تتيح Gemini API ميزة "التوليد المعزّز بالاسترجاع" (RAG) من خلال أداة "البحث في الملفات". تستورد ميزة "البحث عن الملفات" بياناتك وتقسّمها إلى أجزاء وتفهرسها لإتاحة استرجاع المعلومات ذات الصلة بسرعة استنادًا إلى طلب مقدَّم. ويتم بعد ذلك استخدام هذه المعلومات كسياق للنموذج، ما يتيح له تقديم إجابات أكثر دقة وملاءمةً.
لتوفير ميزة "البحث عن الملفات" للمطوّرين بطريقة بسيطة وفعّالة من حيث التكلفة، سنوفّر لهم مساحة تخزين الملفات وإنشاء عمليات التضمين في وقت طلب البحث بدون أي رسوم. لا تدفع مقابل إنشاء عمليات التضمين إلا عند فهرسة ملفاتك للمرة الأولى (بتكلفة نموذج التضمين السارية) وتكلفة الرموز المميزة العادية للإدخال والإخراج في نموذج Gemini. يساهم نموذج الفوترة الجديد هذا في تسهيل عملية إنشاء "أداة البحث عن الملفات" وتوسيع نطاقها، كما يجعلها أكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة.
التحميل مباشرةً إلى "متجر البحث عن الملفات"
يوضّح المثال التالي كيفية تحميل ملف مباشرةً إلى مخزن البحث عن الملفات:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file='sample.txt',
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
config={
'display_name' : 'display-file-name',
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
راجِع مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات uploadToFileSearchStore للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات.
استيراد الملفات
بدلاً من ذلك، يمكنك تحميل ملف حالي واستيراده إلى مساحة تخزين البحث عن الملفات باتّباع الخطوات التالية:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
sample_file = client.files.upload(file='sample.txt', config={'name': 'display_file_name'})
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const sampleFile = await ai.files.upload({
file: 'sample.txt',
config: { name: 'file-name' }
});
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation: operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
راجِع مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات importFile للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات.
إعدادات التقسيم
عند استيراد ملف إلى مستودع "البحث عن الملفات"، يتم تقسيمه تلقائيًا إلى أجزاء، وتضمينه، وفهرسته، وتحميله إلى مستودع "البحث عن الملفات". إذا كنت بحاجة إلى مزيد من التحكّم في استراتيجية التقسيم، يمكنك تحديد إعداد chunking_config لضبط الحد الأقصى لعدد الرموز المميزة لكل جزء والحد الأقصى لعدد الرموز المميزة المتداخلة.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
config={
'chunking_config': {
'white_space_config': {
'max_tokens_per_chunk': 200,
'max_overlap_tokens': 20
}
}
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
print("Custom chunking complete.")
JavaScript
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
chunkingConfig: {
whiteSpaceConfig: {
maxTokensPerChunk: 200,
maxOverlapTokens: 20
}
}
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
console.log("Custom chunking complete.");
لاستخدام متجر "البحث في الملفات"، مرِّره كأداة إلى طريقة generateContent، كما هو موضّح في المثالَين تحميل واستيراد.
آلية العمل
تستخدم ميزة "البحث عن الملفات" أسلوبًا يُعرف باسم البحث الدلالي للعثور على معلومات ذات صلة بطلب المستخدم. على عكس البحث العادي المستند إلى الكلمات الرئيسية، يفهم البحث الدلالي المعنى والسياق الخاصين بطلب البحث.
عند استيراد ملف، يتم تحويله إلى تمثيلات رقمية تُعرف باسم التضمينات، وهي تلتقط المعنى الدلالي للنص. يتم تخزين هذه التضمينات في قاعدة بيانات متخصصة في "البحث عن الملفات". عندما تُجري طلب بحث، يتم تحويله أيضًا إلى تضمين. بعد ذلك، يجري النظام عملية "البحث في الملفات" للعثور على أجزاء المستندات الأكثر تشابهًا وملاءمةً من مستودع "البحث في الملفات".
لا تتوفّر مدة بقاء (TTL) للتضمينات والملفات، بل تبقى متاحة إلى أن يتم حذفها يدويًا أو عند إيقاف النموذج نهائيًا.
في ما يلي تفصيل لعملية استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات File Search
uploadToFileSearchStore:
إنشاء مستودع "بحث في الملفات": يحتوي مستودع "بحث في الملفات" على البيانات المعالَجة من ملفاتك. وهي الحاوية الثابتة لعمليات التضمين التي سيستند إليها البحث الدلالي.
تحميل ملف واستيراده إلى مستودع "البحث في الملفات": يمكنك تحميل ملف واستيراد النتائج إلى مستودع "البحث في الملفات" في الوقت نفسه. يؤدي ذلك إلى إنشاء كائن
Fileمؤقت، وهو مرجع إلى مستندك الأولي. بعد ذلك، يتم تقسيم هذه البيانات إلى أجزاء وتحويلها إلى تضمينات "بحث الملفات" وفهرستها. يتم حذف عنصرFileبعد 48 ساعة، بينما يتم تخزين البيانات التي تم استيرادها إلى مساحة تخزين "البحث عن الملفات" إلى أجل غير مسمى إلى أن تختار حذفها.طلب البحث باستخدام "البحث عن الملفات": أخيرًا، يمكنك استخدام أداة
FileSearchفي مكالمةgenerateContent. في إعدادات الأداة، عليك تحديدFileSearchRetrievalResource، الذي يشير إلىFileSearchStoreالذي تريد البحث فيه. يطلب ذلك من النموذج إجراء بحث دلالي في مخزن "بحث الملفات" المحدّد للعثور على المعلومات ذات الصلة التي يمكنه الاستناد إليها في رده.
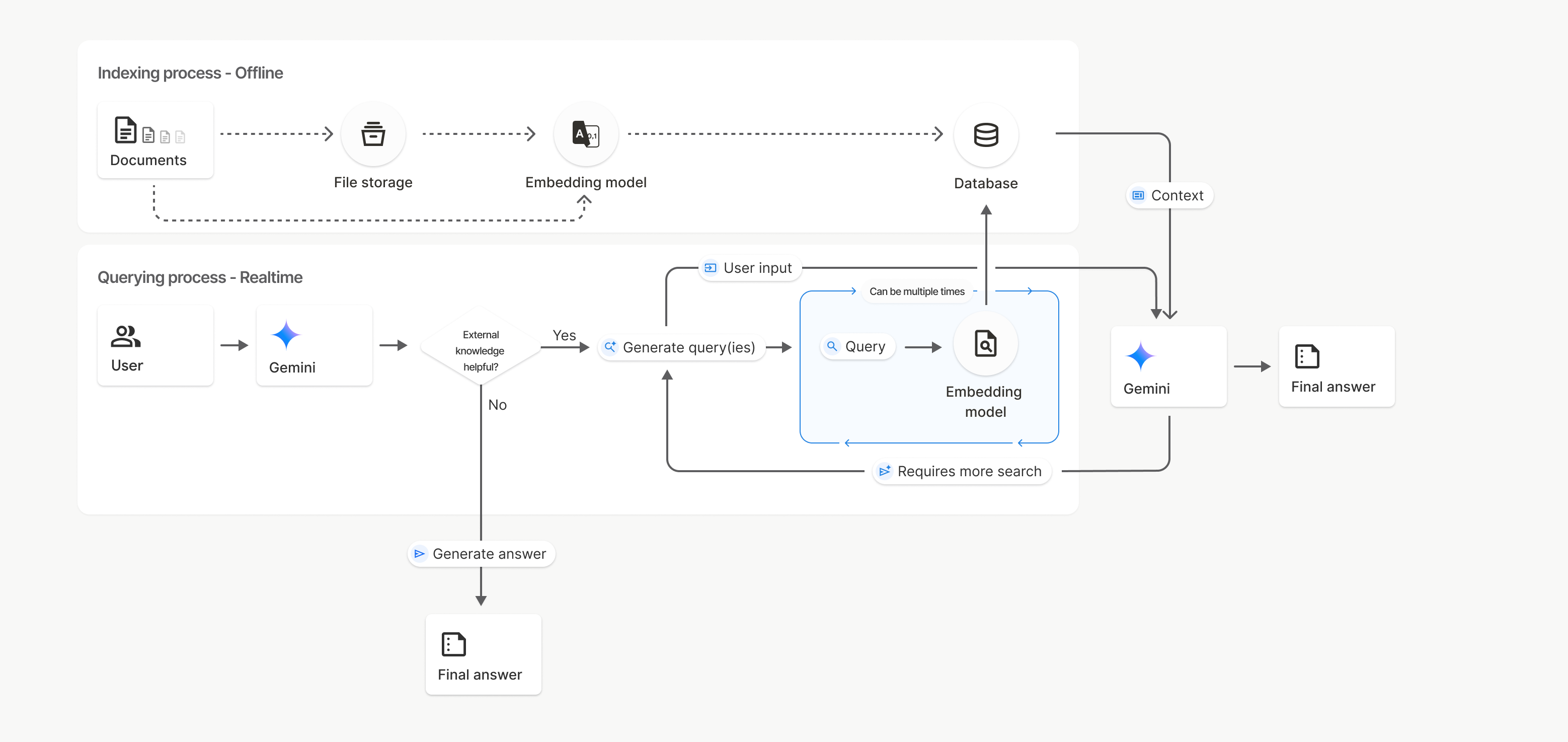
في هذا الرسم التخطيطي، يمثّل الخط المتقطّع من المستندات إلى نموذج التضمين
(باستخدام gemini-embedding-001)
واجهة برمجة التطبيقات uploadToFileSearchStore (مع تجاوز تخزين الملفات).
في حال عدم توفّر ذلك، يؤدي استخدام Files API لإنشاء الملفات بشكل منفصل ثم استيرادها إلى نقل عملية الفهرسة من المستندات إلى مساحة تخزين الملفات ثم إلى نموذج التضمين.
متاجر "بحث الملفات"
مستودع "البحث عن الملفات" هو حاوية لتضمينات المستندات. في حين يتم حذف الملفات الأولية التي تم تحميلها من خلال File API بعد 48 ساعة، يتم تخزين البيانات التي تم استيرادها إلى مستودع "بحث الملفات" إلى أجل غير مسمى إلى أن تحذفها يدويًا. يمكنك إنشاء عدة مستودعات بحث في الملفات لتنظيم مستنداتك. تتيح لك واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
FileSearchStore إنشاء قوائم وعرضها والحصول عليها وحذفها لإدارة
متاجر البحث عن الملفات. يتم تحديد نطاق أسماء متاجر "بحث الملفات" على مستوى العالم.
في ما يلي بعض الأمثلة على كيفية إدارة متاجر "بحث الملفات":
Python
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'my-file_search-store-123'})
for file_search_store in client.file_search_stores.list():
print(file_search_store)
my_file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123')
client.file_search_stores.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123', config={'force': True})
JavaScript
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'my-file_search-store-123' }
});
const fileSearchStores = await ai.fileSearchStores.list();
for await (const store of fileSearchStores) {
console.log(store);
}
const myFileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123',
config: { force: true }
});
REST
curl -X POST "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{ "displayName": "My Store" }'
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
مستندات البحث في الملفات
يمكنك إدارة المستندات الفردية في مخازن الملفات باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
File Search Documents من أجل list كل مستند
في مخزن بحث الملفات، وget معلومات حول مستند، وdelete مستند
حسب الاسم.
Python
for document_in_store in client.file_search_stores.documents.list(parent='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'):
print(document_in_store)
file_search_document = client.file_search_stores.documents.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
print(file_search_document)
client.file_search_stores.documents.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
JavaScript
const documents = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.list({
parent: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
for await (const doc of documents) {
console.log(doc);
}
const fileSearchDocument = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
البيانات الوصفية للملف
يمكنك إضافة بيانات وصفية مخصّصة إلى ملفاتك للمساعدة في فلترتها أو تقديم سياق إضافي. بيانات التعريف هي مجموعة من أزواج المفاتيح والقيم.
Python
op = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
custom_metadata=[
{"key": "author", "string_value": "Robert Graves"},
{"key": "year", "numeric_value": 1934}
]
)
JavaScript
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name,
config: {
customMetadata: [
{ key: "author", stringValue: "Robert Graves" },
{ key: "year", numericValue: 1934 }
]
}
});
يكون ذلك مفيدًا عندما يكون لديك مستندات متعددة في متجر "بحث الملفات" وتريد البحث في مجموعة فرعية منها فقط.
Python
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name],
metadata_filter="author=Robert Graves",
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
JavaScript
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name],
metadataFilter: 'author="Robert Graves"',
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[{"text": "Tell me about the book I, Claudius"}]
}],
"tools": [{
"file_search": {
"file_search_store_names":["'$STORE_NAME'"],
"metadata_filter": "author = \"Robert Graves\""
}
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
يمكنك الاطّلاع على إرشادات حول تنفيذ بنية فلتر القائمة الخاصة بـ metadata_filter على الرابط google.aip.dev/160.
الاقتباسات
عند استخدام "البحث في الملفات"، قد يتضمّن ردّ النموذج اقتباسات تحدّد الأجزاء من المستندات التي حمّلتها والتي تم استخدامها لإنشاء الإجابة. ويساعد ذلك في التحقّق من صحة المعلومات.
يمكنك الوصول إلى معلومات الاقتباس من خلال السمة grounding_metadata في الرد.
Python
print(response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata)
JavaScript
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.candidates?.[0]?.groundingMetadata, null, 2));
الناتج المنظَّم
بدءًا من نماذج Gemini 3، يمكنك دمج أداة البحث عن الملفات مع النتائج المنظَّمة.
Python
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Money(BaseModel):
amount: str = Field(description="The numerical part of the amount.")
currency: str = Field(description="The currency of amount.")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
],
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=Money.model_json_schema()
)
)
result = Money.model_validate_json(response.text)
print(result)
JavaScript
import { z } from "zod";
const moneySchema = z.object({
amount: z.string().describe("The numerical part of the amount."),
currency: z.string().describe("The currency of amount."),
});
async function run() {
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [file_search_store.name],
},
},
],
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseJsonSchema: z.toJSONSchema(moneySchema),
},
});
const result = moneySchema.parse(JSON.parse(response.text));
console.log(result);
}
run();
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts": [{"text": "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?"}]
}],
"tools": [
{
"fileSearch": {
"fileSearchStoreNames": ["$FILE_SEARCH_STORE_NAME"]
}
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"responseMimeType": "application/json",
"responseJsonSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "string", "description": "The numerical part of the amount."},
"currency": {"type": "string", "description": "The currency of amount."}
},
"required": ["amount", "currency"]
}
}
}'
النماذج المتوافقة
تتيح الطُرز التالية استخدام ميزة "البحث عن الملفات":
أنواع الملفات المعتمدة
يتيح "بحث الملفات" مجموعة كبيرة من تنسيقات الملفات، وهي مدرَجة في الأقسام التالية.
أنواع ملفات التطبيقات
application/dartapplication/ecmascriptapplication/jsonapplication/ms-javaapplication/mswordapplication/pdfapplication/sqlapplication/typescriptapplication/vnd.curlapplication/vnd.dartapplication/vnd.ibm.secure-containerapplication/vnd.jupyterapplication/vnd.ms-excelapplication/vnd.oasis.opendocument.textapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentationapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheetapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.documentapplication/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.templateapplication/x-cshapplication/x-hwpapplication/x-hwp-v5application/x-latexapplication/x-phpapplication/x-powershellapplication/x-shapplication/x-shellscriptapplication/x-texapplication/x-zshapplication/xmlapplication/zip
أنواع الملفات النصية
text/1d-interleaved-parityfectext/REDtext/SGMLtext/cache-manifesttext/calendartext/cqltext/cql-extensiontext/cql-identifiertext/csstext/csvtext/csv-schematext/dnstext/encaprtptext/enrichedtext/exampletext/fhirpathtext/flexfectext/fwdredtext/gff3text/grammar-ref-listtext/hl7v2text/htmltext/javascripttext/jcr-cndtext/jsxtext/markdowntext/mizartext/n3text/parameterstext/parityfectext/phptext/plaintext/provenance-notationtext/prs.fallenstein.rsttext/prs.lines.tagtext/prs.prop.logictext/raptorfectext/rfc822-headerstext/rtftext/rtp-enc-aescm128text/rtploopbacktext/rtxtext/sgmltext/shaclctext/shextext/spdxtext/stringstext/t140text/tab-separated-valuestext/texmacstext/trofftext/tsvtext/tsxtext/turtletext/ulpfectext/uri-listtext/vcardtext/vnd.DMClientScripttext/vnd.IPTC.NITFtext/vnd.IPTC.NewsMLtext/vnd.atext/vnd.abctext/vnd.ascii-arttext/vnd.curltext/vnd.debian.copyrighttext/vnd.dvb.subtitletext/vnd.esmertec.theme-descriptortext/vnd.exchangeabletext/vnd.familysearch.gedcomtext/vnd.ficlab.flttext/vnd.flytext/vnd.fmi.flexstortext/vnd.gmltext/vnd.graphviztext/vnd.hanstext/vnd.hgltext/vnd.in3d.3dmltext/vnd.in3d.spottext/vnd.latex-ztext/vnd.motorola.reflextext/vnd.ms-mediapackagetext/vnd.net2phone.commcenter.commandtext/vnd.radisys.msml-basic-layouttext/vnd.senx.warpscripttext/vnd.sositext/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptortext/vnd.trolltech.linguisttext/vnd.wap.sitext/vnd.wap.sltext/vnd.wap.wmltext/vnd.wap.wmlscripttext/vtttext/wgsltext/x-asmtext/x-bibtextext/x-bootext/x-ctext/x-c++hdrtext/x-c++srctext/x-cassandratext/x-chdrtext/x-coffeescripttext/x-componenttext/x-cshtext/x-csharptext/x-csrctext/x-cudatext/x-dtext/x-difftext/x-dsrctext/x-emacs-lisptext/x-erlangtext/x-gff3text/x-gotext/x-haskelltext/x-javatext/x-java-propertiestext/x-java-sourcetext/x-kotlintext/x-lilypondtext/x-lisptext/x-literate-haskelltext/x-luatext/x-moctext/x-objcsrctext/x-pascaltext/x-pcs-gcdtext/x-perltext/x-perl-scripttext/x-pythontext/x-python-scripttext/x-r-markdowntext/x-rsrctext/x-rsttext/x-ruby-scripttext/x-rusttext/x-sasstext/x-scalatext/x-schemetext/x-script.pythontext/x-scsstext/x-setexttext/x-sfvtext/x-shtext/x-siestatext/x-sostext/x-sqltext/x-swifttext/x-tcltext/x-textext/x-vbasictext/x-vcalendartext/xmltext/xml-dtdtext/xml-external-parsed-entitytext/yaml
القيود
- واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المباشرة: لا تتوفّر ميزة "البحث عن الملفات" في واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المباشرة.
- عدم توافق الأداة: لا يمكن حاليًا استخدام "البحث عن ملف" مع أدوات أخرى، مثل الاستناد إلى "بحث Google" وسياق عنوان URL وغير ذلك.
حدود معدّل الاستخدام
تفرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات "بحث الملفات" الحدود التالية لضمان استقرار الخدمة:
- الحدّ الأقصى لحجم الملف / الحدّ الأقصى لكل مستند: 100 ميغابايت
- إجمالي حجم مساحات تخزين "البحث عن الملفات" في المشروع (استنادًا إلى مستوى المستخدم):
- الخطة المجانية: 1 غيغابايت
- المستوى 1: 10 غيغابايت
- المستوى 2: 100 غيغابايت
- المستوى 3: 1 تيرابايت
- اقتراح: يجب ألا يتجاوز حجم كل مستودع بيانات في "بحث الملفات" 20 غيغابايت لضمان أفضل أوقات استرجاع.
الأسعار
- يتم تحصيل رسوم من المطوّرين مقابل عمليات التضمين في وقت الفهرسة استنادًا إلى أسعار التضمين الحالية (0.15 دولار أمريكي لكل مليون رمز مميز).
- تتوفر خدمة التخزين بدون أي رسوم.
- إنّ تضمينات وقت طلب البحث مجانية.
- يتم تحصيل رسوم عن الرموز المميزة للمستندات التي تم استرجاعها باعتبارها رموزًا مميزة للسياق عادية.
الخطوات التالية
- انتقِل إلى مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات File Search Stores وDocuments في File Search.
