The Gemini API provides a code execution tool that enables the model to generate and run Python code. The model can then learn iteratively from the code execution results until it arrives at a final output. You can use code execution to build applications that benefit from code-based reasoning. For example, you can use code execution to solve equations or process text. You can also use the libraries included in the code execution environment to perform more specialized tasks.
Gemini is only able to execute code in Python. You can still ask Gemini to generate code in another language, but the model can't use the code execution tool to run it.
Enable code execution
To enable code execution, configure the code execution tool on the model. This allows the model to generate and run code.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.",
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
const parts = response?.candidates?.[0]?.content?.parts || [];
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode && part.executableCode.code) {
console.log(part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult && part.codeExecutionResult.output) {
console.log(part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
});
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
result, _ := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
genai.Text("What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."),
config,
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d ' {"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": {
"parts":
{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}
},
}'
The output might look something like the following, which has been formatted for readability:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
This output combines several content parts that the model returns when using code execution:
text: Inline text generated by the modelexecutableCode: Code generated by the model that is meant to be executedcodeExecutionResult: Result of the executable code
The naming conventions for these parts vary by programming language.
Code Execution with images (Gemini 3)
The Gemini 3 Flash model can now write and execute Python code to actively manipulate and inspect images.
Use cases
- Zoom and inspect: The model implicitly detects when details are too small (e.g., reading a distant gauge) and writes code to crop and re-examine the area at higher resolution.
- Visual math: The model can run multi-step calculations using code (e.g., summing line items on a receipt).
- Image annotation: The model can annotate images to answer questions, such as drawing arrows to show relationships.
Enable Code Execution with images
Code Execution with images is officially supported in Gemini 3 Flash. You can activate this behavior by enabling both Code Execution as a tool and Thinking.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
from PIL import Image
import io
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
image = types.Part.from_bytes(
data=image_bytes, mime_type="image/jpeg"
)
# Ensure you have your API key set
client = genai.Client()
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[image, "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
if part.as_image() is not None:
# display() is a standard function in Jupyter/Colab notebooks
display(Image.open(io.BytesIO(part.as_image().image_bytes)))
JavaScript
async function main() {
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({ });
// 1. Prepare Image Data
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
// 2. Call the API with Code Execution enabled
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: [
{
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
},
{ text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?" }
],
config: {
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }],
},
});
// 3. Process the response (Text, Code, and Execution Results)
const candidates = result.candidates;
if (candidates && candidates[0].content.parts) {
for (const part of candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.text) {
console.log("Text:", part.text);
}
if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(`\nGenerated Code (${part.executableCode.language}):\n`, part.executableCode.code);
}
if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(`\nExecution Output (${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}):\n`, part.codeExecutionResult.output);
}
}
}
}
main();
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initialize Client (Reads GEMINI_API_KEY from env)
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 1. Download the image
imageResp, err := http.Get("https://goo.gle/instrument-img")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer imageResp.Body.Close()
imageBytes, err := io.ReadAll(imageResp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 2. Configure Code Execution Tool
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
// 3. Generate Content
result, err := client.Models.GenerateContent(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
[]*genai.Content{
{
Parts: []*genai.Part{
{InlineData: &genai.Blob{MIMEType: "image/jpeg", Data: imageBytes}},
{Text: "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"},
},
Role: "user",
},
},
config,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 4. Parse Response (Text, Code, Output)
for _, cand := range result.Candidates {
for _, part := range cand.Content.Parts {
if part.Text != "" {
fmt.Println("Text:", part.Text)
}
if part.ExecutableCode != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nGenerated Code (%s):\n%s\n",
part.ExecutableCode.Language,
part.ExecutableCode.Code)
}
if part.CodeExecutionResult != nil {
fmt.Printf("\nExecution Output (%s):\n%s\n",
part.CodeExecutionResult.Outcome,
part.CodeExecutionResult.Output)
}
}
}
}
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MODEL="gemini-3-flash-preview"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/$MODEL:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[
{
"inline_data": {
"mime_type":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
},
{"text": "Zoom into the expression pedals and tell me how many pedals are there?"}
]
}],
"tools": [
{
"code_execution": {}
}
]
}'
Use code execution in chat
You can also use code execution as part of a chat.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
chat = client.chats.create(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[types.Tool(code_execution=types.ToolCodeExecution)]
),
)
response = chat.send_message("I have a math question for you.")
print(response.text)
response = chat.send_message(
"What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? "
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.text is not None:
print(part.text)
if part.executable_code is not None:
print(part.executable_code.code)
if part.code_execution_result is not None:
print(part.code_execution_result.output)
JavaScript
import {GoogleGenAI} from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
history: [
{
role: "user",
parts: [{ text: "I have a math question for you:" }],
},
{
role: "model",
parts: [{ text: "Great! I'm ready for your math question. Please ask away." }],
},
],
config: {
tools: [{codeExecution:{}}],
}
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({
message: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
});
console.log("Chat response:", response.text);
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"os"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := genai.NewClient(ctx, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
config := &genai.GenerateContentConfig{
Tools: []*genai.Tool{
{CodeExecution: &genai.ToolCodeExecution{}},
},
}
chat, _ := client.Chats.Create(
ctx,
"gemini-3-flash-preview",
config,
nil,
)
result, _ := chat.SendMessage(
ctx,
genai.Part{Text: "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and " +
"make sure you get all 50.",
},
)
fmt.Println(result.Text())
fmt.Println(result.ExecutableCode())
fmt.Println(result.CodeExecutionResult())
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"tools": [{"code_execution": {}}],
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "Can you print \"Hello world!\"?"
}]
},{
"role": "model",
"parts": [
{
"text": ""
},
{
"executable_code": {
"language": "PYTHON",
"code": "\nprint(\"hello world!\")\n"
}
},
{
"code_execution_result": {
"outcome": "OUTCOME_OK",
"output": "hello world!\n"
}
},
{
"text": "I have printed \"hello world!\" using the provided python code block. \n"
}
],
},{
"role": "user",
"parts": [{
"text": "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
}]
}
]
}'
Input/output (I/O)
Starting with Gemini 2.0 Flash, code execution supports file input and graph output. Using these input and output capabilities, you can upload CSV and text files, ask questions about the files, and have Matplotlib graphs generated as part of the response. The output files are returned as inline images in the response.
I/O pricing
When using code execution I/O, you're charged for input tokens and output tokens:
Input tokens:
- User prompt
Output tokens:
- Code generated by the model
- Code execution output in the code environment
- Thinking tokens
- Summary generated by the model
I/O details
When you're working with code execution I/O, be aware of the following technical details:
- The maximum runtime of the code environment is 30 seconds.
- If the code environment generates an error, the model may decide to regenerate the code output. This can happen up to 5 times.
- The maximum file input size is limited by the model token window. In AI Studio, using Gemini Flash 2.0, the maximum input file size is 1 million tokens (roughly 2MB for text files of the supported input types). If you upload a file that's too large, AI Studio won't let you send it.
- Code execution works best with text and CSV files.
- The input file can be passed in
part.inlineDataorpart.fileData(uploaded via the Files API), and the output file is always returned aspart.inlineData.
| Single turn | Bidirectional (Multimodal Live API) | |
|---|---|---|
| Models supported | All Gemini 2.0 and 2.5 models | Only Flash experimental models |
| File input types supported | .png, .jpeg, .csv, .xml, .cpp, .java, .py, .js, .ts | .png, .jpeg, .csv, .xml, .cpp, .java, .py, .js, .ts |
| Plotting libraries supported | Matplotlib, seaborn | Matplotlib, seaborn |
| Multi-tool use | Yes (code execution + grounding only) | Yes |
Billing
There's no additional charge for enabling code execution from the Gemini API. You'll be billed at the current rate of input and output tokens based on the Gemini model you're using.
Here are a few other things to know about billing for code execution:
- You're only billed once for the input tokens you pass to the model, and you're billed for the final output tokens returned to you by the model.
- Tokens representing generated code are counted as output tokens. Generated code can include text and multimodal output like images.
- Code execution results are also counted as output tokens.
The billing model is shown in the following diagram:
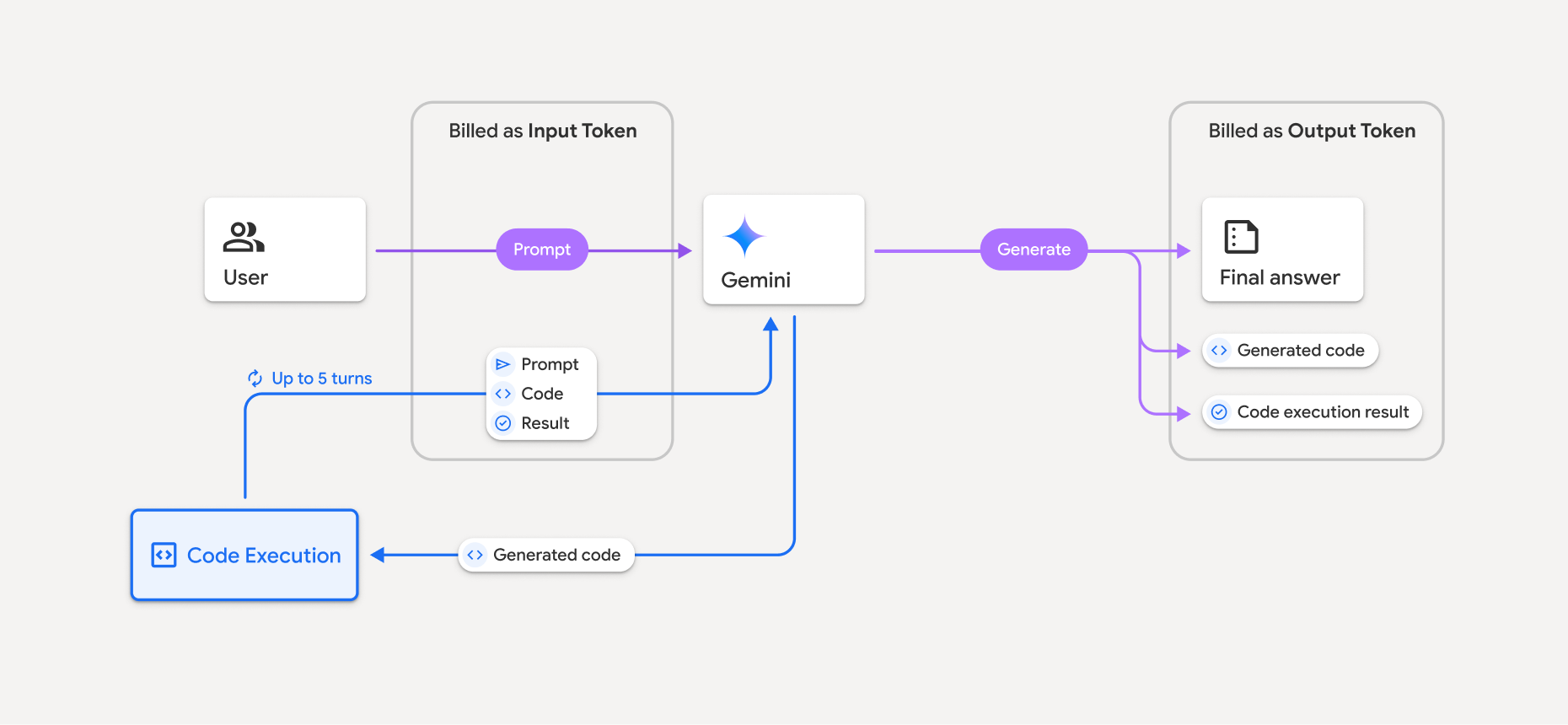
- You're billed at the current rate of input and output tokens based on the Gemini model you're using.
- If Gemini uses code execution when generating your response, the original prompt, the generated code, and the result of the executed code are labeled intermediate tokens and are billed as input tokens.
- Gemini then generates a summary and returns the generated code, the result of the executed code, and the final summary. These are billed as output tokens.
- The Gemini API includes an intermediate token count in the API response, so you know why you're getting additional input tokens beyond your initial prompt.
Limitations
- The model can only generate and execute code. It can't return other artifacts like media files.
- In some cases, enabling code execution can lead to regressions in other areas of model output (for example, writing a story).
- There is some variation in the ability of the different models to use code execution successfully.
Supported tools combinations
Code execution tool can be combined with Grounding with Google Search to power more complex use cases.
Supported libraries
The code execution environment includes the following libraries:
- attrs
- chess
- contourpy
- fpdf
- geopandas
- imageio
- jinja2
- joblib
- jsonschema
- jsonschema-specifications
- lxml
- matplotlib
- mpmath
- numpy
- opencv-python
- openpyxl
- packaging
- pandas
- pillow
- protobuf
- pylatex
- pyparsing
- PyPDF2
- python-dateutil
- python-docx
- python-pptx
- reportlab
- scikit-learn
- scipy
- seaborn
- six
- striprtf
- sympy
- tabulate
- tensorflow
- toolz
- xlrd
You can't install your own libraries.
What's next
- Try the code execution Colab.
- Learn about other Gemini API tools:
