수를 사용하세요. 이 함수는 반드시 호출된 후에
Interpreter::ModifyGraphWithDelegate()입니다. 또한 추론 출력은 다음과 같습니다.
기본적으로 GPU 메모리에서 CPU 메모리로 복사됩니다. 이 동작을 사용 중지할 수 있습니다.
다음 동안 Interpreter::SetAllowBufferHandleOutput(true) 호출
초기화하지 않아도 됩니다
C++
#include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate.h" #include "tensorflow/lite/delegates/gpu/metal_delegate_internal.h" // ... // Prepare GPU delegate. auto* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(nullptr); if (interpreter->ModifyGraphWithDelegate(delegate) != kTfLiteOk) return false; interpreter->SetAllowBufferHandleOutput(true); // disable default gpu->cpu copy if (!TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor( delegate, interpreter->inputs()[0], user_provided_input_buffer)) { return false; } if (!TFLGpuDelegateBindMetalBufferToTensor( delegate, interpreter->outputs()[0], user_provided_output_buffer)) { return false; } // Run inference. if (interpreter->Invoke() != kTfLiteOk) return false;
기본 동작이 사용 중지되면 GPU에서 추론 출력을 복사합니다.
CPU 메모리에 메모리를 할당하려면
각 출력 텐서의 Interpreter::EnsureTensorDataIsReadable(). 이
이 접근 방식은 양자화 모델에서도 작동하지만 여전히
float32 크기의 버퍼를 사용합니다. 버퍼가
내부 역양자화 버퍼입니다.
양자화 모델
iOS GPU 위임 라이브러리는 기본적으로 양자화 모델을 지원합니다. 부적절한 콘텐츠 GPU 대리자와 함께 양자화 모델을 사용하려면 코드를 변경해야 합니다. 이 다음 섹션에서는 테스트 또는 배포를 위해 양자화 지원을 중지하는 방법을 설명합니다. 있습니다.
양자화 모델 지원 사용 중지
다음 코드는 양자화 모델에 대한 지원을 사용 중지하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
Swift
var options = MetalDelegate.Options() options.isQuantizationEnabled = false let delegate = MetalDelegate(options: options)
Objective-C
TFLMetalDelegateOptions* options = [[TFLMetalDelegateOptions alloc] init]; options.quantizationEnabled = false;
C
TFLGpuDelegateOptions options = TFLGpuDelegateOptionsDefault(); options.enable_quantization = false; TfLiteDelegate* delegate = TFLGpuDelegateCreate(options);
GPU 가속으로 양자화 모델을 실행하는 방법에 관한 자세한 내용은 GPU 위임 개요
