Function calling lets you connect models to external tools and APIs. Instead of generating text responses, the model determines when to call specific functions and provides the necessary parameters to execute real-world actions. This allows the model to act as a bridge between natural language and real-world actions and data. Function calling has 3 primary use cases:
- Augment Knowledge: Access information from external sources like databases, APIs, and knowledge bases.
- Extend Capabilities: Use external tools to perform computations and extend the limitations of the model, such as using a calculator or creating charts.
- Take Actions: Interact with external systems using APIs, such as scheduling appointments, creating invoices, sending emails, or controlling smart home devices.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function declaration for the model
schedule_meeting_function = {
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting.",
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')",
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')",
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting.",
},
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"],
},
}
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[schedule_meeting_function])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/14/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.",
config=config,
)
# Check for a function call
if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call:
function_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
print(f"Function to call: {function_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {function_call.args}")
# In a real app, you would call your function here:
# result = schedule_meeting(**function_call.args)
else:
print("No function call found in the response.")
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define the function declaration for the model
const scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'schedule_meeting',
description: 'Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
attendees: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
items: { type: Type.STRING },
description: 'List of people attending the meeting.',
},
date: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Date of the meeting (e.g., "2024-07-29")',
},
time: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Time of the meeting (e.g., "15:00")',
},
topic: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'The subject or topic of the meeting.',
},
},
required: ['attendees', 'date', 'time', 'topic'],
},
};
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: 'Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.',
config: {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration]
}],
},
});
// Check for function calls in the response
if (response.functionCalls && response.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = response.functionCalls[0]; // Assuming one function call
console.log(`Function to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
console.log(`Arguments: ${JSON.stringify(functionCall.args)}`);
// In a real app, you would call your actual function here:
// const result = await scheduleMeeting(functionCall.args);
} else {
console.log("No function call found in the response.");
console.log(response.text);
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting."
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')"
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')"
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting."
}
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
How function calling works
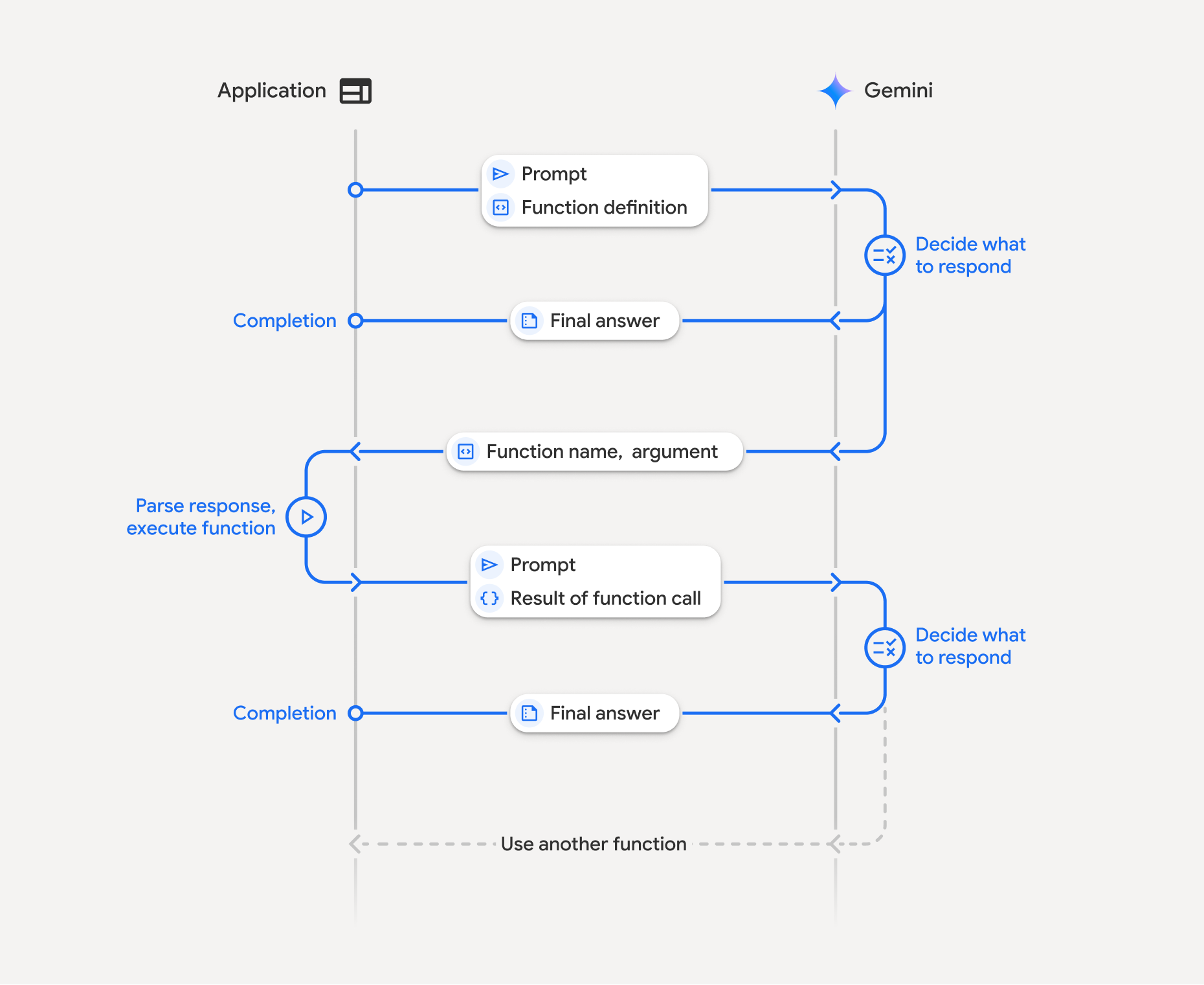
Function calling involves a structured interaction between your application, the model, and external functions. Here's a breakdown of the process:
- Define Function Declaration: Define the function declaration in your application code. Function Declarations describe the function's name, parameters, and purpose to the model.
- Call LLM with function declarations: Send user prompt along with the function declaration(s) to the model. It analyzes the request and determines if a function call would be helpful. If so, it responds with a structured JSON object.
- Execute Function Code (Your Responsibility): The Model does not
execute the function itself. It's your application's responsibility to
process the response and check for Function Call, if
- Yes: Extract the name and args of the function and execute the corresponding function in your application.
- No: The model has provided a direct text response to the prompt (this flow is less emphasized in the example but is a possible outcome).
- Create User friendly response: If a function was executed, capture the result and send it back to the model in a subsequent turn of the conversation. It will use the result to generate a final, user-friendly response that incorporates the information from the function call.
This process can be repeated over multiple turns, allowing for complex interactions and workflows. The model also supports calling multiple functions in a single turn (parallel function calling) and in sequence (compositional function calling).
Step 1: Define a function declaration
Define a function and its declaration within your application code that allows users to set light values and make an API request. This function could call external services or APIs.
Python
# Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
set_light_values_declaration = {
"name": "set_light_values",
"description": "Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness",
},
"color_temp": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"],
"description": "Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.",
},
},
"required": ["brightness", "color_temp"],
},
}
# This is the actual function that would be called based on the model's suggestion
def set_light_values(brightness: int, color_temp: str) -> dict[str, int | str]:
"""Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API).
Args:
brightness: Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
color_temp: Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness, "colorTemperature": color_temp}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
// Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
const setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'set_light_values',
description: 'Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness',
},
color_temp: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm'],
description: 'Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.',
},
},
required: ['brightness', 'color_temp'],
},
};
/**
* Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API)
* @param {number} brightness - Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
* @param {string} color_temp - Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
* @return {Object} A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
*/
function setLightValues(brightness, color_temp) {
return {
brightness: brightness,
colorTemperature: color_temp
};
}
Step 2: Call the model with function declarations
Once you have defined your function declarations, you can prompt the model to use them. It analyzes the prompt and function declarations and decides whether to respond directly or to call a function. If a function is called, the response object will contain a function call suggestion.
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[set_light_values_declaration])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Define user prompt
contents = [
types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="Turn the lights down to a romantic level")]
)
]
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=contents,
config=config,
)
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Generation config with function declaration
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration]
}]
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define user prompt
const contents = [
{
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: 'Turn the lights down to a romantic level' }]
}
];
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(response.functionCalls[0]);
The model then returns a functionCall object in an OpenAPI compatible
schema specifying how to call one or more of the declared functions in order to
respond to the user's question.
Python
id=None args={'color_temp': 'warm', 'brightness': 25} name='set_light_values'
JavaScript
{
name: 'set_light_values',
args: { brightness: 25, color_temp: 'warm' }
}
Step 3: Execute set_light_values function code
Extract the function call details from the model's response, parse the arguments
, and execute the set_light_values function.
Python
# Extract tool call details, it may not be in the first part.
tool_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
if tool_call.name == "set_light_values":
result = set_light_values(**tool_call.args)
print(f"Function execution result: {result}")
JavaScript
// Extract tool call details
const tool_call = response.functionCalls[0]
let result;
if (tool_call.name === 'set_light_values') {
result = setLightValues(tool_call.args.brightness, tool_call.args.color_temp);
console.log(`Function execution result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
Step 4: Create user friendly response with function result and call the model again
Finally, send the result of the function execution back to the model so it can incorporate this information into its final response to the user.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Create a function response part
function_response_part = types.Part.from_function_response(
name=tool_call.name,
response={"result": result},
)
# Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.append(response.candidates[0].content) # Append the content from the model's response.
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
client = genai.Client()
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
JavaScript
// Create a function response part
const function_response_part = {
name: tool_call.name,
response: { result }
}
// Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.push(response.candidates[0].content);
contents.push({ role: 'user', parts: [{ functionResponse: function_response_part }] });
// Get the final response from the model
const final_response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(final_response.text);
This completes the function calling flow. The model successfully used the
set_light_values function to perform the request action of the user.
Function declarations
When you implement function calling in a prompt, you create a tools object,
which contains one or more function declarations. You define functions using
JSON, specifically with a select subset
of the OpenAPI schema format. A
single function declaration can include the following parameters:
name(string): A unique name for the function (get_weather_forecast,send_email). Use descriptive names without spaces or special characters (use underscores or camelCase).description(string): A clear and detailed explanation of the function's purpose and capabilities. This is crucial for the model to understand when to use the function. Be specific and provide examples if helpful ("Finds theaters based on location and optionally movie title which is currently playing in theaters.").parameters(object): Defines the input parameters the function expects.type(string): Specifies the overall data type, such asobject.properties(object): Lists individual parameters, each with:type(string): The data type of the parameter, such asstring,integer,boolean, array.description(string): A description of the parameter's purpose and format. Provide examples and constraints ("The city and state, e.g., 'San Francisco, CA' or a zip code e.g., '95616'.").enum(array, optional): If the parameter values are from a fixed set, use "enum" to list the allowed values instead of just describing them in the description. This improves accuracy ("enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"]).
required(array): An array of strings listing the parameter names that are mandatory for the function to operate.
You can also construct FunctionDeclarations from Python functions directly using
types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(client=client, callable=your_function).
Function calling with thinking models
Gemini 3 and 2.5 series models use an internal "thinking" process to reason through requests. This significantly improves function calling performance, allowing the model to better determine when to call a function and which parameters to use. Because the Gemini API is stateless, models use thought signatures to maintain context across multi-turn conversations.
This section covers advanced management of thought signatures and is only necessary if you're manually constructing API requests (e.g., via REST) or manipulating conversation history.
If you're using the Google GenAI SDKs (our official libraries), you don't need to manage this process. The SDKs automatically handle the necessary steps, as shown in the earlier example.
Managing conversation history manually
If you modify the conversation history manually, instead of sending the
complete previous response you
must correctly handle the thought_signature included in the model's turn.
Follow these rules to ensure the model's context is preserved:
- Always send the
thought_signatureback to the model inside its originalPart. - Don't merge a
Partcontaining a signature with one that does not. This breaks the positional context of the thought. - Don't combine two
Partsthat both contain signatures, as the signature strings cannot be merged.
Gemini 3 thought signatures
In Gemini 3, any Part of a model response
may contain a thought signature.
While we generally recommend returning signatures from all Part types,
passing back thought signatures is mandatory for function calling. Unless you
are manipulating conversation history manually, the Google GenAI SDK will
handle thought signatures automatically.
If you are manipulating conversation history manually, refer to the Thoughts Signatures page for complete guidance and details on handling thought signatures for Gemini 3.
Inspecting thought signatures
While not necessary for implementation, you can inspect the response to see the
thought_signature for debugging or educational purposes.
Python
import base64
# After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
# response = client.models.generate_content(...)
# The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0]
if part.thought_signature:
print(base64.b64encode(part.thought_signature).decode("utf-8"))
JavaScript
// After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
// const response = await ai.models.generateContent(...)
// The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
const part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0];
if (part.thoughtSignature) {
console.log(part.thoughtSignature);
}
Learn more about limitations and usage of thought signatures, and about thinking models in general, on the Thinking page.
Parallel function calling
In addition to single turn function calling, you can also call multiple functions at once. Parallel function calling lets you execute multiple functions at once and is used when the functions are not dependent on each other. This is useful in scenarios like gathering data from multiple independent sources, such as retrieving customer details from different databases or checking inventory levels across various warehouses or performing multiple actions such as converting your apartment into a disco.
Python
power_disco_ball = {
"name": "power_disco_ball",
"description": "Powers the spinning disco ball.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"power": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.",
}
},
"required": ["power"],
},
}
start_music = {
"name": "start_music",
"description": "Play some music matching the specified parameters.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"energetic": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is energetic or not.",
},
"loud": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is loud or not.",
},
},
"required": ["energetic", "loud"],
},
}
dim_lights = {
"name": "dim_lights",
"description": "Dim the lights.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.",
}
},
"required": ["brightness"],
},
}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
const powerDiscoBall = {
name: 'power_disco_ball',
description: 'Powers the spinning disco ball.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
power: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.'
}
},
required: ['power']
}
};
const startMusic = {
name: 'start_music',
description: 'Play some music matching the specified parameters.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
energetic: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is energetic or not.'
},
loud: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is loud or not.'
}
},
required: ['energetic', 'loud']
}
};
const dimLights = {
name: 'dim_lights',
description: 'Dim the lights.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.'
}
},
required: ['brightness']
}
};
Configure the function calling mode to allow using all of the specified tools. To learn more, you can read about configuring function calling.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
house_tools = [
types.Tool(function_declarations=[power_disco_ball, start_music, dim_lights])
]
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=house_tools,
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
disable=True
),
# Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
tool_config=types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(mode='ANY')
),
)
chat = client.chats.create(model="gemini-3-flash-preview", config=config)
response = chat.send_message("Turn this place into a party!")
# Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
print("Example 1: Forced function calling")
for fn in response.function_calls:
args = ", ".join(f"{key}={val}" for key, val in fn.args.items())
print(f"{fn.name}({args})")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Set up function declarations
const houseFns = [powerDiscoBall, startMusic, dimLights];
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: houseFns
}],
// Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
toolConfig: {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: 'any'
}
}
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Create a chat session
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
config: config
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({message: 'Turn this place into a party!'});
// Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
console.log("Example 1: Forced function calling");
for (const fn of response.functionCalls) {
const args = Object.entries(fn.args)
.map(([key, val]) => `${key}=${val}`)
.join(', ');
console.log(`${fn.name}(${args})`);
}
Each of the printed results reflects a single function call that the model has requested. To send the results back, include the responses in the same order as they were requested.
The Python SDK supports automatic function calling, which automatically converts Python functions to declarations, handles the function call execution and response cycle for you. Following is an example for the disco use case.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Actual function implementations
def power_disco_ball_impl(power: bool) -> dict:
"""Powers the spinning disco ball.
Args:
power: Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.
Returns:
A status dictionary indicating the current state.
"""
return {"status": f"Disco ball powered {'on' if power else 'off'}"}
def start_music_impl(energetic: bool, loud: bool) -> dict:
"""Play some music matching the specified parameters.
Args:
energetic: Whether the music is energetic or not.
loud: Whether the music is loud or not.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the music settings.
"""
music_type = "energetic" if energetic else "chill"
volume = "loud" if loud else "quiet"
return {"music_type": music_type, "volume": volume}
def dim_lights_impl(brightness: float) -> dict:
"""Dim the lights.
Args:
brightness: The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the new brightness setting.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[power_disco_ball_impl, start_music_impl, dim_lights_impl]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Do everything you need to this place into party!",
config=config,
)
print("\nExample 2: Automatic function calling")
print(response.text)
# I've turned on the disco ball, started playing loud and energetic music, and dimmed the lights to 50% brightness. Let's get this party started!
Compositional function calling
Compositional or sequential function calling allows Gemini to chain multiple
function calls together to fulfill a complex request. For example, to answer
"Get the temperature in my current location", the Gemini API might first invoke
a get_current_location() function followed by a get_weather() function that
takes the location as a parameter.
The following example demonstrates how to implement compositional function calling using the Python SDK and automatic function calling.
Python
This example uses the automatic function calling feature of the
google-genai Python SDK. The SDK automatically converts the Python
functions to the required schema, executes the function calls when requested
by the model, and sends the results back to the model to complete the task.
import os
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Example Functions
def get_weather_forecast(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current weather temperature for a given location."""
print(f"Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location={location})")
# TODO: Make API call
print("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}")
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "celsius"} # Dummy response
def set_thermostat_temperature(temperature: int) -> dict:
"""Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature."""
print(f"Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature={temperature})")
# TODO: Interact with a thermostat API
print("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configure the client and model
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_weather_forecast, set_thermostat_temperature]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
config=config,
)
# Print the final, user-facing response
print(response.text)
Expected Output
When you run the code, you will see the SDK orchestrating the function
calls. The model first calls get_weather_forecast, receives the
temperature, and then calls set_thermostat_temperature with the correct
value based on the logic in the prompt.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
JavaScript
This example shows how to use JavaScript/TypeScript SDK to do comopositional function calling using a manual execution loop.
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from "@google/genai";
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Example Functions
function get_weather_forecast({ location }) {
console.log(`Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=${location})`);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}");
return { temperature: 25, unit: "celsius" };
}
function set_thermostat_temperature({ temperature }) {
console.log(
`Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=${temperature})`,
);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}");
return { status: "success" };
}
const toolFunctions = {
get_weather_forecast,
set_thermostat_temperature,
};
const tools = [
{
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "get_weather_forecast",
description:
"Gets the current weather temperature for a given location.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
location: {
type: Type.STRING,
},
},
required: ["location"],
},
},
{
name: "set_thermostat_temperature",
description: "Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
temperature: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
},
},
required: ["temperature"],
},
},
],
},
];
// Prompt for the model
let contents = [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
},
],
},
];
// Loop until the model has no more function calls to make
while (true) {
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
config: { tools },
});
if (result.functionCalls && result.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = result.functionCalls[0];
const { name, args } = functionCall;
if (!toolFunctions[name]) {
throw new Error(`Unknown function call: ${name}`);
}
// Call the function and get the response.
const toolResponse = toolFunctions[name](args);
const functionResponsePart = {
name: functionCall.name,
response: {
result: toolResponse,
},
};
// Send the function response back to the model.
contents.push({
role: "model",
parts: [
{
functionCall: functionCall,
},
],
});
contents.push({
role: "user",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: functionResponsePart,
},
],
});
} else {
// No more function calls, break the loop.
console.log(result.text);
break;
}
}
Expected Output
When you run the code, you will see the SDK orchestrating the function
calls. The model first calls get_weather_forecast, receives the
temperature, and then calls set_thermostat_temperature with the correct
value based on the logic in the prompt.
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. It's 25°C in London, so I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
Compositional function calling is a native Live API feature. This means Live API can handle the function calling similar to the Python SDK.
Python
# Light control schemas
turn_on_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_on_the_lights'}
turn_off_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_off_the_lights'}
prompt = """
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
"""
tools = [
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]}
]
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Light control schemas
const turnOnTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_on_the_lights' };
const turnOffTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_off_the_lights' };
const prompt = `
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
`;
const tools = [
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] }
];
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
Function calling modes
The Gemini API lets you control how the model uses the provided tools
(function declarations). Specifically, you can set the mode within
the.function_calling_config.
AUTO (Default): The model decides whether to generate a natural language response or suggest a function call based on the prompt and context. This is the most flexible mode and recommended for most scenarios.ANY: The model is constrained to always predict a function call and guarantees function schema adherence. Ifallowed_function_namesis not specified, the model can choose from any of the provided function declarations. Ifallowed_function_namesis provided as a list, the model can only choose from the functions in that list. Use this mode when you require a function call response to every prompt (if applicable).NONE: The model is prohibited from making function calls. This is equivalent to sending a request without any function declarations. Use this to temporarily disable function calling without removing your tool definitions.VALIDATED(Preview): The model is constrained to predict either function calls or natural language, and ensures function schema adherence. Ifallowed_function_namesis not provided, the model picks from all of the available function declarations. Ifallowed_function_namesis provided, the model picks from the set of allowed functions.
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure function calling mode
tool_config = types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(
mode="ANY", allowed_function_names=["get_current_temperature"]
)
)
# Create the generation config
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tools], # not defined here.
tool_config=tool_config,
)
JavaScript
import { FunctionCallingConfigMode } from '@google/genai';
// Configure function calling mode
const toolConfig = {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: FunctionCallingConfigMode.ANY,
allowedFunctionNames: ['get_current_temperature']
}
};
// Create the generation config
const config = {
tools: tools, // not defined here.
toolConfig: toolConfig,
};
Automatic function calling (Python only)
When using the Python SDK, you can provide Python functions directly as tools. The SDK converts these functions into declarations, manages the function call execution, and handles the response cycle for you. Define your function with type hints and a docstring. For optimal results, it is recommended to use Google-style docstrings. The SDK will then automatically:
- Detect function call responses from the model.
- Call the corresponding Python function in your code.
- Send the function's response back to the model.
- Return the model's final text response.
The SDK currently does not parse argument descriptions into the property description slots of the generated function declaration. Instead, it sends the entire docstring as the top-level function description.
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function with type hints and docstring
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current temperature for a given location.
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
Returns:
A dictionary containing the temperature and unit.
"""
# ... (implementation) ...
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "Celsius"}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature]
) # Pass the function itself
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What's the temperature in Boston?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text) # The SDK handles the function call and returns the final text
You can disable automatic function calling with:
Python
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature],
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(disable=True)
)
Automatic function schema declaration
The API is able to describe any of the following types. Pydantic types are
allowed, as long as the fields defined on them are also composed of allowed
types. Dict types (like dict[str: int]) are not well supported here, don't
use them.
Python
AllowedType = (
int | float | bool | str | list['AllowedType'] | pydantic.BaseModel)
To see what the inferred schema looks like, you can convert it using
from_callable:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
"""Returns a * b."""
return a * b
client = genai.Client()
fn_decl = types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(callable=multiply, client=client)
# to_json_dict() provides a clean JSON representation.
print(fn_decl.to_json_dict())
Multi-tool use: Combine native tools with function calling
You can enable multiple tools combining native tools with function calling at the same time. Here's an example that enables two tools, Grounding with Google Search and code execution, in a request using the Live API.
Python
# Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
prompt = """
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
"""
tools = [
{'google_search': {}},
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]} # not defined here.
]
# Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
const prompt = `
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
`;
const tools = [
{ googleSearch: {} },
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] } // not defined here.
];
// Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, {tools: tools, modality: "AUDIO"});
Python developers can try this out in the Live API Tool Use notebook.
Multimodal function responses
For Gemini 3 series models, you can include multimodal content in the function response parts that you send to the model. The model can process this multimodal content in its next turn to produce a more informed response. The following MIME types are supported for multimodal content in function responses:
- Images:
image/png,image/jpeg,image/webp - Documents:
application/pdf,text/plain
To include multimodal data in a function response, include it as one or more
parts nested within the functionResponse part. Each multimodal part must
contain inlineData. If you reference a multimodal part from
within the structured response field, it must contain a unique displayName.
You can also reference a multimodal part from within the structured response
field of the functionResponse part by using the JSON reference format
{"$ref": "<displayName>"}. The model substitutes the reference with the
multimodal content when processing the response. Each displayName can only be
referenced once in the structured response field.
The following example shows a message containing a functionResponse for a
function named get_image and a nested part containing image data with
displayName: "instrument.jpg". The functionResponse's response field
references this image part:
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
client = genai.Client()
# This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
# 1. Define the function tool
get_image_declaration = types.FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_image",
description="Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"item_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument')."
}
},
"required": ["item_name"],
},
)
tool_config = types.Tool(function_declarations=[get_image_declaration])
# 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
prompt = "Show me the instrument I ordered last month."
response_1 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
)
)
# 3. Handle the function call
function_call = response_1.function_calls[0]
requested_item = function_call.args["item_name"]
print(f"Model wants to call: {function_call.name}")
# Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
# (This is a mock response for the example)
print(f"Calling external tool for: {requested_item}")
function_response_data = {
"image_ref": {"$ref": "instrument.jpg"},
}
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
function_response_multimodal_data = types.FunctionResponsePart(
inline_data=types.FunctionResponseBlob(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
display_name="instrument.jpg",
data=image_bytes,
)
)
# 4. Send the tool's result back
# Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
history = [
types.Content(role="user", parts=[types.Part(text=prompt)]),
response_1.candidates[0].content,
types.Content(
role="tool",
parts=[
types.Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response=function_response_data,
parts=[function_response_multimodal_data]
)
],
)
]
response_2 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=history,
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(include_thoughts=True)
),
)
print(f"\nFinal model response: {response_2.text}")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
const client = new GoogleGenAI({ apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY });
// This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
// 1. Define the function tool
const getImageDeclaration = {
name: 'get_image',
description: 'Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
item_name: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument').",
},
},
required: ['item_name'],
},
};
const toolConfig = {
functionDeclarations: [getImageDeclaration],
};
// 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
const prompt = 'Show me the instrument I ordered last month.';
const response1 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: prompt,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
},
});
// 3. Handle the function call
const functionCall = response1.functionCalls[0];
const requestedItem = functionCall.args.item_name;
console.log(`Model wants to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
// Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
// (This is a mock response for the example)
console.log(`Calling external tool for: ${requestedItem}`);
const functionResponseData = {
image_ref: { $ref: 'instrument.jpg' },
};
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
const functionResponseMultimodalData = {
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
displayName: 'instrument.jpg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
};
// 4. Send the tool's result back
// Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
const history = [
{ role: 'user', parts: [{ text: prompt }] },
response1.candidates[0].content,
{
role: 'tool',
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: functionResponseData,
parts: [functionResponseMultimodalData],
},
},
],
},
];
const response2 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: history,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
thinkingConfig: { includeThoughts: true },
},
});
console.log(`\nFinal model response: ${response2.text}`);
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
# Check for macOS
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
...,
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_image",
"response": {
"image_ref": {
"$ref": "instrument.jpg"
}
},
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"displayName": "instrument.jpg",
"mimeType":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
Function calling with Structured output
For Gemini 3 series models, you can use function calling with structured output. This lets the model predict function calls or outputs that adhere to a specific schema. As a result, you receive consistently formatted responses when the model doesn't generate function calls.
Model context protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard for connecting AI applications with external tools and data. MCP provides a common protocol for models to access context, such as functions (tools), data sources (resources), or predefined prompts.
The Gemini SDKs have built-in support for the MCP, reducing boilerplate code and offering automatic tool calling for MCP tools. When the model generates an MCP tool call, the Python and JavaScript client SDK can automatically execute the MCP tool and send the response back to the model in a subsequent request, continuing this loop until no more tool calls are made by the model.
Here, you can find an example of how to use a local MCP server with Gemini and
mcp SDK.
Python
Make sure the latest version of the
mcp SDK is installed on
your platform of choice.
pip install mcp
import os
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
# Create server parameters for stdio connection
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="npx", # Executable
args=["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"], # MCP Server
env=None, # Optional environment variables
)
async def run():
async with stdio_client(server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read, write) as session:
# Prompt to get the weather for the current day in London.
prompt = f"What is the weather in London in {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}?"
# Initialize the connection between client and server
await session.initialize()
# Send request to the model with MCP function declarations
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=prompt,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0,
tools=[session], # uses the session, will automatically call the tool
# Uncomment if you **don't** want the SDK to automatically call the tool
# automatic_function_calling=genai.types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
# disable=True
# ),
),
)
print(response.text)
# Start the asyncio event loop and run the main function
asyncio.run(run())
JavaScript
Make sure the latest version of the mcp SDK is installed on your platform
of choice.
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StdioClientTransport({
command: "npx", // Executable
args: ["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"] // MCP Server
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection
await client.close();
Limitations with built-in MCP support
Built-in MCP support is a experimental feature in our SDKs and has the following limitations:
- Only tools are supported, not resources nor prompts
- It is available for the Python and JavaScript/TypeScript SDK.
- Breaking changes might occur in future releases.
Manual integration of MCP servers is always an option if these limit what you're building.
Supported models
This section lists models and their function calling capabilities. Experimental models are not included. You can find a comprehensive capabilities overview on the model overview page.
| Model | Function Calling | Parallel Function Calling | Compositional Function Calling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite | X | X | X |
Best practices
- Function and Parameter Descriptions: Be extremely clear and specific in your descriptions. The model relies on these to choose the correct function and provide appropriate arguments.
- Naming: Use descriptive function names (without spaces, periods, or dashes).
- Strong Typing: Use specific types (integer, string, enum) for parameters to reduce errors. If a parameter has a limited set of valid values, use an enum.
- Tool Selection: While the model can use an arbitrary number of tools, providing too many can increase the risk of selecting an incorrect or suboptimal tool. For best results, aim to provide only the relevant tools for the context or task, ideally keeping the active set to a maximum of 10-20. Consider dynamic tool selection based on conversation context if you have a large total number of tools.
- Prompt Engineering:
- Provide context: Tell the model its role (e.g., "You are a helpful weather assistant.").
- Give instructions: Specify how and when to use functions (e.g., "Don't guess dates; always use a future date for forecasts.").
- Encourage clarification: Instruct the model to ask clarifying questions if needed.
- See Agentic workflows for further strategies on designing these prompts. Here is an example of a tested system instruction.
Temperature: Use a low temperature (e.g., 0) for more deterministic and reliable function calls.
Validation: If a function call has significant consequences (e.g., placing an order), validate the call with the user before executing it.
Check Finish Reason: Always check the
finishReasonin the model's response to handle cases where the model failed to generate a valid function call.Error Handling: Implement robust error handling in your functions to gracefully handle unexpected inputs or API failures. Return informative error messages that the model can use to generate helpful responses to the user.
Security: Be mindful of security when calling external APIs. Use appropriate authentication and authorization mechanisms. Avoid exposing sensitive data in function calls.
Token Limits: Function descriptions and parameters count towards your input token limit. If you're hitting token limits, consider limiting the number of functions or the length of the descriptions, break down complex tasks into smaller, more focused function sets.
Notes and limitations
- Only a subset of the OpenAPI schema is supported.
- For
ANYmode, the API may reject very large or deeply nested schemas. If you encounter errors, try simplifying your function parameter and response schemas by shortening property names, reducing nesting, or limiting the number of function declarations. - Supported parameter types in Python are limited.
- Automatic function calling is a Python SDK feature only.
