Google 검색을 사용한 그라운딩은 Gemini 모델을 실시간 웹 콘텐츠에 연결하며, 사용 가능한 모든 언어로 작동합니다. 이를 통해 Gemini는 지식 컷오프를 넘어 더 정확한 답변을 제공하고 검증 가능한 출처를 인용할 수 있습니다.
그라운딩을 사용하면 다음을 수행할 수 있는 애플리케이션을 빌드할 수 있습니다.
- 사실에 기반한 정확성 향상: 실제 정보를 기반으로 대답하여 모델 할루시네이션을 줄입니다.
- 실시간 정보 액세스: 최근 이벤트 및 주제에 관한 질문에 답합니다.
인용 제공: 모델의 주장에 대한 출처를 표시하여 사용자 신뢰를 구축합니다.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
client = genai.Client()
grounding_tool = types.Tool(
google_search=types.GoogleSearch()
)
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[grounding_tool]
)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Who won the euro 2024?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text)
자바스크립트
import { GoogleGenAI } from "@google/genai";
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
const groundingTool = {
googleSearch: {},
};
const config = {
tools: [groundingTool],
};
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Who won the euro 2024?",
config,
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"parts": [
{"text": "Who won the euro 2024?"}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"google_search": {}
}
]
}'
검색 도구 노트북을 사용해 자세히 알아보세요.
Google 검색을 사용한 그라운딩 작동 방식
google_search 도구를 사용 설정하면 모델이 정보 검색, 처리, 인용의 전체 워크플로를 자동으로 처리합니다.
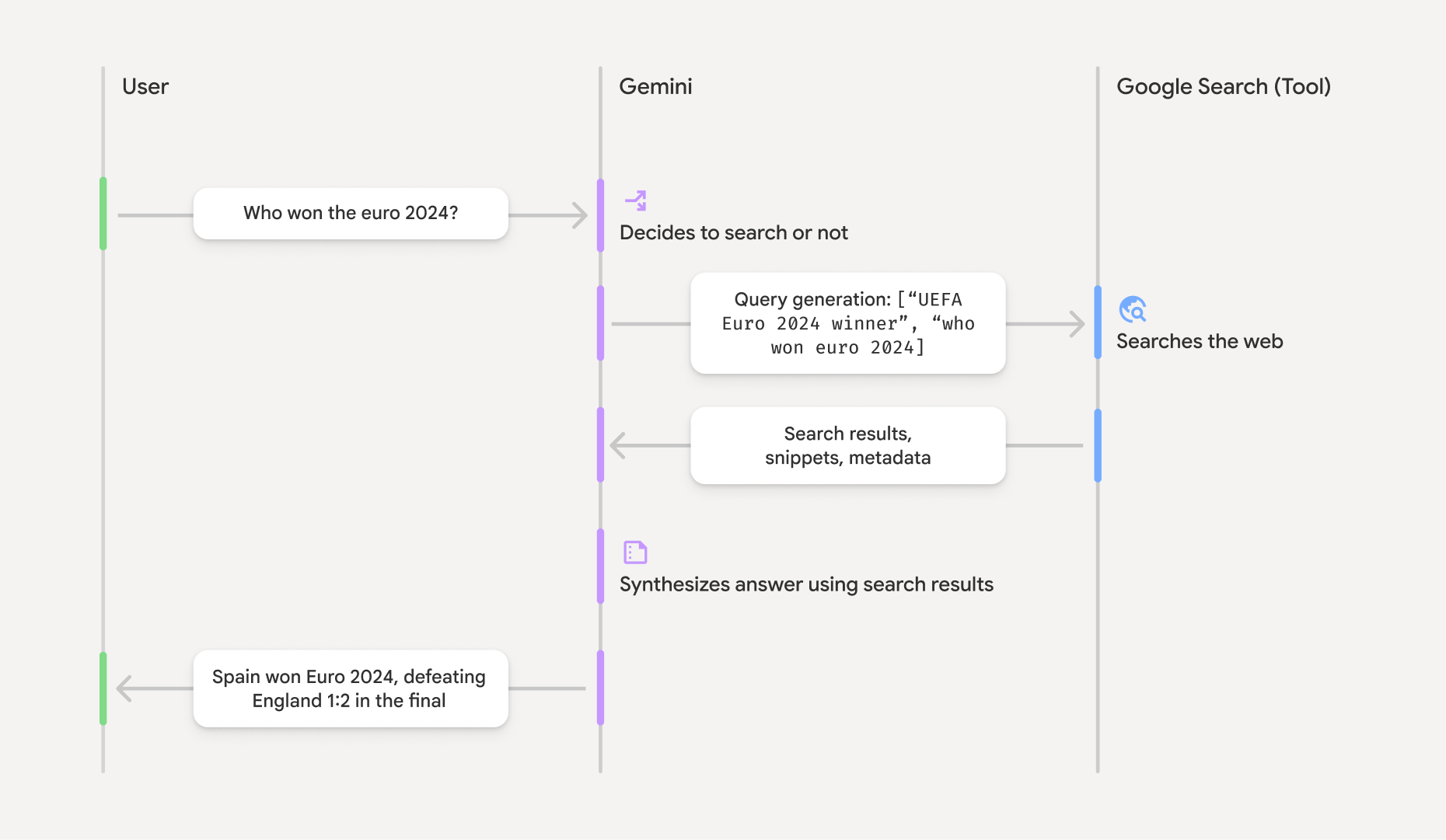
- 사용자 프롬프트: 애플리케이션이
google_search도구가 사용 설정된 상태로 사용자의 프롬프트를 Gemini API로 전송합니다. - 프롬프트 분석: 모델이 프롬프트를 분석하고 Google 검색으로 대답을 개선할 수 있는지 확인합니다.
- Google 검색: 필요한 경우 모델이 하나 이상의 검색어를 자동으로 생성하고 실행합니다.
- 검색 결과 처리: 모델이 검색 결과를 처리하고, 정보를 합성하고, 대답을 구성합니다.
- 그라운딩된 대답: API는 검색 결과를 기반으로 하는 최종적이고 사용자 친화적인 대답을 반환합니다. 이 대답에는 모델의 텍스트 대답과 검색어, 웹 결과, 인용이 포함된
groundingMetadata가 포함됩니다.
그라운딩 응답 이해하기
대답이 그라운딩되면 대답에 groundingMetadata 필드가 포함됩니다. 이 구조화된 데이터는 클레임을 확인하고 애플리케이션에서 풍부한 인용 환경을 구축하는 데 필수적입니다.
{
"candidates": [
{
"content": {
"parts": [
{
"text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final. This victory marks Spain's record fourth European Championship title."
}
],
"role": "model"
},
"groundingMetadata": {
"webSearchQueries": [
"UEFA Euro 2024 winner",
"who won euro 2024"
],
"searchEntryPoint": {
"renderedContent": "<!-- HTML and CSS for the search widget -->"
},
"groundingChunks": [
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "aljazeera.com"}},
{"web": {"uri": "https://vertexaisearch.cloud.google.com.....", "title": "uefa.com"}}
],
"groundingSupports": [
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 0, "endIndex": 85, "text": "Spain won Euro 2024, defeatin..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0]
},
{
"segment": {"startIndex": 86, "endIndex": 210, "text": "This victory marks Spain's..."},
"groundingChunkIndices": [0, 1]
}
]
}
}
]
}
Gemini API는 groundingMetadata와 함께 다음 정보를 반환합니다.
webSearchQueries: 사용된 검색어의 배열입니다. 이는 디버깅하고 모델의 추론 과정을 이해하는 데 유용합니다.searchEntryPoint: 필수 검색어 추천을 렌더링하는 HTML과 CSS가 포함되어 있습니다. 전체 사용 요구사항은 서비스 약관에 자세히 설명되어 있습니다.groundingChunks: 웹 소스 (uri및title)가 포함된 객체의 배열입니다.groundingSupports: 모델 응답text을groundingChunks의 소스에 연결하는 청크 배열입니다. 각 청크는 텍스트segment(startIndex및endIndex로 정의됨)를 하나 이상의groundingChunkIndices에 연결합니다. 이는 인라인 인용을 만드는 데 핵심적인 요소입니다.
Google 검색으로 그라운딩은 URL 컨텍스트 도구와 함께 사용하여 공개 웹 데이터와 사용자가 제공한 특정 URL 모두에서 대답을 그라운딩할 수도 있습니다.
본문 내 인용으로 출처 표시
API는 구조화된 인용 데이터를 반환하므로 사용자 인터페이스에서 소스를 표시하는 방식을 완전히 제어할 수 있습니다. groundingSupports 및 groundingChunks 필드를 사용하여 모델의 설명을 소스에 직접 연결할 수 있습니다. 다음은 메타데이터를 처리하여 클릭 가능한 인라인 인용이 포함된 대답을 만드는 일반적인 패턴입니다.
Python
def add_citations(response):
text = response.text
supports = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_supports
chunks = response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata.grounding_chunks
# Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
sorted_supports = sorted(supports, key=lambda s: s.segment.end_index, reverse=True)
for support in sorted_supports:
end_index = support.segment.end_index
if support.grounding_chunk_indices:
# Create citation string like [1](link1)[2](link2)
citation_links = []
for i in support.grounding_chunk_indices:
if i < len(chunks):
uri = chunks[i].web.uri
citation_links.append(f"[{i + 1}]({uri})")
citation_string = ", ".join(citation_links)
text = text[:end_index] + citation_string + text[end_index:]
return text
# Assuming response with grounding metadata
text_with_citations = add_citations(response)
print(text_with_citations)
자바스크립트
function addCitations(response) {
let text = response.text;
const supports = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingSupports;
const chunks = response.candidates[0]?.groundingMetadata?.groundingChunks;
// Sort supports by end_index in descending order to avoid shifting issues when inserting.
const sortedSupports = [...supports].sort(
(a, b) => (b.segment?.endIndex ?? 0) - (a.segment?.endIndex ?? 0),
);
for (const support of sortedSupports) {
const endIndex = support.segment?.endIndex;
if (endIndex === undefined || !support.groundingChunkIndices?.length) {
continue;
}
const citationLinks = support.groundingChunkIndices
.map(i => {
const uri = chunks[i]?.web?.uri;
if (uri) {
return `[${i + 1}](${uri})`;
}
return null;
})
.filter(Boolean);
if (citationLinks.length > 0) {
const citationString = citationLinks.join(", ");
text = text.slice(0, endIndex) + citationString + text.slice(endIndex);
}
}
return text;
}
const textWithCitations = addCitations(response);
console.log(textWithCitations);
인라인 인용이 포함된 새로운 대답은 다음과 같습니다.
Spain won Euro 2024, defeating England 2-1 in the final.[1](https:/...), [2](https:/...), [4](https:/...), [5](https:/...) This victory marks Spain's record-breaking fourth European Championship title.[5]((https:/...), [2](https:/...), [3](https:/...), [4](https:/...)
가격 책정
Gemini 3에서 Google 검색을 사용한 그라운딩을 사용하면 모델이 실행하기로 결정한 각 검색어에 대해 프로젝트에 요금이 청구됩니다. 모델이 단일 프롬프트에 답변하기 위해 여러 검색어를 실행하기로 결정하는 경우 (예: 동일한 API 호출 내에서 "UEFA Euro 2024 winner" 및 "Spain vs England Euro 2024 final
score" 검색) 해당 요청에 대해 도구의 청구 가능한 사용 2회로 계산됩니다. 청구 목적으로 고유한 검색어를 집계할 때 빈 웹 검색어는 무시됩니다. 이 청구 모델은 Gemini 3 모델에만 적용됩니다. Gemini 2.5 또는 이전 모델에서 검색 그라운딩을 사용하는 경우 프롬프트당 프로젝트에 요금이 청구됩니다.
자세한 가격 정보는 Gemini API 가격 책정 페이지를 참고하세요.
지원되는 모델
실험용 및 미리보기 모델은 포함되지 않습니다. 모델 개요 페이지에서 기능을 확인할 수 있습니다.
| 모델 | Google 검색을 사용하는 그라운딩 |
|---|---|
| Gemini 3.1 Pro 프리뷰 | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Pro 프리뷰 | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash 프리뷰 | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ |
지원되는 도구 조합
코드 실행, URL 컨텍스트와 같은 다른 도구와 함께 Google 검색으로 그라운딩을 사용하여 더 복잡한 사용 사례를 지원할 수 있습니다.
다음 단계
- Gemini API 설명서의 Google 검색으로 그라운딩을 사용해 보세요.
- 함수 호출과 같은 다른 사용 가능한 도구에 대해 알아봅니다.
- URL 컨텍스트 도구를 사용하여 특정 URL로 프롬프트를 보강하는 방법을 알아보세요.
