رابط برنامهنویسی نرمافزار Gemini از طریق ابزار جستجوی فایل، امکان بازیابی افزوده ("RAG") را فراهم میکند. جستجوی فایل، دادههای شما را وارد، تکهبندی و فهرستبندی میکند تا بازیابی سریع اطلاعات مرتبط را بر اساس یک درخواست ارائه شده امکانپذیر سازد. سپس این اطلاعات به عنوان زمینه برای مدل استفاده میشود و به مدل اجازه میدهد پاسخهای دقیقتر و مرتبطتری ارائه دهد.
برای اینکه جستجوی فایل برای توسعهدهندگان ساده و مقرونبهصرفه باشد، ما ذخیرهسازی فایل و تولید جاسازی در زمان جستجو را رایگان میکنیم. شما فقط برای ایجاد جاسازیها زمانی که برای اولین بار فایلهای خود را فهرستبندی میکنید (با هزینه مدل جاسازی مربوطه) و هزینه توکنهای ورودی/خروجی مدل Gemini معمولی هزینه پرداخت میکنید. این الگوی جدید صورتحساب، ساخت و مقیاسپذیری ابزار جستجوی فایل را آسانتر و مقرونبهصرفهتر میکند.
مستقیماً در فروشگاه جستجوی فایل بارگذاری کنید
این مثالها نحوه آپلود مستقیم فایل به فروشگاه جستجوی فایل را نشان میدهند:
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file='sample.txt',
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
config={
'display_name' : 'display-file-name',
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
جاوا اسکریپت
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
برای اطلاعات بیشتر، مرجع API مربوط به uploadToFileSearchStore را بررسی کنید.
وارد کردن فایلها
از طرف دیگر، میتوانید یک فایل موجود را آپلود کرده و آن را به فروشگاه جستجوی فایل خود وارد کنید :
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
# File name will be visible in citations
sample_file = client.files.upload(file='sample.txt', config={'name': 'display_file_name'})
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'your-fileSearchStore-name'})
operation = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="""Can you tell me about [insert question]""",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
جاوا اسکریپت
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
async function run() {
// File name will be visible in citations
const sampleFile = await ai.files.upload({
file: 'sample.txt',
config: { name: 'file-name' }
});
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'your-fileSearchStore-name' }
});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation: operation });
}
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Can you tell me about [insert question]",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name]
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
}
run();
برای اطلاعات بیشتر، مرجع API برای importFile را بررسی کنید.
پیکربندی قطعهبندی
وقتی فایلی را به یک فروشگاه جستجوی فایل وارد میکنید، به طور خودکار به تکههایی تقسیم میشود، جاسازی میشود، فهرستبندی میشود و در فروشگاه جستجوی فایل شما آپلود میشود. اگر به کنترل بیشتری بر استراتژی قطعهبندی نیاز دارید، میتوانید تنظیم chunking_config را برای تنظیم حداکثر تعداد توکنها در هر قطعه و حداکثر تعداد توکنهای همپوشانی مشخص کنید.
پایتون
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import time
client = genai.Client()
operation = client.file_search_stores.upload_to_file_search_store(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
config={
'chunking_config': {
'white_space_config': {
'max_tokens_per_chunk': 200,
'max_overlap_tokens': 20
}
}
}
)
while not operation.done:
time.sleep(5)
operation = client.operations.get(operation)
print("Custom chunking complete.")
جاوا اسکریپت
const { GoogleGenAI } = require('@google/genai');
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.uploadToFileSearchStore({
file: 'file.txt',
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
config: {
displayName: 'file-name',
chunkingConfig: {
whiteSpaceConfig: {
maxTokensPerChunk: 200,
maxOverlapTokens: 20
}
}
}
});
while (!operation.done) {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
operation = await ai.operations.get({ operation });
}
console.log("Custom chunking complete.");
برای استفاده از مخزن جستجوی فایل خود، آن را به عنوان ابزاری به متد generateContent ارسال کنید، همانطور که در مثالهای آپلود و وارد کردن نشان داده شده است.
چگونه کار میکند؟
جستجوی فایل از تکنیکی به نام جستجوی معنایی برای یافتن اطلاعات مرتبط با درخواست کاربر استفاده میکند. برخلاف جستجوی استاندارد مبتنی بر کلمات کلیدی، جستجوی معنایی معنا و زمینهی عبارت مورد نظر شما را درک میکند.
وقتی فایلی را وارد میکنید، به نمایشهای عددی به نام جاسازی تبدیل میشود که معنای معنایی متن را در بر میگیرد. این جاسازیها در یک پایگاه داده تخصصی جستجوی فایل ذخیره میشوند. وقتی یک پرسوجو انجام میدهید، آن نیز به یک جاسازی تبدیل میشود. سپس سیستم یک جستجوی فایل انجام میدهد تا شبیهترین و مرتبطترین تکههای سند را از فروشگاه جستجوی فایل پیدا کند.
هیچ زمان ماندگاری (TTL) برای جاسازیها و فایلها وجود ندارد؛ آنها تا زمانی که به صورت دستی حذف شوند یا زمانی که مدل منسوخ شود، باقی میمانند.
در اینجا خلاصهای از فرآیند استفاده از API جستجوی فایل uploadToFileSearchStore آمده است:
ایجاد یک مخزن جستجوی فایل : یک مخزن جستجوی فایل شامل دادههای پردازششده از فایلهای شما است. این مخزن، محفظهای دائمی برای جاسازیهایی است که جستجوی معنایی روی آنها عمل خواهد کرد.
آپلود فایل و وارد کردن آن به فروشگاه جستجوی فایل : همزمان یک فایل را آپلود کنید و نتایج را به فروشگاه جستجوی فایل خود وارد کنید. این کار یک شیء موقت
Fileایجاد میکند که مرجعی برای سند خام شما است. سپس این دادهها تکهتکه میشوند، به جاسازیهای جستجوی فایل تبدیل میشوند و فهرستبندی میشوند. شیءFileپس از ۴۸ ساعت حذف میشود، در حالی که دادههای وارد شده به فروشگاه جستجوی فایل تا زمانی که تصمیم به حذف آن بگیرید، به طور نامحدود ذخیره میشوند.پرسوجو با جستجوی فایل : در نهایت، شما از ابزار
FileSearchدر فراخوانیgenerateContentاستفاده میکنید. در پیکربندی ابزار، یکFileSearchRetrievalResourceمشخص میکنید که بهFileSearchStoreمورد نظر برای جستجو اشاره میکند. این به مدل میگوید که یک جستجوی معنایی در آن فروشگاه جستجوی فایل خاص انجام دهد تا اطلاعات مرتبط را برای پایهگذاری پاسخ خود پیدا کند.
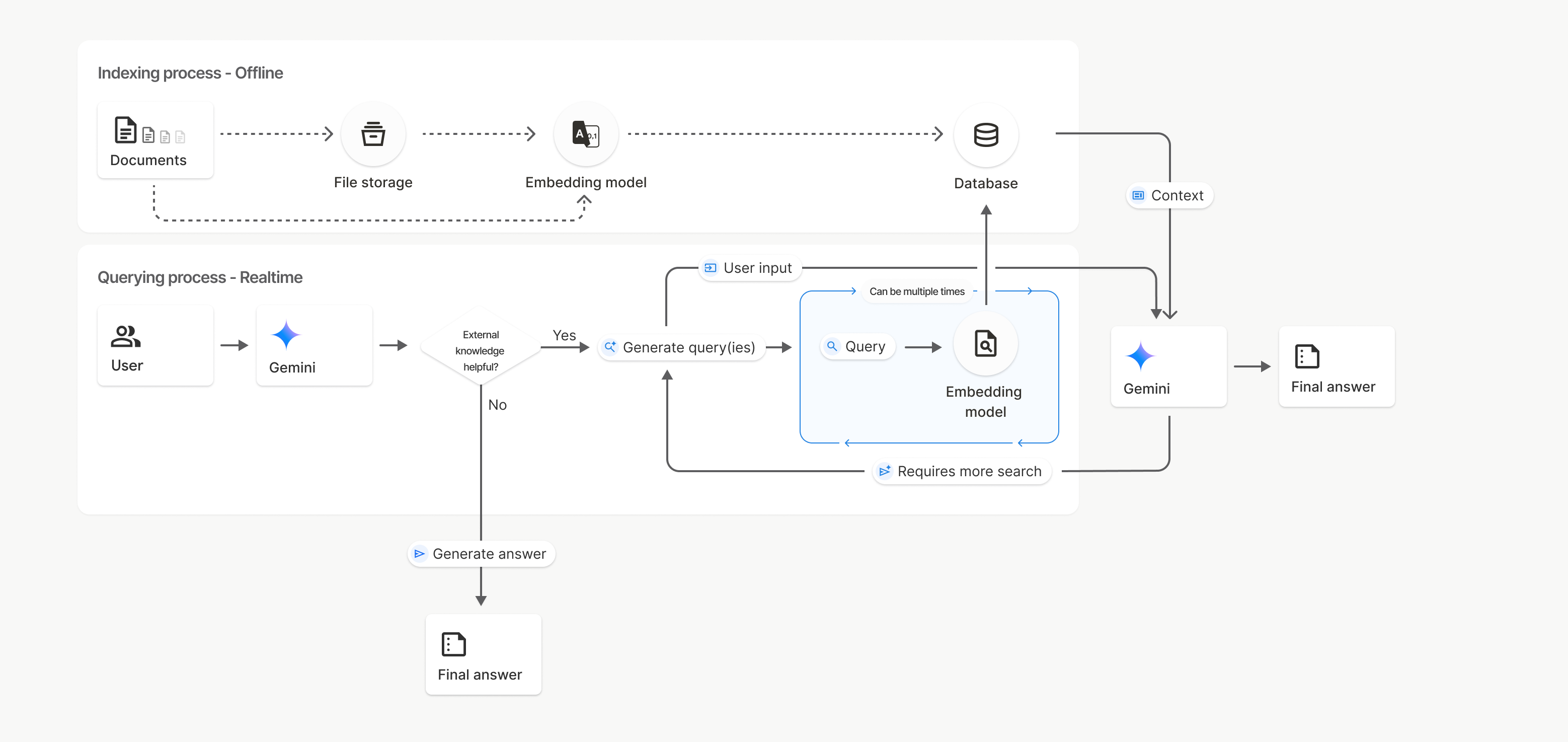
در این نمودار، خط چین از مدل Documents به Embedding (با استفاده از gemini-embedding-001 ) نشان دهنده API مربوط به uploadToFileSearchStore (با صرف نظر از File storage ) است. در غیر این صورت، استفاده از Files API برای ایجاد و سپس وارد کردن جداگانه فایلها، فرآیند ایندکس گذاری را از Documents به File storage و سپس به Embedding model منتقل میکند.
جستجوی فایل فروشگاهها
یک مخزن جستجوی فایل، محفظهای برای جاسازی اسناد شماست. در حالی که فایلهای خام آپلود شده از طریق API فایل پس از ۴۸ ساعت حذف میشوند، دادههای وارد شده به یک مخزن جستجوی فایل به طور نامحدود ذخیره میشوند تا زمانی که آن را به صورت دستی حذف کنید. میتوانید چندین مخزن جستجوی فایل برای سازماندهی اسناد خود ایجاد کنید. API FileSearchStore به شما امکان میدهد تا مخازن جستجوی فایل خود را ایجاد، فهرست، دریافت و حذف کنید. نامهای مخزن جستجوی فایل به صورت سراسری تعریف شدهاند.
در اینجا چند نمونه از نحوه مدیریت فروشگاههای جستجوی فایل شما آورده شده است:
پایتون
file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.create(config={'display_name': 'my-file_search-store-123'})
for file_search_store in client.file_search_stores.list():
print(file_search_store)
my_file_search_store = client.file_search_stores.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123')
client.file_search_stores.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123', config={'force': True})
جاوا اسکریپت
const fileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.create({
config: { displayName: 'my-file_search-store-123' }
});
const fileSearchStores = await ai.fileSearchStores.list();
for await (const store of fileSearchStores) {
console.log(store);
}
const myFileSearchStore = await ai.fileSearchStores.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123',
config: { force: true }
});
استراحت
curl -X POST "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{ "displayName": "My Store" }'
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
جستجوی اسناد فایل
شما میتوانید اسناد تکی را در انبارههای فایل خود با استفاده از API جستجوی فایل مدیریت کنید تا هر سند را در یک انباره جستجوی فایل list ، اطلاعات مربوط به یک سند را get و یک سند را بر اساس نام delete .
پایتون
for document_in_store in client.file_search_stores.documents.list(parent='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'):
print(document_in_store)
file_search_document = client.file_search_stores.documents.get(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
print(file_search_document)
client.file_search_stores.documents.delete(name='fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc')
جاوا اسکریپت
const documents = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.list({
parent: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123'
});
for await (const doc of documents) {
console.log(doc);
}
const fileSearchDocument = await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.get({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
await ai.fileSearchStores.documents.delete({
name: 'fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc'
});
استراحت
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
curl -X DELETE "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/fileSearchStores/my-file_search-store-123/documents/my_doc?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}"
فراداده فایل
شما میتوانید فرادادههای سفارشی را به فایلهای خود اضافه کنید تا به فیلتر کردن آنها یا ارائه زمینههای اضافی کمک کنید. فراداده مجموعهای از جفتهای کلید-مقدار است.
پایتون
op = client.file_search_stores.import_file(
file_search_store_name=file_search_store.name,
file_name=sample_file.name,
custom_metadata=[
{"key": "author", "string_value": "Robert Graves"},
{"key": "year", "numeric_value": 1934}
]
)
جاوا اسکریپت
let operation = await ai.fileSearchStores.importFile({
fileSearchStoreName: fileSearchStore.name,
fileName: sampleFile.name,
config: {
customMetadata: [
{ key: "author", stringValue: "Robert Graves" },
{ key: "year", numericValue: 1934 }
]
}
});
این قابلیت زمانی مفید است که چندین سند در یک مخزن جستجوی فایل داشته باشید و بخواهید فقط زیرمجموعهای از آنها را جستجو کنید.
پایتون
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name],
metadata_filter="author=Robert Graves",
)
)
]
)
)
print(response.text)
جاوا اسکریپت
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "Tell me about the book 'I, Claudius'",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [fileSearchStore.name],
metadataFilter: 'author="Robert Graves"',
}
}
]
}
});
console.log(response.text);
استراحت
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent?key=${GEMINI_API_KEY}" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts":[{"text": "Tell me about the book I, Claudius"}]
}],
"tools": [{
"file_search": {
"file_search_store_names":["'$STORE_NAME'"],
"metadata_filter": "author = \"Robert Graves\""
}
}]
}' 2> /dev/null > response.json
cat response.json
راهنمایی در مورد پیادهسازی سینتکس فیلتر لیست برای metadata_filter را میتوانید در google.aip.dev/160 بیابید.
نقل قولها
وقتی از جستجوی فایل استفاده میکنید، پاسخ مدل ممکن است شامل استنادهایی باشد که مشخص میکند کدام بخشهای اسناد آپلود شده شما برای تولید پاسخ استفاده شدهاند. این به بررسی و تأیید صحت اطلاعات کمک میکند.
شما میتوانید از طریق ویژگی grounding_metadata پاسخ، به اطلاعات استناد دسترسی پیدا کنید.
پایتون
print(response.candidates[0].grounding_metadata)
جاوا اسکریپت
console.log(JSON.stringify(response.candidates?.[0]?.groundingMetadata, null, 2));
خروجی ساختاریافته
با شروع از مدلهای Gemini 3، میتوانید ابزار جستجوی فایل را با خروجیهای ساختاریافته ترکیب کنید.
پایتون
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Money(BaseModel):
amount: str = Field(description="The numerical part of the amount.")
currency: str = Field(description="The currency of amount.")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[
types.Tool(
file_search=types.FileSearch(
file_search_store_names=[file_search_store.name]
)
)
],
response_mime_type="application/json",
response_schema=Money.model_json_schema()
)
)
result = Money.model_validate_json(response.text)
print(result)
جاوا اسکریپت
import { z } from "zod";
const moneySchema = z.object({
amount: z.string().describe("The numerical part of the amount."),
currency: z.string().describe("The currency of amount."),
});
async function run() {
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents: "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?",
config: {
tools: [
{
fileSearch: {
fileSearchStoreNames: [file_search_store.name],
},
},
],
responseMimeType: "application/json",
responseJsonSchema: z.toJSONSchema(moneySchema),
},
});
const result = moneySchema.parse(JSON.parse(response.text));
console.log(result);
}
run();
استراحت
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [{
"parts": [{"text": "What is the minimum hourly wage in Tokyo right now?"}]
}],
"tools": [
{
"fileSearch": {
"fileSearchStoreNames": ["$FILE_SEARCH_STORE_NAME"]
}
}
],
"generationConfig": {
"responseMimeType": "application/json",
"responseJsonSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"amount": {"type": "string", "description": "The numerical part of the amount."},
"currency": {"type": "string", "description": "The currency of amount."}
},
"required": ["amount", "currency"]
}
}
}'
مدلهای پشتیبانیشده
مدلهای زیر از جستجوی فایل پشتیبانی میکنند:
انواع فایلهای پشتیبانیشده
جستجوی فایل از طیف گستردهای از فرمتهای فایل پشتیبانی میکند که در بخشهای زیر فهرست شدهاند.
انواع فایلهای کاربردی
-
application/dart -
application/ecmascript -
application/json -
application/ms-java -
application/msword -
application/pdf -
application/sql -
application/typescript -
application/vnd.curl -
application/vnd.dart -
application/vnd.ibm.secure-container -
application/vnd.jupyter -
application/vnd.ms-excel -
application/vnd.oasis.opendocument.text -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document -
application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.template -
application/x-csh -
application/x-hwp -
application/x-hwp-v5 -
application/x-latex -
application/x-php -
application/x-powershell -
application/x-sh -
application/x-shellscript -
application/x-tex -
application/x-zsh -
application/xml -
application/zip
انواع فایلهای متنی
-
text/1d-interleaved-parityfec -
text/RED -
text/SGML -
text/cache-manifest -
text/calendar -
text/cql -
text/cql-extension -
text/cql-identifier -
text/css -
text/csv -
text/csv-schema -
text/dns -
text/encaprtp -
text/enriched -
text/example -
text/fhirpath -
text/flexfec -
text/fwdred -
text/gff3 -
text/grammar-ref-list -
text/hl7v2 -
text/html -
text/javascript -
text/jcr-cnd -
text/jsx -
text/markdown -
text/mizar -
text/n3 -
text/parameters -
text/parityfec -
text/php -
text/plain -
text/provenance-notation -
text/prs.fallenstein.rst -
text/prs.lines.tag -
text/prs.prop.logic -
text/raptorfec -
text/rfc822-headers -
text/rtf -
text/rtp-enc-aescm128 -
text/rtploopback -
text/rtx -
text/sgml -
text/shaclc -
text/shex -
text/spdx -
text/strings -
text/t140 -
text/tab-separated-values -
text/texmacs -
text/troff -
text/tsv -
text/tsx -
text/turtle -
text/ulpfec -
text/uri-list -
text/vcard -
text/vnd.DMClientScript -
text/vnd.IPTC.NITF -
text/vnd.IPTC.NewsML -
text/vnd.a -
text/vnd.abc -
text/vnd.ascii-art -
text/vnd.curl -
text/vnd.debian.copyright -
text/vnd.dvb.subtitle -
text/vnd.esmertec.theme-descriptor -
text/vnd.exchangeable -
text/vnd.familysearch.gedcom -
text/vnd.ficlab.flt -
text/vnd.fly -
text/vnd.fmi.flexstor -
text/vnd.gml -
text/vnd.graphviz -
text/vnd.hans -
text/vnd.hgl -
text/vnd.in3d.3dml -
text/vnd.in3d.spot -
text/vnd.latex-z -
text/vnd.motorola.reflex -
text/vnd.ms-mediapackage -
text/vnd.net2phone.commcenter.command -
text/vnd.radisys.msml-basic-layout -
text/vnd.senx.warpscript -
text/vnd.sosi -
text/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptor -
text/vnd.trolltech.linguist -
text/vnd.wap.si -
text/vnd.wap.sl -
text/vnd.wap.wml -
text/vnd.wap.wmlscript -
text/vtt -
text/wgsl -
text/x-asm -
text/x-bibtex -
text/x-boo -
text/xc -
text/x-c++hdr -
text/x-c++src -
text/x-cassandra -
text/x-chdr -
text/x-coffeescript -
text/x-component -
text/x-csh -
text/x-csharp -
text/x-csrc -
text/x-cuda -
text/xd -
text/x-diff -
text/x-dsrc -
text/x-emacs-lisp -
text/x-erlang -
text/x-gff3 -
text/x-go -
text/x-haskell -
text/x-java -
text/x-java-properties -
text/x-java-source -
text/x-kotlin -
text/x-lilypond -
text/x-lisp -
text/x-literate-haskell -
text/x-lua -
text/x-moc -
text/x-objcsrc -
text/x-pascal -
text/x-pcs-gcd -
text/x-perl -
text/x-perl-script -
text/x-python -
text/x-python-script -
text/xr-markdown -
text/x-rsrc -
text/x-rst -
text/x-ruby-script -
text/x-rust -
text/x-sass -
text/x-scala -
text/x-scheme -
text/x-script.python -
text/x-scss -
text/x-setext -
text/x-sfv -
text/x-sh -
text/x-siesta -
text/x-sos -
text/x-sql -
text/x-swift -
text/x-tcl -
text/x-tex -
text/x-vbasic -
text/x-vcalendar -
text/xml -
text/xml-dtd -
text/xml-external-parsed-entity -
text/yaml
محدودیتها
- API زنده: جستجوی فایل در API زنده پشتیبانی نمیشود.
- ناسازگاری ابزار: جستجوی فایل در حال حاضر نمیتواند با ابزارهای دیگری مانند Grounding with Google Search ، URL Context و غیره ترکیب شود.
محدودیتهای نرخ
API جستجوی فایل برای افزایش پایداری سرویس، محدودیتهای زیر را دارد:
- حداکثر اندازه فایل / به ازای هر سند : ۱۰۰ مگابایت
- اندازه کل فروشگاههای جستجوی فایل پروژه (بر اساس سطح کاربری):
- رایگان : ۱ گیگابایت
- سطح ۱ : ۱۰ گیگابایت
- ردیف ۲ : ۱۰۰ گیگابایت
- ردیف ۳ : ۱ ترابایت
- توصیه : اندازه هر مخزن جستجوی فایل را به کمتر از 20 گیگابایت محدود کنید تا از تأخیر بهینه در بازیابی اطمینان حاصل شود.
قیمتگذاری
- توسعهدهندگان در زمان ایندکس کردن، بر اساس قیمتگذاری موجود برای جاسازیها (۰.۱۵ دلار به ازای هر ۱ میلیون توکن) هزینهای برای جاسازیها دریافت میکنند.
- انبارداری رایگان است.
- جاسازیهای زمان پرسوجو رایگان هستند.
- توکنهای سند بازیابیشده به عنوان توکنهای زمینهای معمولی محاسبه میشوند.
قدم بعدی چیست؟
- برای «ذخیرههای جستجوی فایل» و « اسناد جستجوی فایل» به مرجع API مراجعه کنید.

