การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันช่วยให้คุณเชื่อมต่อโมเดลกับเครื่องมือและ API ภายนอกได้ โมเดลจะพิจารณาเวลาที่จะเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่เฉพาะเจาะจงและระบุพารามิเตอร์ที่จำเป็นเพื่อดำเนินการในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริงแทนที่จะสร้างคำตอบเป็นข้อความ ซึ่งช่วยให้โมเดลทำหน้าที่เป็นตัวเชื่อมระหว่างภาษาธรรมชาติกับ การดำเนินการและข้อมูลในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริงได้ การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันมีกรณีการใช้งานหลัก 3 กรณีดังนี้
- เพิ่มพูนความรู้: เข้าถึงข้อมูลจากแหล่งที่มาภายนอก เช่น ฐานข้อมูล, API และฐานความรู้
- ขยายขีดความสามารถ: ใช้เครื่องมือภายนอกเพื่อทำการคำนวณและขยายข้อจำกัดของโมเดล เช่น การใช้เครื่องคิดเลขหรือการสร้างแผนภูมิ
- ดำเนินการ: โต้ตอบกับระบบภายนอกโดยใช้ API เช่น กำหนดเวลานัดหมาย สร้างใบแจ้งหนี้ ส่งอีเมล หรือควบคุม อุปกรณ์สมาร์ทโฮม
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function declaration for the model
schedule_meeting_function = {
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting.",
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')",
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')",
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting.",
},
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"],
},
}
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[schedule_meeting_function])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/14/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.",
config=config,
)
# Check for a function call
if response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call:
function_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
print(f"Function to call: {function_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {function_call.args}")
# In a real app, you would call your function here:
# result = schedule_meeting(**function_call.args)
else:
print("No function call found in the response.")
print(response.text)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define the function declaration for the model
const scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'schedule_meeting',
description: 'Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
attendees: {
type: Type.ARRAY,
items: { type: Type.STRING },
description: 'List of people attending the meeting.',
},
date: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Date of the meeting (e.g., "2024-07-29")',
},
time: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'Time of the meeting (e.g., "15:00")',
},
topic: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'The subject or topic of the meeting.',
},
},
required: ['attendees', 'date', 'time', 'topic'],
},
};
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: 'Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning.',
config: {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [scheduleMeetingFunctionDeclaration]
}],
},
});
// Check for function calls in the response
if (response.functionCalls && response.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = response.functionCalls[0]; // Assuming one function call
console.log(`Function to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
console.log(`Arguments: ${JSON.stringify(functionCall.args)}`);
// In a real app, you would call your actual function here:
// const result = await scheduleMeeting(functionCall.args);
} else {
console.log("No function call found in the response.");
console.log(response.text);
}
REST
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"text": "Schedule a meeting with Bob and Alice for 03/27/2025 at 10:00 AM about the Q3 planning."
}
]
}
],
"tools": [
{
"functionDeclarations": [
{
"name": "schedule_meeting",
"description": "Schedules a meeting with specified attendees at a given time and date.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"attendees": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
"description": "List of people attending the meeting."
},
"date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date of the meeting (e.g., '2024-07-29')"
},
"time": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time of the meeting (e.g., '15:00')"
},
"topic": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The subject or topic of the meeting."
}
},
"required": ["attendees", "date", "time", "topic"]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
วิธีการทำงานของการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
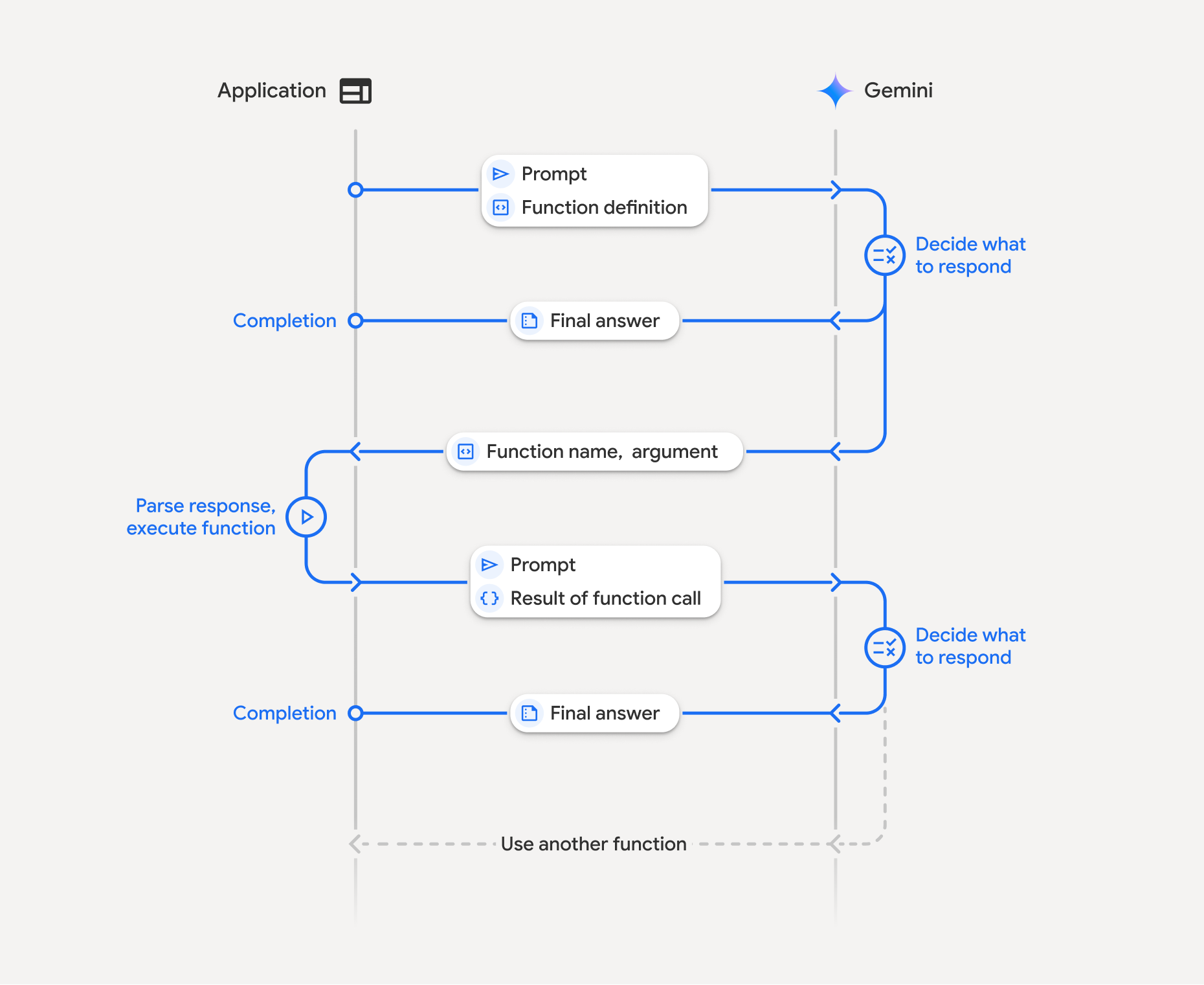
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเกี่ยวข้องกับการโต้ตอบที่มีโครงสร้างระหว่างแอปพลิเคชัน โมเดล และฟังก์ชันภายนอก รายละเอียดของกระบวนการมีดังนี้
- กำหนดการประกาศฟังก์ชัน: กำหนดการประกาศฟังก์ชันในโค้ดแอปพลิเคชัน การประกาศฟังก์ชันจะอธิบายชื่อ พารามิเตอร์ และวัตถุประสงค์ของฟังก์ชันต่อโมเดล
- เรียกใช้ LLM ด้วยการประกาศฟังก์ชัน: ส่งพรอมต์ของผู้ใช้พร้อมกับการประกาศฟังก์ชันไปยังโมเดล โดยจะวิเคราะห์คำขอและพิจารณา ว่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจะมีประโยชน์หรือไม่ หากเป็นเช่นนั้น ระบบจะตอบกลับด้วยออบเจ็กต์ JSON ที่มีโครงสร้าง
- เรียกใช้โค้ดฟังก์ชัน (ความรับผิดชอบของคุณ): โมเดลไม่
เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันด้วยตัวเอง แอปพลิเคชันของคุณมีหน้าที่
ประมวลผลการตอบกลับและตรวจสอบการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน หาก
- ใช่: แยกชื่อและอาร์กิวเมนต์ของฟังก์ชัน แล้วเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่เกี่ยวข้องในแอปพลิเคชัน
- ไม่ได้: โมเดลได้ให้คำตอบเป็นข้อความโดยตรงต่อพรอมต์ (โฟลว์นี้ไม่ได้เน้นในตัวอย่าง แต่เป็นผลลัพธ์ที่เป็นไปได้)
- สร้างคำตอบที่ใช้งานง่าย: หากมีการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ให้บันทึก ผลลัพธ์และส่งกลับไปยังโมเดลในการสนทนาครั้งถัดไป โดยจะใช้ผลลัพธ์เพื่อสร้างคำตอบสุดท้ายที่ใช้งานง่าย ซึ่งรวมข้อมูลจากการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
กระบวนการนี้สามารถทำซ้ำได้หลายรอบ ซึ่งช่วยให้เกิดการโต้ตอบและเวิร์กโฟลว์ที่ซับซ้อน นอกจากนี้ โมเดลยังรองรับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายรายการ ในเทิร์นเดียว (การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบขนาน) และแบบ ลำดับ (การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิต)
ขั้นตอนที่ 1: กำหนดการประกาศฟังก์ชัน
กำหนดฟังก์ชันและการประกาศภายในโค้ดแอปพลิเคชันที่อนุญาตให้ ผู้ใช้ตั้งค่าแสงและส่งคำขอ API ฟังก์ชันนี้อาจเรียกใช้บริการหรือ API ภายนอก
Python
# Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
set_light_values_declaration = {
"name": "set_light_values",
"description": "Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness",
},
"color_temp": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"],
"description": "Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.",
},
},
"required": ["brightness", "color_temp"],
},
}
# This is the actual function that would be called based on the model's suggestion
def set_light_values(brightness: int, color_temp: str) -> dict[str, int | str]:
"""Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API).
Args:
brightness: Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
color_temp: Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness, "colorTemperature": color_temp}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
// Define a function that the model can call to control smart lights
const setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'set_light_values',
description: 'Sets the brightness and color temperature of a light.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness',
},
color_temp: {
type: Type.STRING,
enum: ['daylight', 'cool', 'warm'],
description: 'Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.',
},
},
required: ['brightness', 'color_temp'],
},
};
/**
* Set the brightness and color temperature of a room light. (mock API)
* @param {number} brightness - Light level from 0 to 100. Zero is off and 100 is full brightness
* @param {string} color_temp - Color temperature of the light fixture, which can be `daylight`, `cool` or `warm`.
* @return {Object} A dictionary containing the set brightness and color temperature.
*/
function setLightValues(brightness, color_temp) {
return {
brightness: brightness,
colorTemperature: color_temp
};
}
ขั้นตอนที่ 2: เรียกใช้โมเดลด้วยการประกาศฟังก์ชัน
เมื่อกำหนดการประกาศฟังก์ชันแล้ว คุณสามารถแจ้งให้โมเดล ใช้ฟังก์ชันเหล่านั้นได้ โดยจะวิเคราะห์พรอมต์และการประกาศฟังก์ชัน แล้วตัดสินใจว่าจะตอบกลับโดยตรงหรือเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน หากมีการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ออบเจ็กต์การตอบกลับ จะมีคำแนะนำในการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
tools = types.Tool(function_declarations=[set_light_values_declaration])
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(tools=[tools])
# Define user prompt
contents = [
types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="Turn the lights down to a romantic level")]
)
]
# Send request with function declarations
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=contents,
config=config,
)
print(response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call)
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Generation config with function declaration
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: [setLightValuesFunctionDeclaration]
}]
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Define user prompt
const contents = [
{
role: 'user',
parts: [{ text: 'Turn the lights down to a romantic level' }]
}
];
// Send request with function declarations
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(response.functionCalls[0]);
จากนั้นโมเดลจะแสดงออบเจ็กต์ functionCall ในสคีมาที่เข้ากันได้กับ OpenAPI
ซึ่งระบุวิธีเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่ประกาศไว้อย่างน้อย 1 รายการเพื่อ
ตอบคำถามของผู้ใช้
Python
id=None args={'color_temp': 'warm', 'brightness': 25} name='set_light_values'
JavaScript
{
name: 'set_light_values',
args: { brightness: 25, color_temp: 'warm' }
}
ขั้นตอนที่ 3: เรียกใช้โค้ดฟังก์ชัน set_light_values
ดึงรายละเอียดการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจากการตอบกลับของโมเดล แยกวิเคราะห์อาร์กิวเมนต์
และเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน set_light_values
Python
# Extract tool call details, it may not be in the first part.
tool_call = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].function_call
if tool_call.name == "set_light_values":
result = set_light_values(**tool_call.args)
print(f"Function execution result: {result}")
JavaScript
// Extract tool call details
const tool_call = response.functionCalls[0]
let result;
if (tool_call.name === 'set_light_values') {
result = setLightValues(tool_call.args.brightness, tool_call.args.color_temp);
console.log(`Function execution result: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`);
}
ขั้นตอนที่ 4: สร้างคำตอบที่ใช้งานง่ายพร้อมผลลัพธ์ของฟังก์ชันและเรียกใช้โมเดลอีกครั้ง
สุดท้าย ให้ส่งผลลัพธ์ของการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันกลับไปยังโมเดลเพื่อให้โมเดลสามารถ รวมข้อมูลนี้ไว้ในการตอบกลับสุดท้ายต่อผู้ใช้
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Create a function response part
function_response_part = types.Part.from_function_response(
name=tool_call.name,
response={"result": result},
)
# Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.append(response.candidates[0].content) # Append the content from the model's response.
contents.append(types.Content(role="user", parts=[function_response_part])) # Append the function response
client = genai.Client()
final_response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
config=config,
contents=contents,
)
print(final_response.text)
JavaScript
// Create a function response part
const function_response_part = {
name: tool_call.name,
response: { result }
}
// Append function call and result of the function execution to contents
contents.push(response.candidates[0].content);
contents.push({ role: 'user', parts: [{ functionResponse: function_response_part }] });
// Get the final response from the model
const final_response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: contents,
config: config
});
console.log(final_response.text);
ซึ่งจะเป็นการเสร็จสิ้นขั้นตอนการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน โมเดลใช้ฟังก์ชัน
set_light_values เพื่อดำเนินการตามคำขอของผู้ใช้ได้สำเร็จ
การประกาศฟังก์ชัน
เมื่อใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันในพรอมต์ คุณจะสร้างออบเจ็กต์ tools
ซึ่งมี function declarations อย่างน้อย 1 รายการ คุณกำหนดฟังก์ชันโดยใช้ JSON โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งกับชุดย่อยที่เลือก
ของรูปแบบสคีมา OpenAPI การประกาศฟังก์ชันเดียวอาจมีพารามิเตอร์ต่อไปนี้
name(สตริง): ชื่อที่ไม่ซ้ำกันสำหรับฟังก์ชัน (get_weather_forecast,send_email) ใช้ชื่อที่สื่อความหมายโดยไม่มีช่องว่างหรืออักขระพิเศษ (ใช้อักขระขีดล่างหรือรูปแบบ CamelCase)description(string): คำอธิบายที่ชัดเจนและละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ วัตถุประสงค์และความสามารถของฟังก์ชัน ซึ่งเป็นสิ่งสําคัญเพื่อให้โมเดลเข้าใจว่าเมื่อใดควรใช้ฟังก์ชัน ระบุรายละเอียดและยกตัวอย่างหากเป็นประโยชน์ ("ค้นหา โรงภาพยนตร์ตามสถานที่ตั้งและชื่อภาพยนตร์ (ไม่บังคับ) ซึ่งกำลัง ฉายอยู่ในโรงภาพยนตร์")parameters(ออบเจ็กต์): กำหนดพารามิเตอร์อินพุตที่ฟังก์ชัน คาดหวังtype(สตริง): ระบุประเภทข้อมูลโดยรวม เช่นobjectproperties(ออบเจ็กต์): แสดงรายการพารามิเตอร์แต่ละรายการ โดยแต่ละรายการมีข้อมูลต่อไปนี้type(string): ประเภทข้อมูลของพารามิเตอร์ เช่นstring,integer,boolean, arraydescription(สตริง): คำอธิบายวัตถุประสงค์และรูปแบบของพารามิเตอร์ ระบุตัวอย่างและข้อจำกัด ("เมืองและรัฐ เช่น "ซานฟรานซิสโก แคลิฟอร์เนีย" หรือรหัสไปรษณีย์ เช่น '95616'")enum(อาร์เรย์ ไม่บังคับ): หากค่าพารามิเตอร์มาจากชุดค่าที่กำหนด ให้ใช้ "enum" เพื่อแสดงค่าที่อนุญาตแทนการอธิบายค่าเหล่านั้นในคำอธิบาย ซึ่งจะช่วยปรับปรุงความแม่นยำ ("enum": ["daylight", "cool", "warm"])
required(อาร์เรย์): อาร์เรย์ของสตริงที่แสดงชื่อพารามิเตอร์ที่ จำเป็นต่อการทำงานของฟังก์ชัน
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังสร้าง FunctionDeclarations จากฟังก์ชัน Python ได้โดยตรงโดยใช้
types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(client=client, callable=your_function)
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันด้วยโมเดลการคิด
โมเดล Gemini 3 และ 2.5 ใช้กระบวนการ"การคิด"ภายในเพื่อให้เหตุผลผ่านคำขอ ซึ่งจะช่วยปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันได้อย่างมาก ทำให้โมเดลกำหนดได้ดียิ่งขึ้นว่าจะเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเมื่อใดและจะใช้พารามิเตอร์ใด เนื่องจาก Gemini API เป็นแบบไม่เก็บสถานะ โมเดลจึงใช้ลายเซ็นความคิดเพื่อรักษาบริบท ในการสนทนาแบบหลายรอบ
ส่วนนี้ครอบคลุมการจัดการลายเซ็นความคิดขั้นสูง และจำเป็นเฉพาะในกรณีที่คุณสร้างคำขอ API ด้วยตนเอง (เช่น ผ่าน REST) หรือจัดการประวัติการสนทนา
หากใช้ SDK ของ GenAI ของ Google (ไลบรารีอย่างเป็นทางการของเรา) คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องจัดการกระบวนการนี้ SDK จะจัดการขั้นตอนที่จำเป็นโดยอัตโนมัติ ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้า
การจัดการประวัติการสนทนาด้วยตนเอง
หากคุณแก้ไขประวัติการสนทนาด้วยตนเองแทนที่จะส่งคำตอบก่อนหน้าทั้งหมด คุณต้องจัดการ thought_signature ที่รวมอยู่ในเทิร์นของโมเดลให้ถูกต้อง
ทำตามกฎต่อไปนี้เพื่อให้บริบทของโมเดลยังคงอยู่
- ส่ง
thought_signatureกลับไปยังโมเดลภายในPartเดิมเสมอ - อย่าผสาน
Partที่มีลายเซ็นกับPartที่ไม่มีลายเซ็น ซึ่ง จะทำลายบริบทเชิงตำแหน่งของความคิด - อย่ารวม
Parts2 รายการที่มีลายเซ็น เนื่องจากระบบรวมสตริงลายเซ็นไม่ได้
ลายเซ็นความคิดของ Gemini 3
ใน Gemini 3 Part ของคำตอบจากโมเดล
อาจมีลายเซ็นความคิด
แม้ว่าโดยทั่วไปเราจะแนะนำให้ส่งคืนลายเซ็นจากPartทุกประเภท
แต่การส่งคืนลายเซ็นความคิดเป็นข้อบังคับสำหรับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน เว้นแต่คุณจะ
จัดการประวัติการสนทนาด้วยตนเอง Google GenAI SDK จะ
จัดการลายเซ็นความคิดโดยอัตโนมัติ
หากคุณจัดการประวัติการสนทนาด้วยตนเอง โปรดดูคำแนะนำและรายละเอียดทั้งหมดเกี่ยวกับการจัดการลายเซ็นความคิดสำหรับ Gemini 3 ในหน้าลายเซ็นความคิด
การตรวจสอบลายเซ็นความคิด
แม้ว่าจะไม่จำเป็นสำหรับการติดตั้งใช้งาน แต่คุณสามารถตรวจสอบการตอบกลับเพื่อดู
thought_signatureเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ในการแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องหรือเพื่อการศึกษา
Python
import base64
# After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
# response = client.models.generate_content(...)
# The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0]
if part.thought_signature:
print(base64.b64encode(part.thought_signature).decode("utf-8"))
JavaScript
// After receiving a response from a model with thinking enabled
// const response = await ai.models.generateContent(...)
// The signature is attached to the response part containing the function call
const part = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0];
if (part.thoughtSignature) {
console.log(part.thoughtSignature);
}
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับข้อจำกัดและการใช้งานลายเซ็นความคิด รวมถึงเกี่ยวกับโมเดลการคิดโดยทั่วไปได้ในหน้าการคิด
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคู่ขนาน
นอกจากการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบครั้งเดียวแล้ว คุณยังเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายรายการพร้อมกันได้ด้วย การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบขนานช่วยให้คุณเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายรายการ พร้อมกันได้ และใช้เมื่อฟังก์ชันไม่ได้ขึ้นอยู่กับฟังก์ชันอื่น ซึ่งมีประโยชน์ในสถานการณ์ต่างๆ เช่น การรวบรวมข้อมูลจากแหล่งข้อมูลอิสระหลายแหล่ง เช่น การดึงรายละเอียดลูกค้าจากฐานข้อมูลต่างๆ หรือการตรวจสอบระดับสินค้าคงคลังในคลังสินค้าต่างๆ หรือการดำเนินการหลายอย่าง เช่น การเปลี่ยนอพาร์ตเมนต์ให้เป็นดิสโก้
Python
power_disco_ball = {
"name": "power_disco_ball",
"description": "Powers the spinning disco ball.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"power": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.",
}
},
"required": ["power"],
},
}
start_music = {
"name": "start_music",
"description": "Play some music matching the specified parameters.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"energetic": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is energetic or not.",
},
"loud": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Whether the music is loud or not.",
},
},
"required": ["energetic", "loud"],
},
}
dim_lights = {
"name": "dim_lights",
"description": "Dim the lights.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"brightness": {
"type": "number",
"description": "The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.",
}
},
"required": ["brightness"],
},
}
JavaScript
import { Type } from '@google/genai';
const powerDiscoBall = {
name: 'power_disco_ball',
description: 'Powers the spinning disco ball.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
power: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.'
}
},
required: ['power']
}
};
const startMusic = {
name: 'start_music',
description: 'Play some music matching the specified parameters.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
energetic: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is energetic or not.'
},
loud: {
type: Type.BOOLEAN,
description: 'Whether the music is loud or not.'
}
},
required: ['energetic', 'loud']
}
};
const dimLights = {
name: 'dim_lights',
description: 'Dim the lights.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
brightness: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
description: 'The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.'
}
},
required: ['brightness']
}
};
กำหนดค่าโหมดการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเพื่อให้ใช้เครื่องมือที่ระบุทั้งหมดได้ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่หัวข้อ การกำหนดค่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Configure the client and tools
client = genai.Client()
house_tools = [
types.Tool(function_declarations=[power_disco_ball, start_music, dim_lights])
]
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=house_tools,
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
disable=True
),
# Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
tool_config=types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(mode='ANY')
),
)
chat = client.chats.create(model="gemini-3-flash-preview", config=config)
response = chat.send_message("Turn this place into a party!")
# Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
print("Example 1: Forced function calling")
for fn in response.function_calls:
args = ", ".join(f"{key}={val}" for key, val in fn.args.items())
print(f"{fn.name}({args})")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
// Set up function declarations
const houseFns = [powerDiscoBall, startMusic, dimLights];
const config = {
tools: [{
functionDeclarations: houseFns
}],
// Force the model to call 'any' function, instead of chatting.
toolConfig: {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: 'any'
}
}
};
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Create a chat session
const chat = ai.chats.create({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
config: config
});
const response = await chat.sendMessage({message: 'Turn this place into a party!'});
// Print out each of the function calls requested from this single call
console.log("Example 1: Forced function calling");
for (const fn of response.functionCalls) {
const args = Object.entries(fn.args)
.map(([key, val]) => `${key}=${val}`)
.join(', ');
console.log(`${fn.name}(${args})`);
}
ผลลัพธ์ที่พิมพ์แต่ละรายการแสดงถึงการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเดียวที่โมเดลได้ ขอ หากต้องการส่งผลลัพธ์กลับ ให้ใส่คำตอบตามลำดับเดียวกับที่ขอ
Python SDK รองรับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติ ซึ่งจะแปลงฟังก์ชัน Python เป็นการประกาศโดยอัตโนมัติ จัดการ วงจรการดำเนินการและการตอบกลับของการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันให้คุณ ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างสำหรับ กรณีการใช้งาน Disco
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Actual function implementations
def power_disco_ball_impl(power: bool) -> dict:
"""Powers the spinning disco ball.
Args:
power: Whether to turn the disco ball on or off.
Returns:
A status dictionary indicating the current state.
"""
return {"status": f"Disco ball powered {'on' if power else 'off'}"}
def start_music_impl(energetic: bool, loud: bool) -> dict:
"""Play some music matching the specified parameters.
Args:
energetic: Whether the music is energetic or not.
loud: Whether the music is loud or not.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the music settings.
"""
music_type = "energetic" if energetic else "chill"
volume = "loud" if loud else "quiet"
return {"music_type": music_type, "volume": volume}
def dim_lights_impl(brightness: float) -> dict:
"""Dim the lights.
Args:
brightness: The brightness of the lights, 0.0 is off, 1.0 is full.
Returns:
A dictionary containing the new brightness setting.
"""
return {"brightness": brightness}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[power_disco_ball_impl, start_music_impl, dim_lights_impl]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="Do everything you need to this place into party!",
config=config,
)
print("\nExample 2: Automatic function calling")
print(response.text)
# I've turned on the disco ball, started playing loud and energetic music, and dimmed the lights to 50% brightness. Let's get this party started!
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิต
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบเรียงซ้อนหรือแบบลำดับช่วยให้ Gemini สามารถเชื่อมโยงการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายรายการเข้าด้วยกันเพื่อตอบสนองคำขอที่ซับซ้อน เช่น หากต้องการตอบคำถาม "ขออุณหภูมิในตำแหน่งปัจจุบัน" Gemini API อาจเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน get_current_location() ก่อน แล้วจึงเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน get_weather() ที่ใช้ตำแหน่งเป็นพารามิเตอร์
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิชัน โดยใช้ Python SDK และการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติ
Python
ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ฟีเจอร์การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติของ
google-genai Python SDK SDK จะแปลงฟังก์ชัน Python
เป็นสคีมาที่จำเป็นโดยอัตโนมัติ ดำเนินการเรียกฟังก์ชันเมื่อโมเดลร้องขอ
และส่งผลลัพธ์กลับไปยังโมเดลเพื่อทำงานให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์
import os
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Example Functions
def get_weather_forecast(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current weather temperature for a given location."""
print(f"Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location={location})")
# TODO: Make API call
print("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}")
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "celsius"} # Dummy response
def set_thermostat_temperature(temperature: int) -> dict:
"""Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature."""
print(f"Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature={temperature})")
# TODO: Interact with a thermostat API
print("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configure the client and model
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_weather_forecast, set_thermostat_temperature]
)
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
config=config,
)
# Print the final, user-facing response
print(response.text)
ผลลัพธ์ที่คาดไว้
เมื่อเรียกใช้โค้ด คุณจะเห็น SDK จัดการการเรียกฟังก์ชัน
โมเดลจะเรียกใช้ get_weather_forecast ก่อน จากนั้นจะรับ
อุณหภูมิ แล้วเรียกใช้ set_thermostat_temperature โดยมีค่าที่ถูกต้อง
ตามตรรกะในพรอมต์
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
JavaScript
ตัวอย่างนี้แสดงวิธีใช้ JavaScript/TypeScript SDK เพื่อเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิชัน โดยใช้ลูปการดำเนินการด้วยตนเอง
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from "@google/genai";
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Example Functions
function get_weather_forecast({ location }) {
console.log(`Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=${location})`);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}");
return { temperature: 25, unit: "celsius" };
}
function set_thermostat_temperature({ temperature }) {
console.log(
`Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=${temperature})`,
);
// TODO: Make API call
console.log("Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}");
return { status: "success" };
}
const toolFunctions = {
get_weather_forecast,
set_thermostat_temperature,
};
const tools = [
{
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "get_weather_forecast",
description:
"Gets the current weather temperature for a given location.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
location: {
type: Type.STRING,
},
},
required: ["location"],
},
},
{
name: "set_thermostat_temperature",
description: "Sets the thermostat to a desired temperature.",
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
temperature: {
type: Type.NUMBER,
},
},
required: ["temperature"],
},
},
],
},
];
// Prompt for the model
let contents = [
{
role: "user",
parts: [
{
text: "If it's warmer than 20°C in London, set the thermostat to 20°C, otherwise set it to 18°C.",
},
],
},
];
// Loop until the model has no more function calls to make
while (true) {
const result = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents,
config: { tools },
});
if (result.functionCalls && result.functionCalls.length > 0) {
const functionCall = result.functionCalls[0];
const { name, args } = functionCall;
if (!toolFunctions[name]) {
throw new Error(`Unknown function call: ${name}`);
}
// Call the function and get the response.
const toolResponse = toolFunctions[name](args);
const functionResponsePart = {
name: functionCall.name,
response: {
result: toolResponse,
},
};
// Send the function response back to the model.
contents.push({
role: "model",
parts: [
{
functionCall: functionCall,
},
],
});
contents.push({
role: "user",
parts: [
{
functionResponse: functionResponsePart,
},
],
});
} else {
// No more function calls, break the loop.
console.log(result.text);
break;
}
}
ผลลัพธ์ที่คาดไว้
เมื่อเรียกใช้โค้ด คุณจะเห็น SDK จัดการการเรียกฟังก์ชัน
โมเดลจะเรียกใช้ get_weather_forecast ก่อน จากนั้นจะรับ
อุณหภูมิ แล้วเรียกใช้ set_thermostat_temperature โดยมีค่าที่ถูกต้อง
ตามตรรกะในพรอมต์
Tool Call: get_weather_forecast(location=London)
Tool Response: {'temperature': 25, 'unit': 'celsius'}
Tool Call: set_thermostat_temperature(temperature=20)
Tool Response: {'status': 'success'}
OK. It's 25°C in London, so I've set the thermostat to 20°C.
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิชันเป็นฟีเจอร์ของ Live API ในตัว ซึ่งหมายความว่า Live API สามารถจัดการการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันได้คล้ายกับ Python SDK
Python
# Light control schemas
turn_on_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_on_the_lights'}
turn_off_the_lights_schema = {'name': 'turn_off_the_lights'}
prompt = """
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
"""
tools = [
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]}
]
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Light control schemas
const turnOnTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_on_the_lights' };
const turnOffTheLightsSchema = { name: 'turn_off_the_lights' };
const prompt = `
Hey, can you write run some python code to turn on the lights, wait 10s and then turn off the lights?
`;
const tools = [
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] }
];
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
โหมดการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
Gemini API ช่วยให้คุณควบคุมวิธีที่โมเดลใช้เครื่องมือที่ระบุ (การประกาศฟังก์ชัน) ได้
โดยคุณสามารถตั้งค่าโหมดได้ภายใน
function_calling_config
AUTO (Default): โมเดลจะตัดสินใจว่าจะสร้างคำตอบเป็นภาษาธรรมชาติหรือแนะนำการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันโดยอิงตามพรอมต์และบริบท ซึ่งเป็น โหมดที่ยืดหยุ่นที่สุดและแนะนำสำหรับสถานการณ์ส่วนใหญ่ANY: โมเดลถูกจำกัดให้คาดการณ์การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเสมอและรับประกันการยึดมั่นในสคีมาของฟังก์ชัน หากไม่ได้ระบุallowed_function_namesโมเดลจะเลือกจากประกาศฟังก์ชันที่ระบุไว้ได้ หากระบุallowed_function_namesเป็นรายการ โมเดลจะเลือกได้เฉพาะฟังก์ชันในรายการนั้น ใช้โหมดนี้เมื่อคุณต้องการให้ฟังก์ชัน เรียกใช้การตอบกลับทุกพรอมต์ (หากมี)NONE: โมเดลถูกห้ามไม่ให้ทำการเรียกฟังก์ชัน ซึ่งเทียบเท่ากับการส่งคำขอโดยไม่มีการประกาศฟังก์ชันใดๆ ใช้เพื่อ ปิดใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันชั่วคราวโดยไม่ต้องนำคำจำกัดความของเครื่องมือออกVALIDATED(ตัวอย่าง): โมเดลจะถูกจำกัดให้คาดการณ์ได้เฉพาะฟังก์ชัน หรือภาษาธรรมชาติ และตรวจสอบว่าสคีมาฟังก์ชันเป็นไปตามข้อกำหนด หากไม่ได้ระบุallowed_function_namesโมเดลจะเลือกจากประกาศฟังก์ชันทั้งหมดที่ใช้ได้ หากระบุallowed_function_namesโมเดลจะเลือกจากชุดฟังก์ชันที่อนุญาต
Python
from google.genai import types
# Configure function calling mode
tool_config = types.ToolConfig(
function_calling_config=types.FunctionCallingConfig(
mode="ANY", allowed_function_names=["get_current_temperature"]
)
)
# Create the generation config
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tools], # not defined here.
tool_config=tool_config,
)
JavaScript
import { FunctionCallingConfigMode } from '@google/genai';
// Configure function calling mode
const toolConfig = {
functionCallingConfig: {
mode: FunctionCallingConfigMode.ANY,
allowedFunctionNames: ['get_current_temperature']
}
};
// Create the generation config
const config = {
tools: tools, // not defined here.
toolConfig: toolConfig,
};
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติ (Python เท่านั้น)
เมื่อใช้ Python SDK คุณจะระบุฟังก์ชัน Python เป็นเครื่องมือได้โดยตรง SDK จะแปลงฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้เป็นการประกาศ จัดการการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน การดำเนินการ และจัดการวงจรการตอบกลับให้คุณ กำหนดฟังก์ชันด้วย คำแนะนำประเภทและสตริงเอกสาร ขอแนะนำให้ใช้สตริงเอกสารสไตล์ Google เพื่อให้ได้ผลลัพธ์ที่ดีที่สุด จากนั้น SDK จะดำเนินการต่อไปนี้โดยอัตโนมัติ
- ตรวจหาการตอบกลับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจากโมเดล
- เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน Python ที่เกี่ยวข้องในโค้ด
- ส่งการตอบกลับของฟังก์ชันกลับไปยังโมเดล
- แสดงคำตอบข้อความสุดท้ายของโมเดล
ปัจจุบัน SDK ยังไม่ได้แยกวิเคราะห์คำอธิบายอาร์กิวเมนต์ลงในช่องพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ คำอธิบายของการประกาศฟังก์ชันที่สร้างขึ้น แต่จะส่งสตริงเอกสารทั้งหมดเป็นคำอธิบายฟังก์ชันระดับบนสุดแทน
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
# Define the function with type hints and docstring
def get_current_temperature(location: str) -> dict:
"""Gets the current temperature for a given location.
Args:
location: The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA
Returns:
A dictionary containing the temperature and unit.
"""
# ... (implementation) ...
return {"temperature": 25, "unit": "Celsius"}
# Configure the client
client = genai.Client()
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature]
) # Pass the function itself
# Make the request
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents="What's the temperature in Boston?",
config=config,
)
print(response.text) # The SDK handles the function call and returns the final text
คุณปิดใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติได้โดยใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้
Python
config = types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[get_current_temperature],
automatic_function_calling=types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(disable=True)
)
การประกาศสคีมาฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติ
API สามารถอธิบายประเภทต่อไปนี้ได้ Pydantic ประเภทจะได้รับอนุญาต
ตราบใดที่ฟิลด์ที่กำหนดไว้ในฟิลด์เหล่านั้นประกอบด้วยประเภทที่ได้รับอนุญาต
ด้วย ระบบไม่รองรับประเภท Dict (เช่น dict[str: int]) ที่นี่ ดังนั้นโปรดอย่าใช้
Python
AllowedType = (
int | float | bool | str | list['AllowedType'] | pydantic.BaseModel)
หากต้องการดูว่าสคีมาที่อนุมานมีลักษณะอย่างไร คุณสามารถแปลงสคีมาได้โดยใช้
from_callable
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
"""Returns a * b."""
return a * b
client = genai.Client()
fn_decl = types.FunctionDeclaration.from_callable(callable=multiply, client=client)
# to_json_dict() provides a clean JSON representation.
print(fn_decl.to_json_dict())
การใช้เครื่องมือหลายอย่าง: รวมเครื่องมือเนทีฟเข้ากับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
คุณเปิดใช้เครื่องมือหลายอย่างได้โดยการรวมเครื่องมือดั้งเดิมเข้ากับ การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันพร้อมกัน นี่คือตัวอย่างที่เปิดใช้เครื่องมือ 2 รายการ ได้แก่ Grounding with Google Search และการเรียกใช้โค้ด ในคำขอที่ใช้ Live API
Python
# Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
prompt = """
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
"""
tools = [
{'google_search': {}},
{'code_execution': {}},
{'function_declarations': [turn_on_the_lights_schema, turn_off_the_lights_schema]} # not defined here.
]
# Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, tools=tools, modality="AUDIO")
JavaScript
// Multiple tasks example - combining lights, code execution, and search
const prompt = `
Hey, I need you to do three things for me.
1. Turn on the lights.
2. Then compute the largest prime palindrome under 100000.
3. Then use Google Search to look up information about the largest earthquake in California the week of Dec 5 2024.
Thanks!
`;
const tools = [
{ googleSearch: {} },
{ codeExecution: {} },
{ functionDeclarations: [turnOnTheLightsSchema, turnOffTheLightsSchema] } // not defined here.
];
// Execute the prompt with specified tools in audio modality
await run(prompt, {tools: tools, modality: "AUDIO"});
นักพัฒนา Python สามารถลองใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ได้ในสมุดบันทึกการใช้เครื่องมือ API แบบสด
การตอบกลับฟังก์ชันหลายรูปแบบ
สำหรับโมเดล Gemini 3 คุณสามารถรวมเนื้อหาแบบมัลติโมดัลไว้ในส่วนการตอบกลับฟังก์ชันที่คุณส่งไปยังโมเดลได้ โมเดลสามารถประมวลผล เนื้อหามัลติโมดัลนี้ในรอบถัดไปเพื่อสร้างคำตอบที่แม่นยำยิ่งขึ้น ระบบรองรับประเภท MIME ต่อไปนี้สำหรับเนื้อหามัลติโมดัลในคำตอบของฟังก์ชัน
- รูปภาพ:
image/png,image/jpeg,image/webp - เอกสาร:
application/pdf,text/plain
หากต้องการรวมข้อมูลมัลติโมดัลในการตอบกลับของฟังก์ชัน ให้รวมข้อมูลดังกล่าวเป็นส่วนอย่างน้อย 1 ส่วนที่ซ้อนอยู่ภายในส่วน functionResponse ชิ้นส่วนมัลติโมดัลแต่ละชิ้นต้องมีinlineData หากอ้างอิงชิ้นส่วนมัลติโมดัลจากภายในฟิลด์ response ที่มีโครงสร้าง จะต้องมี displayName ที่ไม่ซ้ำกัน
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังอ้างอิงชิ้นส่วนมัลติโมดัลจากภายในresponseฟิลด์ของ functionResponse ที่มีโครงสร้างได้โดยใช้รูปแบบการอ้างอิง JSON {"$ref": "<displayName>"} โมเดลจะแทนที่ข้อมูลอ้างอิงด้วย
เนื้อหามัลติโมดัลเมื่อประมวลผลคำตอบ displayName แต่ละรายการจะอ้างอิงได้เพียงครั้งเดียวในฟิลด์ response ที่มีโครงสร้าง
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงข้อความที่มี functionResponse สำหรับฟังก์ชันชื่อ get_image และส่วนที่ซ้อนกันซึ่งมีข้อมูลรูปภาพพร้อม displayName: "instrument.jpg" ฟิลด์ functionResponse's response
อ้างอิงส่วนของรูปภาพนี้
Python
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
client = genai.Client()
# This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
# 1. Define the function tool
get_image_declaration = types.FunctionDeclaration(
name="get_image",
description="Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.",
parameters={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"item_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument')."
}
},
"required": ["item_name"],
},
)
tool_config = types.Tool(function_declarations=[get_image_declaration])
# 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
prompt = "Show me the instrument I ordered last month."
response_1 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=[prompt],
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
)
)
# 3. Handle the function call
function_call = response_1.function_calls[0]
requested_item = function_call.args["item_name"]
print(f"Model wants to call: {function_call.name}")
# Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
# (This is a mock response for the example)
print(f"Calling external tool for: {requested_item}")
function_response_data = {
"image_ref": {"$ref": "instrument.jpg"},
}
image_path = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
image_bytes = requests.get(image_path).content
function_response_multimodal_data = types.FunctionResponsePart(
inline_data=types.FunctionResponseBlob(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
display_name="instrument.jpg",
data=image_bytes,
)
)
# 4. Send the tool's result back
# Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
history = [
types.Content(role="user", parts=[types.Part(text=prompt)]),
response_1.candidates[0].content,
types.Content(
role="tool",
parts=[
types.Part.from_function_response(
name=function_call.name,
response=function_response_data,
parts=[function_response_multimodal_data]
)
],
)
]
response_2 = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
contents=history,
config=types.GenerateContentConfig(
tools=[tool_config],
thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(include_thoughts=True)
),
)
print(f"\nFinal model response: {response_2.text}")
JavaScript
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
const client = new GoogleGenAI({ apiKey: process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY });
// This is a manual, two turn multimodal function calling workflow:
// 1. Define the function tool
const getImageDeclaration = {
name: 'get_image',
description: 'Retrieves the image file reference for a specific order item.',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
properties: {
item_name: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: "The name or description of the item ordered (e.g., 'instrument').",
},
},
required: ['item_name'],
},
};
const toolConfig = {
functionDeclarations: [getImageDeclaration],
};
// 2. Send a message that triggers the tool
const prompt = 'Show me the instrument I ordered last month.';
const response1 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: prompt,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
},
});
// 3. Handle the function call
const functionCall = response1.functionCalls[0];
const requestedItem = functionCall.args.item_name;
console.log(`Model wants to call: ${functionCall.name}`);
// Execute your tool (e.g., call an API)
// (This is a mock response for the example)
console.log(`Calling external tool for: ${requestedItem}`);
const functionResponseData = {
image_ref: { $ref: 'instrument.jpg' },
};
const imageUrl = "https://goo.gle/instrument-img";
const response = await fetch(imageUrl);
const imageArrayBuffer = await response.arrayBuffer();
const base64ImageData = Buffer.from(imageArrayBuffer).toString('base64');
const functionResponseMultimodalData = {
inlineData: {
mimeType: 'image/jpeg',
displayName: 'instrument.jpg',
data: base64ImageData,
},
};
// 4. Send the tool's result back
// Append this turn's messages to history for a final response.
const history = [
{ role: 'user', parts: [{ text: prompt }] },
response1.candidates[0].content,
{
role: 'tool',
parts: [
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: functionResponseData,
parts: [functionResponseMultimodalData],
},
},
],
},
];
const response2 = await client.models.generateContent({
model: 'gemini-3-flash-preview',
contents: history,
config: {
tools: [toolConfig],
thinkingConfig: { includeThoughts: true },
},
});
console.log(`\nFinal model response: ${response2.text}`);
REST
IMG_URL="https://goo.gle/instrument-img"
MIME_TYPE=$(curl -sIL "$IMG_URL" | grep -i '^content-type:' | awk -F ': ' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\r$//' | head -n 1)
if [[ -z "$MIME_TYPE" || ! "$MIME_TYPE" == image/* ]]; then
MIME_TYPE="image/jpeg"
fi
# Check for macOS
if [[ "$(uname)" == "Darwin" ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -b 0)
elif [[ "$(base64 --version 2>&1)" = *"FreeBSD"* ]]; then
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64)
else
IMAGE_B64=$(curl -sL "$IMG_URL" | base64 -w0)
fi
curl "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-3-flash-preview:generateContent" \
-H "x-goog-api-key: $GEMINI_API_KEY" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-X POST \
-d '{
"contents": [
...,
{
"role": "user",
"parts": [
{
"functionResponse": {
"name": "get_image",
"response": {
"image_ref": {
"$ref": "instrument.jpg"
}
},
"parts": [
{
"inlineData": {
"displayName": "instrument.jpg",
"mimeType":"'"$MIME_TYPE"'",
"data": "'"$IMAGE_B64"'"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}'
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่มีเอาต์พุตที่มีโครงสร้าง
สำหรับรุ่น Gemini 3 คุณสามารถใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันกับเอาต์พุตที่มีโครงสร้างได้ ซึ่งจะช่วยให้โมเดลคาดการณ์การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหรือเอาต์พุตที่เป็นไปตามสคีมาที่เฉพาะเจาะจงได้ ด้วยเหตุนี้ คุณจึงได้รับคำตอบที่มีการจัดรูปแบบอย่างสม่ำเสมอเมื่อโมเดลไม่ได้สร้างการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) คือ มาตรฐานแบบเปิดสำหรับการเชื่อมต่อแอปพลิเคชัน AI กับเครื่องมือและข้อมูลภายนอก MCP มีโปรโตคอลทั่วไปสำหรับโมเดลในการเข้าถึงบริบท เช่น ฟังก์ชัน (เครื่องมือ) แหล่งข้อมูล (ทรัพยากร) หรือพรอมต์ที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้า
SDK ของ Gemini มีการรองรับ MCP ในตัว ซึ่งจะช่วยลดโค้ดที่ซ้ำซ้อนและ มีการเรียกใช้เครื่องมืออัตโนมัติ สำหรับเครื่องมือ MCP เมื่อโมเดลสร้างการเรียกใช้เครื่องมือ MCP แล้ว SDK ไคลเอ็นต์ Python และ JavaScript จะเรียกใช้เครื่องมือ MCP โดยอัตโนมัติและส่งการตอบกลับกลับไปยังโมเดลในคำขอที่ตามมา โดยจะทำซ้ำลูปนี้จนกว่าโมเดลจะไม่เรียกใช้เครื่องมืออีก
ในส่วนนี้ คุณจะเห็นตัวอย่างวิธีใช้เซิร์ฟเวอร์ MCP ในพื้นที่กับ Gemini และ
mcp SDK
Python
ตรวจสอบว่าได้ติดตั้ง SDK ของ
mcp เวอร์ชันล่าสุดใน
แพลตฟอร์มที่คุณเลือกแล้ว
pip install mcp
import os
import asyncio
from datetime import datetime
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
from google import genai
client = genai.Client()
# Create server parameters for stdio connection
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command="npx", # Executable
args=["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"], # MCP Server
env=None, # Optional environment variables
)
async def run():
async with stdio_client(server_params) as (read, write):
async with ClientSession(read, write) as session:
# Prompt to get the weather for the current day in London.
prompt = f"What is the weather in London in {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}?"
# Initialize the connection between client and server
await session.initialize()
# Send request to the model with MCP function declarations
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=prompt,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
temperature=0,
tools=[session], # uses the session, will automatically call the tool
# Uncomment if you **don't** want the SDK to automatically call the tool
# automatic_function_calling=genai.types.AutomaticFunctionCallingConfig(
# disable=True
# ),
),
)
print(response.text)
# Start the asyncio event loop and run the main function
asyncio.run(run())
JavaScript
ตรวจสอบว่าได้ติดตั้ง mcp SDK เวอร์ชันล่าสุดบนแพลตฟอร์ม
ที่คุณเลือกแล้ว
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk
import { GoogleGenAI, FunctionCallingConfigMode , mcpToTool} from '@google/genai';
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StdioClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/stdio.js";
// Create server parameters for stdio connection
const serverParams = new StdioClientTransport({
command: "npx", // Executable
args: ["-y", "@philschmid/weather-mcp"] // MCP Server
});
const client = new Client(
{
name: "example-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
);
// Configure the client
const ai = new GoogleGenAI({});
// Initialize the connection between client and server
await client.connect(serverParams);
// Send request to the model with MCP tools
const response = await ai.models.generateContent({
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
contents: `What is the weather in London in ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}?`,
config: {
tools: [mcpToTool(client)], // uses the session, will automatically call the tool
// Uncomment if you **don't** want the sdk to automatically call the tool
// automaticFunctionCalling: {
// disable: true,
// },
},
});
console.log(response.text)
// Close the connection
await client.close();
ข้อจำกัดของการรองรับ MCP ในตัว
การรองรับ MCP ในตัวเป็นฟีเจอร์ทดลอง ใน SDK ของเราและมีข้อจำกัดต่อไปนี้
- รองรับเฉพาะเครื่องมือ ไม่รองรับทรัพยากรหรือพรอมต์
- พร้อมให้บริการสำหรับ Python และ JavaScript/TypeScript SDK
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งผลกับส่วนอื่นในระบบอาจเกิดขึ้นในรุ่นต่อๆ ไป
การผสานรวมเซิร์ฟเวอร์ MCP ด้วยตนเองเป็นตัวเลือกเสมอหากข้อจำกัดเหล่านี้จำกัดสิ่งที่คุณ กำลังสร้าง
รุ่นที่รองรับ
ส่วนนี้แสดงรายการโมเดลและความสามารถในการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันของโมเดล แต่ไม่รวมโมเดลเวอร์ชันทดลอง คุณดูภาพรวมความสามารถแบบครอบคลุมได้ในหน้าภาพรวมโมเดล
| รุ่น | การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน | การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคู่ขนาน | การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบคอมโพสิต |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini 3 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 3 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Gemini 2.0 Flash-Lite | X | X | X |
แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำ
- คำอธิบายฟังก์ชันและพารามิเตอร์: อธิบายให้ชัดเจนและเฉพาะเจาะจงที่สุด โมเดลจะใช้ข้อมูลเหล่านี้เพื่อเลือกฟังก์ชันที่ถูกต้อง และระบุอาร์กิวเมนต์ที่เหมาะสม
- การตั้งชื่อ: ใช้ชื่อฟังก์ชันที่สื่อความหมาย (ไม่มีการเว้นวรรค จุด หรือ ขีดกลาง)
- การพิมพ์ที่รัดกุม: ใช้ประเภทที่เฉพาะเจาะจง (จำนวนเต็ม สตริง Enum) สำหรับพารามิเตอร์ เพื่อลดข้อผิดพลาด หากพารามิเตอร์มีชุดค่าที่ถูกต้องแบบจำกัด ให้ใช้ enum
- การเลือกเครื่องมือ: แม้ว่าโมเดลจะใช้เครื่องมือได้ไม่จำกัดจำนวน แต่การระบุเครื่องมือมากเกินไปอาจเพิ่มความเสี่ยงในการเลือกเครื่องมือที่ไม่ถูกต้องหรือไม่เหมาะสม เพื่อให้ได้ผลลัพธ์ที่ดีที่สุด ให้พยายามระบุเฉพาะเครื่องมือที่เกี่ยวข้องกับบริบทหรืองาน โดยควรจำกัดชุดเครื่องมือที่ใช้งานอยู่ไม่เกิน 10-20 รายการ พิจารณาการเลือกเครื่องมือแบบไดนามิกตามบริบทของการสนทนาหากคุณมีเครื่องมือจำนวนมาก
- การออกแบบพรอมต์:
- ระบุบริบท: บอกบทบาทของโมเดล (เช่น "คุณเป็นผู้ช่วยด้านสภาพอากาศที่ มีประโยชน์")
- ให้คำสั่ง: ระบุวิธีและเวลาที่จะใช้ฟังก์ชัน (เช่น "อย่า คาดเดาวันที่ ให้ใช้วันที่ในอนาคตสำหรับการคาดการณ์เสมอ")
- กระตุ้นให้มีการชี้แจง: สั่งให้โมเดลถามคำถามเพื่อช่วยชี้แจง หากจำเป็น
- ดูกลยุทธ์เพิ่มเติมในการออกแบบพรอมต์เหล่านี้ได้ที่เวิร์กโฟลว์ของเอเจนต์ ตัวอย่างคำสั่งของระบบที่ผ่านการทดสอบแล้วมีดังนี้
อุณหภูมิ: ใช้อุณหภูมิต่ำ (เช่น 0) เพื่อให้การเรียกฟังก์ชันมีความแน่นอนและเชื่อถือได้มากขึ้น
การตรวจสอบ: หากการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันมีผลกระทบอย่างมาก (เช่น การสั่งซื้อ) ให้ตรวจสอบการเรียกใช้กับผู้ใช้ก่อนที่จะดำเนินการ
ตรวจสอบเหตุผลที่เสร็จสิ้น: ตรวจสอบ
finishReasonในคำตอบของโมเดลเสมอเพื่อจัดการกรณีที่โมเดลสร้างการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่ถูกต้องไม่สำเร็จการจัดการข้อผิดพลาด: ใช้การจัดการข้อผิดพลาดที่มีประสิทธิภาพในฟังก์ชันเพื่อจัดการอินพุตที่ไม่คาดคิดหรือ API ล้มเหลวอย่างราบรื่น แสดงข้อความแสดงข้อผิดพลาดที่ให้ข้อมูล ซึ่งโมเดลใช้สร้างคำตอบที่เป็นประโยชน์ต่อผู้ใช้ได้
ความปลอดภัย: โปรดคำนึงถึงความปลอดภัยเมื่อเรียกใช้ API ภายนอก ใช้กลไกการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์และการให้สิทธิ์ที่เหมาะสม หลีกเลี่ยงการเปิดเผยข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนในการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
ขีดจำกัดโทเค็น: คำอธิบายฟังก์ชันและพารามิเตอร์จะนับรวมใน ขีดจำกัดโทเค็นอินพุต หากใช้โทเค็นจนถึงขีดจำกัด ให้ลองจำกัดจำนวนฟังก์ชันหรือความยาวของคำอธิบาย แบ่งงานที่ซับซ้อนออกเป็นชุดฟังก์ชันที่เล็กลงและเฉพาะเจาะจงมากขึ้น
หมายเหตุและข้อจำกัด
- รองรับเฉพาะชุดย่อยของสคีมา OpenAPI
- สำหรับโหมด
ANYAPI อาจปฏิเสธสคีมาที่มีขนาดใหญ่มากหรือซ้อนกันลึก หากพบข้อผิดพลาด ให้ลองลดความซับซ้อนของพารามิเตอร์ฟังก์ชันและสคีมาการตอบกลับโดยการย่อชื่อพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ ลดการซ้อน หรือจำกัดจำนวนการประกาศฟังก์ชัน - ประเภทพารามิเตอร์ที่รองรับใน Python มีจำกัด
- การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอัตโนมัติเป็นฟีเจอร์ของ Python SDK เท่านั้น
