API Gemini обеспечивает расширенную генерацию поиска (Retrieval Augmented Generation, RAG) с помощью инструмента поиска по файлам. Поиск по файлам импортирует, разбивает на фрагменты и индексирует ваши данные, обеспечивая быстрый поиск релевантной информации на основе предоставленного запроса. Затем эта информация используется в качестве контекста для модели, что позволяет модели предоставлять более точные и релевантные ответы.
Чтобы сделать поиск файлов простым и доступным для разработчиков, мы предоставляем бесплатное хранение файлов и генерацию встраиваний во время выполнения запроса. Вы платите только за создание встраиваний при первом индексировании файлов (по стоимости соответствующей модели встраивания) и обычной стоимости входных/выходных токенов модели Gemini. Эта новая система оплаты делает инструмент поиска файлов проще и экономичнее в разработке и масштабировании.
Загрузка непосредственно в хранилище файлов с поиском файлов.
В этом примере показано, как напрямую загрузить файл в хранилище поиска файлов :
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file='sample.txt',
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
config={
'display_name' : 'display-file-name',
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
Для получения более подробной информации ознакомьтесь со справочником API для uploadToFileSearchStore .
Импорт файлов
В качестве альтернативы вы можете загрузить существующий файл и импортировать его в свою файловую систему поиска :
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
sample_file = client.files.upload(file='sample.txt', config={'name': 'display_file_name'})
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const sampleFile = await ai.files.upload({
file: 'sample.txt',
config: { name: 'file-name' }
});
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation: operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
Для получения более подробной информации обратитесь к справочнику API для importFile .
Настройка разбиения на блоки
При импорте файла в хранилище файлового поиска он автоматически разбивается на фрагменты, встраивается, индексируется и загружается в ваше хранилище файлового поиска. Если вам нужен больший контроль над стратегией разбиения на фрагменты, вы можете указать параметр chunking_config , чтобы задать максимальное количество токенов на фрагмент и максимальное количество перекрывающихся токенов.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
config={
'chunking_config': {
'white_space_config': {
'max_tokens_per_chunk': 200,
'max_overlap_tokens': 20
}
}
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
print("Custom chunking complete.")
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
chunkingConfig: {
whiteSpaceConfig: {
maxTokensPerChunk: 200,
maxOverlapTokens: 20
}
}
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
console.log("Custom chunking complete.");
Чтобы использовать хранилище файлов, переданное методом generateContent , используйте его в качестве инструмента, как показано в примерах загрузки и импорта .
Как это работает
Поиск файлов использует метод, называемый семантическим поиском, для нахождения информации, релевантной запросу пользователя. В отличие от стандартного поиска по ключевым словам, семантический поиск понимает смысл и контекст вашего запроса.
При импорте файла он преобразуется в числовые представления, называемые эмбеддингами , которые отражают семантическое значение текста. Эти эмбеддинги хранятся в специализированной базе данных поиска файлов. При выполнении запроса он также преобразуется в эмбеддинг. Затем система выполняет поиск файлов, чтобы найти наиболее похожие и релевантные фрагменты документа в хранилище результатов поиска файлов.
Для эмбеддингов и файлов не существует параметра Time To Live (TTL); они сохраняются до тех пор, пока не будут удалены вручную или пока модель не будет признана устаревшей.
Вот подробное описание процесса использования API ` uploadToFileSearchStore для поиска файлов:
Создайте хранилище для поиска по файлам : хранилище для поиска по файлам содержит обработанные данные из ваших файлов. Это постоянный контейнер для векторных представлений, с которыми будет работать семантический поиск.
Загрузка файла и импорт в хранилище File Search : Одновременно загрузите файл и импортируйте результаты в ваше хранилище File Search. Это создаст временный объект
File, который будет являться ссылкой на ваш исходный документ. Затем эти данные будут разбиты на фрагменты, преобразованы в векторные представления File Search и проиндексированы. ОбъектFileудаляется через 48 часов, а данные, импортированные в хранилище File Search, будут храниться неограниченно долго, пока вы не решите их удалить.Запрос с использованием поиска по файлам : Наконец, вы используете инструмент
FileSearchв вызовеgenerateContent. В конфигурации инструмента вы указываетеFileSearchRetrievalResource, который указывает на хранилищеFileSearchStore, в котором вы хотите выполнить поиск. Это указывает модели выполнить семантический поиск в этом конкретном хранилище FileSearchStore, чтобы найти релевантную информацию для обоснования своего ответа.
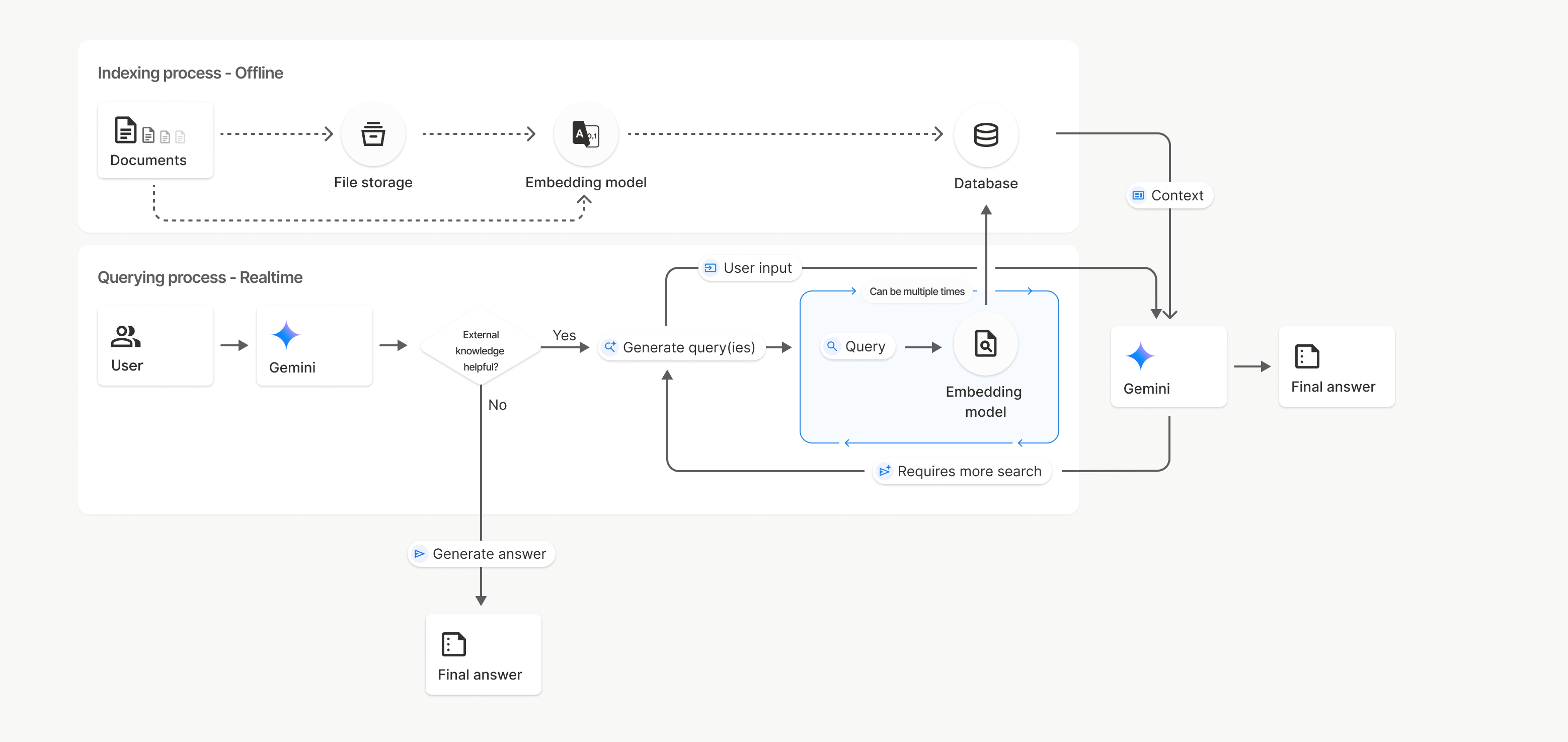
На этой диаграмме пунктирная линия от Documents к модели Embedding (с использованием gemini-embedding-001 ) представляет API uploadToFileSearchStore (в обход хранилища файлов ). В противном случае, использование API Files для отдельного создания и последующего импорта файлов перемещает процесс индексирования из Documents в хранилище файлов , а затем в модель Embedding .
Магазины поиска файлов
Хранилище поиска файлов — это контейнер для встраивания ваших документов. В то время как исходные файлы, загруженные через File API, удаляются через 48 часов, данные, импортированные в хранилище поиска файлов, хранятся неограниченно долго, пока вы не удалите их вручную. Вы можете создать несколько хранилищ поиска файлов для организации ваших документов. API FileSearchStore позволяет создавать, просматривать, получать и удалять хранилища поиска файлов для управления ими. Имена хранилищ поиска файлов имеют глобальную область видимости.
Вот несколько примеров того, как управлять хранилищами файлового поиска:
Python
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'my-file_search-store-123'})
for file_search_store in client.file_search_stores.list():
print(file_search_store)
my_file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123')
client.file_search_stores.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123', config={'force': True})
JavaScript
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'my-file_search-store-123' }
});
const fileSearchStores = await ai.fileSearchStores.list();
for await (const store of fileSearchStores) {
console.log(store);
}
const myFileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123',
config: { force: true }
});
ОТДЫХ
curl -X POST "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{ "displayName": "My Store" }'
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
Поиск файлов документов
С помощью API поиска файлов по документам вы можете управлять отдельными документами в своих файловых хранилищах, получать list всех документов в хранилище поиска, get информацию о документе и delete документ по имени.
Python
for document_in_store in client.file_search_stores.documents.list(parent='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'):
print(document_in_store)
file_search_document = client.file_search_stores.documents.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
print(file_search_document)
client.file_search_stores.documents.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
JavaScript
const documents = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.list({
parent: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
for await (const doc of documents) {
console.log(doc);
}
const fileSearchDocument = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
ОТДЫХ
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
Метаданные файла
Вы можете добавлять пользовательские метаданные к своим файлам, чтобы фильтровать их или предоставлять дополнительный контекст. Метаданные представляют собой набор пар «ключ-значение».
Python
op = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
custom_metadata=[
{"key": "author", "string_value": "Robert Graves"},
{"key": "year", "numeric_value": 1934}
]
)
JavaScript
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name,
config: {
customMetadata: [
{ key: "author", stringValue: "Robert Graves" },
{ key: "year", numericValue: 1934 }
]
}
});
Это полезно, когда у вас в хранилище поиска файлов находится несколько документов, и вы хотите выполнить поиск только в их подмножестве.
Python
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name],
metadata_filter="author=Robert Graves",
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name],
metadataFilter: 'author="Robert Graves"',
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
ОТДЫХ
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[{"text": "Tell me about the book I, Claudius"}]
}],
"tools": [{
"file_search": {
"file_search_store_names":["'$STORE_NAME'"],
"metadata_filter": "author = \"Robert Graves\""
}
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
Инструкции по реализации синтаксиса фильтра списков для metadata_filter можно найти по адресу google.aip.dev/160
Цитаты
При использовании поиска по файлу ответ модели может содержать ссылки, указывающие, какие части загруженных вами документов были использованы для получения ответа. Это помогает в проверке и подтверждении фактов.
Доступ к информации о цитировании можно получить через атрибут grounding_metadata ответа.
Python
print(response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata)
JavaScript
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.candidates?.[0]?.groundingMetadata, null, 2));
Структурированный вывод
Начиная с моделей Gemini 3, вы можете объединить инструмент поиска файлов со структурированным выводом .
Python
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Money(BaseModel):
amount: str = Field(description="The numerical part of the amount.")
currency: str = Field(description="The currency of amount.")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
],
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=Money.model_json_schema()
)
)
result = Money.model_validate_json(response.text)
print(result)
JavaScript
import { z } from "zod";
const moneySchema = z.object({
amount: z.string().describe("The numerical part of the amount."),
currency: z.string().describe("The currency of amount."),
});
async function run() {
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [file_search_store.name],
},
},
],
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseJsonSchema: z.toJSONSchema(moneySchema),
},
});
const result = moneySchema.parse(JSON.parse(response.text));
console.log(result);
}
run();
ОТДЫХ
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts": [{"text": "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?"}]
}],
"tools": [
{
"fileSearch": {
"fileSearchStoreNames": ["$FILE_SEARCH_STORE_NAME"]
}
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"responseMimeType": "application/json",
"responseJsonSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "string", "description": "The numerical part of the amount."},
"currency": {"type": "string", "description": "The currency of amount."}
},
"required": ["amount", "currency"]
}
}
}'
Поддерживаемые модели
Следующие модели поддерживают поиск файлов:
| Модель | Поиск файлов |
|---|---|
| Gemini 3.1 Pro Preview | ✔️ |
| Предварительный просмотр Gemini 3 Pro | ✔️ |
| Предварительный просмотр Gemini 3 Flash | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ |
| Фонарь Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ |
Поддерживаемые типы файлов
Функция поиска файлов поддерживает широкий спектр форматов файлов, перечисленных в следующих разделах.
Типы файлов приложений
-
application/dart -
application/ecmascript -
application/json -
application/ms-java -
application/msword -
application/pdf -
application/sql -
application/typescript -
application/vnd.curl -
application/vnd.dart -
application/vnd.ibm.secure-container -
application/vnd.jupyter -
application/vnd.ms-excel -
application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.text -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.template -
application/x-csh -
application/x-hwp -
application/x-hwp-v5 -
application/x-latex -
application/x-php -
application/x-powershell -
application/x-sh -
application/x-shellscript -
application/x-tex -
application/x-zsh -
application/xml -
application/zip
Типы текстовых файлов
-
text/1d-interleaved-parityfec -
text/RED -
text/SGML -
text/cache-manifest -
text/calendar -
text/cql -
text/cql-extension -
text/cql-identifier -
text/css -
text/csv -
text/csv-schema -
text/dns -
text/encaprtp -
text/enriched -
text/example -
text/fhirpath -
text/flexfec -
text/fwdred -
text/gff3 -
text/grammar-ref-list -
text/hl7v2 -
text/html -
text/javascript -
text/jcr-cnd -
text/jsx -
text/markdown -
text/mizar -
text/n3 -
text/parameters -
text/parityfec -
text/php -
text/plain -
text/provenance-notation -
text/prs.fallenstein.rst -
text/prs.lines.tag -
text/prs.prop.logic -
text/raptorfec -
text/rfc822-headers -
text/rtf -
text/rtp-enc-aescm128 -
text/rtploopback -
text/rtx -
text/sgml -
text/shaclc -
text/shex -
text/spdx -
text/strings -
text/t140 -
text/tab-separated-values -
text/texmacs -
text/troff -
text/tsv -
text/tsx -
text/turtle -
text/ulpfec -
text/uri-list -
text/vcard -
text/vnd.DMClientScript -
text/vnd.IPTC.NITF -
text/vnd.IPTC.NewsML -
text/vnd.a -
text/vnd.abc -
text/vnd.ascii-art -
text/vnd.curl -
text/vnd.debian.copyright -
text/vnd.dvb.subtitle -
text/vnd.esmertec.theme-descriptor -
text/vnd.exchangeable -
text/vnd.familysearch.gedcom -
text/vnd.ficlab.flt -
text/vnd.fly -
text/vnd.fmi.flexstor -
text/vnd.gml -
text/vnd.graphviz -
text/vnd.hans -
text/vnd.hgl -
text/vnd.in3d.3dml -
text/vnd.in3d.spot -
text/vnd.latex-z -
text/vnd.motorola.reflex -
text/vnd.ms-mediapackage -
text/vnd.net2phone.commcenter.command -
text/vnd.radisys.msml-basic-layout -
text/vnd.senx.warpscript -
text/vnd.sosi -
text/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptor -
text/vnd.trolltech.linguist -
text/vnd.wap.si -
text/vnd.wap.sl -
text/vnd.wap.wml -
text/vnd.wap.wmlscript -
text/vtt -
text/wgsl -
text/x-asm -
text/x-bibtex -
text/x-boo -
text/xc -
text/x-c++hdr -
text/x-c++src -
text/x-cassandra -
text/x-chdr -
text/x-coffeescript -
text/x-component -
text/x-csh -
text/x-csharp -
text/x-csrc -
text/x-cuda -
text/xd -
text/x-diff -
text/x-dsrc -
text/x-emacs-lisp -
text/x-erlang -
text/x-gff3 -
text/x-go -
text/x-haskell -
text/x-java -
text/x-java-properties -
text/x-java-source -
text/x-kotlin -
text/x-lilypond -
text/x-lisp -
text/x-literate-haskell -
text/x-lua -
text/x-moc -
text/x-objcsrc -
text/x-pascal -
text/x-pcs-gcd -
text/x-perl -
text/x-perl-script -
text/x-python -
text/x-python-script -
text/xr-markdown -
text/x-rsrc -
text/x-rst -
text/x-ruby-script -
text/x-rust -
text/x-sass -
text/x-scala -
text/x-scheme -
text/x-script.python -
text/x-scss -
text/x-setext -
text/x-sfv -
text/x-sh -
text/x-siesta -
text/x-sos -
text/x-sql -
text/x-swift -
text/x-tcl -
text/x-tex -
text/x-vbasic -
text/x-vcalendar -
text/xml -
text/xml-dtd -
text/xml-external-parsed-entity -
text/yaml
Ограничения
- В Live API поиск файлов не поддерживается.
- Несовместимость инструментов: В настоящее время поиск файлов нельзя комбинировать с другими инструментами, такими как сопоставление с поиском Google , контекст URL и т. д.
Ограничения скорости
Для обеспечения стабильности работы API поиска файлов установлены следующие ограничения:
- Максимальный размер файла / ограничение на один документ : 100 МБ
- Общий размер хранилищ файлового поиска проекта (в зависимости от уровня пользователя):
- Бесплатно : 1 ГБ
- Уровень 1 : 10 ГБ
- Уровень 2 : 100 ГБ
- Уровень 3 : 1 ТБ
- Рекомендация : Ограничьте размер каждого хранилища результатов поиска файлов до 20 ГБ, чтобы обеспечить оптимальную задержку при извлечении данных.
Цены
- Разработчикам взимается плата за встраивание контента во время индексации на основе существующих цен на встраивание (0,15 доллара США за 1 миллион токенов).
- Хранение предоставляется бесплатно.
- Встраивание данных во время выполнения запроса предоставляется бесплатно.
- Полученные токены документа оплачиваются как обычные контекстные токены .
Что дальше?
- Для получения информации о хранилищах файлов и документах, полученных в результате поиска файлов, посетите справочник API.

